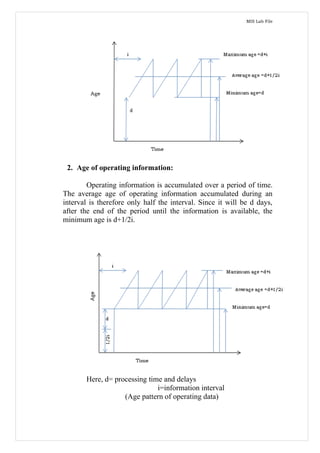
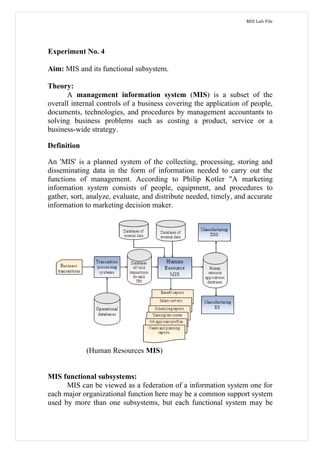
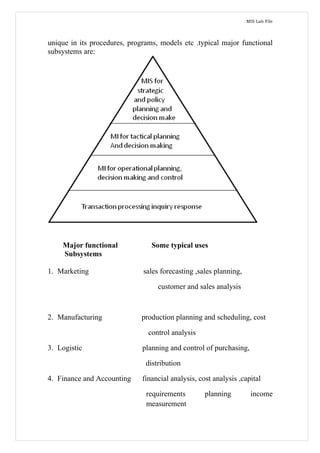
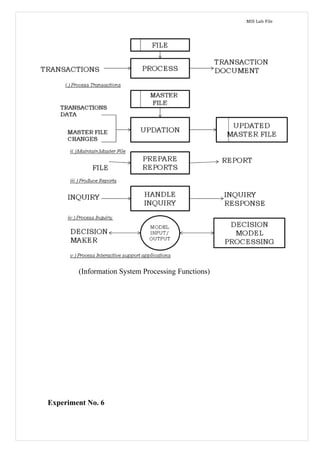
Management information systems provide decision-makers with daily operational information and support strategic planning by incorporating web technologies. Marketing, human resources, and other functional area MIS support related managerial activities through various subsystems and by obtaining inputs from transaction processing systems and external sources. The company's conceptual MIS structure consists of decentralized production/material functions and centralized finance/sales/personnel functions, with plant managers responsible for operations as strategic business units. Physically, the company has a management services department that studies cement business operations to optimize plant capacity utilization, cost control, and maintenance for maximum profitability. Decision support systems help address semi-structured and dynamic problems in the company through various user modes and by facilitating data-driven decision making under changing business