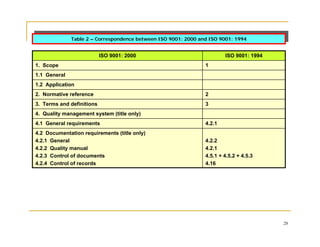
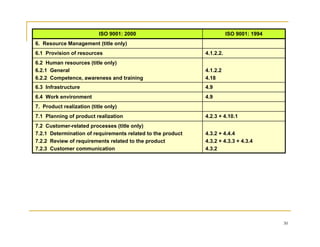
This document provides an overview of quality management systems and ISO 9001. It defines quality, describes the quality cycle, and explains how quality relates to management systems. It then discusses the principles, requirements, and benefits of the ISO 9000 quality management standard. Specifically, it outlines the structure and requirements of ISO 9001:2000, including new elements such as management responsibility and continual improvement. Finally, it provides tables mapping the correspondence between ISO 9001:1994 and ISO 9001:2000.