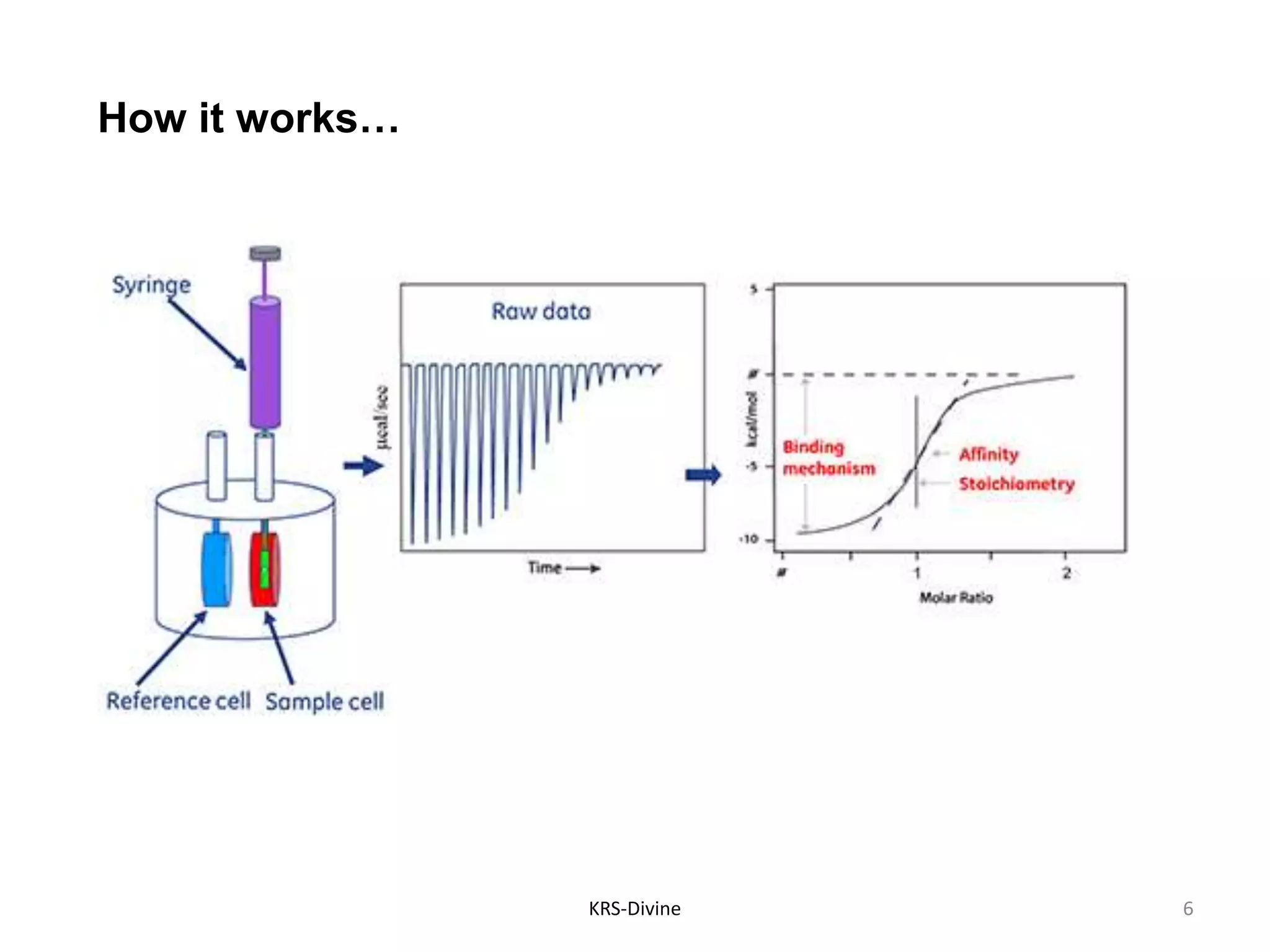
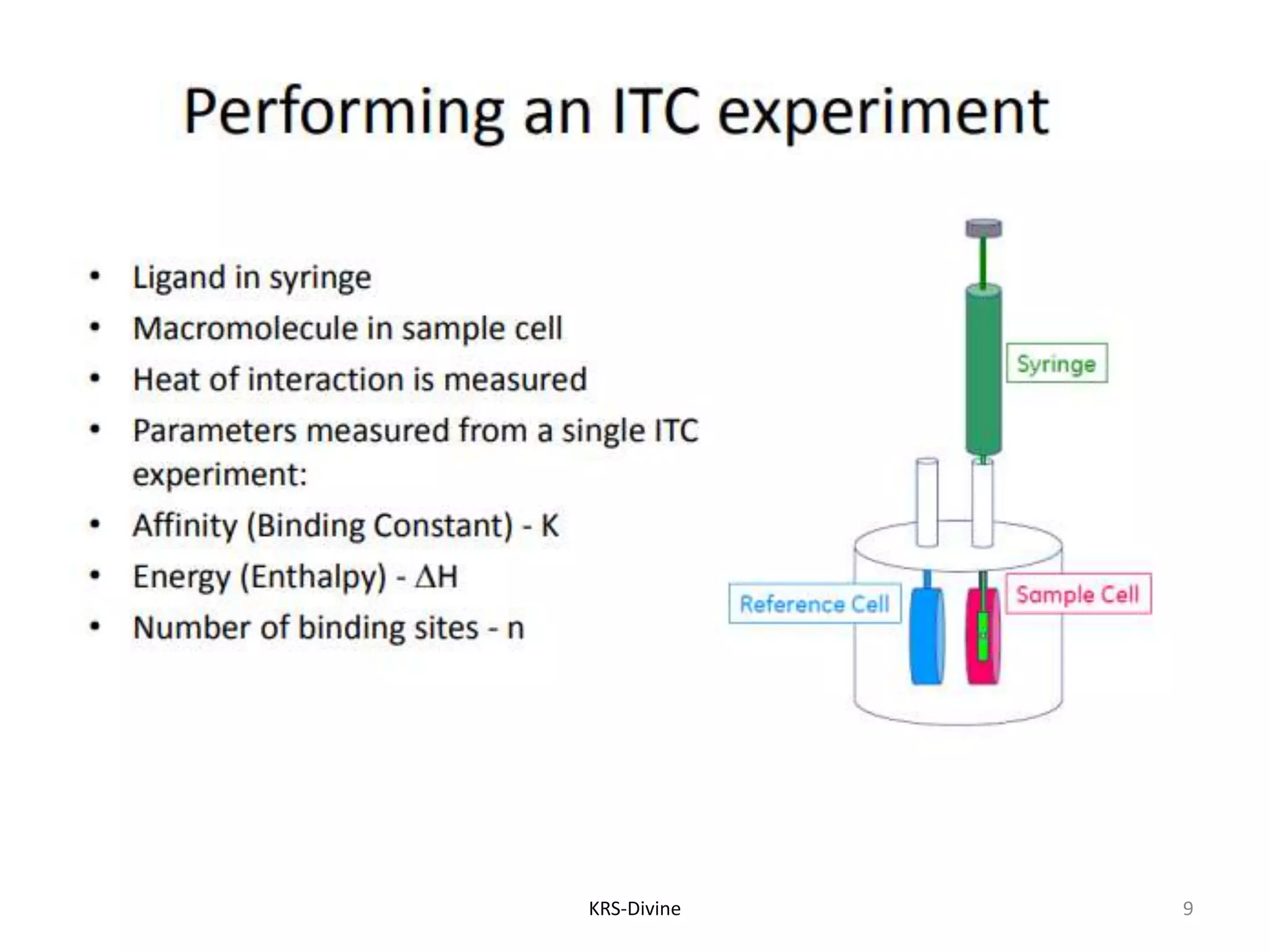
Isothermal Titration Calorimetry (ITC) is a quantitative technique for studying biomolecular interactions, measuring the heat released or absorbed during binding events, which allows for the determination of binding constants, stoichiometry, enthalpy, and entropy in a single experiment without modifications to the molecules. ITC can elucidate the mechanisms behind molecular interactions, aiding in drug discovery, candidate selection, and optimization. While ITC has advantages such as providing a comprehensive thermodynamic profile and being a non-destructive method, it also has drawbacks, including a requirement for larger sample sizes and slower throughput.