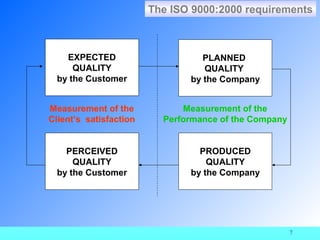
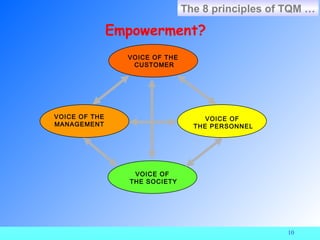
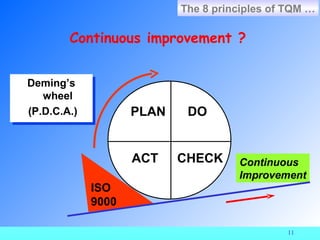
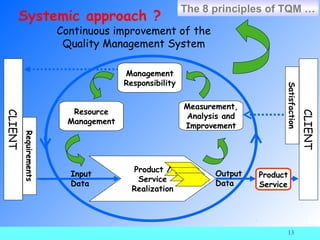
The document provides information about ISO 9000 quality management standards. It defines quality as "the degree to which a set of inherent characteristics fulfils requirements." It then discusses what ISO is, the history and purpose of ISO, the ISO 9000 standards, and the requirements and principles of the ISO 9000:2000 standard. Key points include that ISO aims to harmonize international standards, ISO 9000 was revised in 2000 to be process-based and follow the PDCA model, and the ISO 9000:2000 requirements focus on quality management systems, management responsibility, resource management, product realization, and measurement, analysis and improvement.