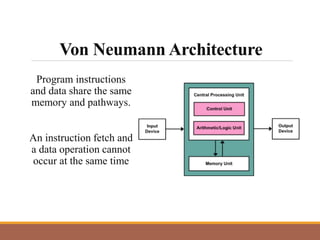
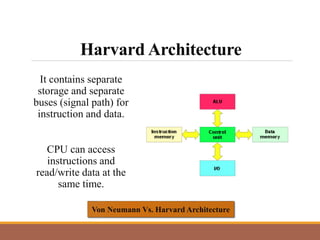
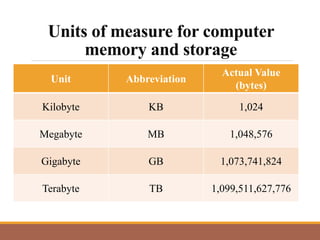
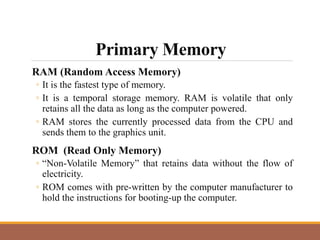
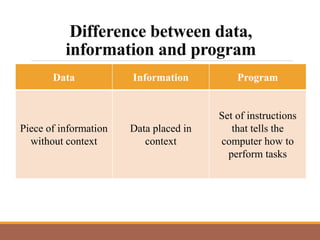
This document provides an introduction to computer systems by discussing the four phases of the information processing cycle, the four categories of computer hardware, units of measure for computer memory and storage, common input and output devices, and the two main categories of computer software. It also defines key concepts like data, information, programs, and the roles of users with personal computers.