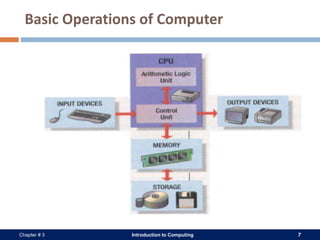
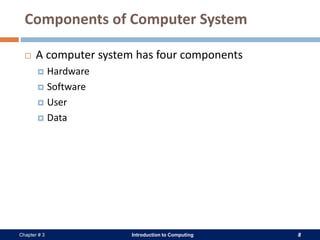
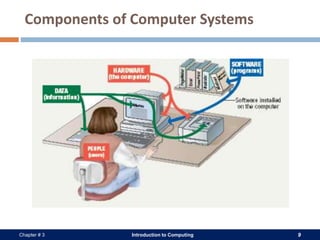
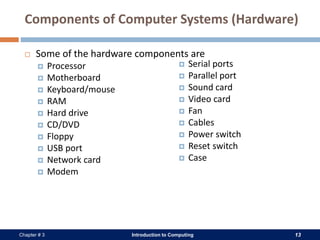
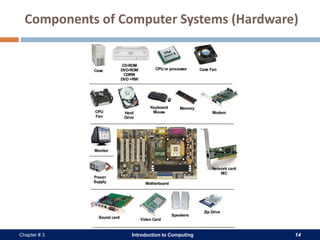
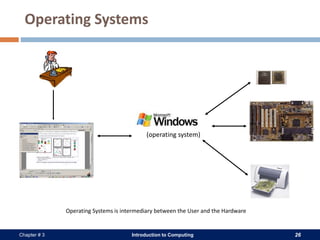
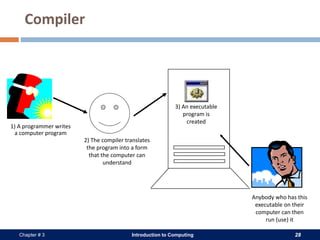
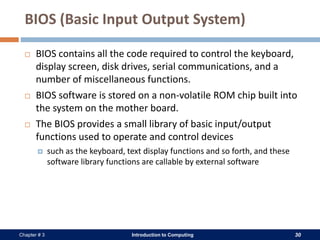
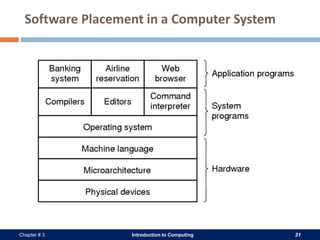
A computer system consists of hardware, software, data, and users. The hardware includes physical components like the processor, memory, storage devices, and input/output devices. Software provides instructions that control the hardware and allow users to manipulate data. There are two main types of software: system software that operates the computer system, and application software that helps users perform tasks. An operating system is a core system software that manages computer resources and acts as an interface between users and hardware.