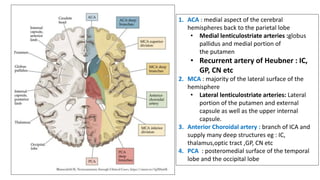
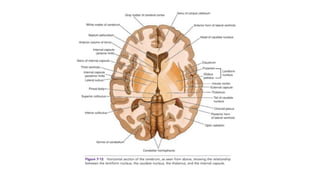
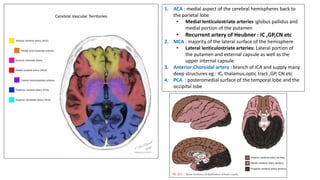
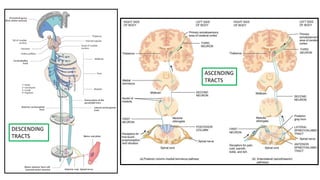
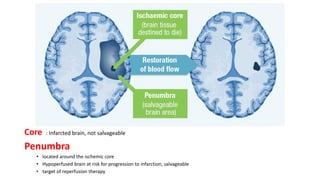
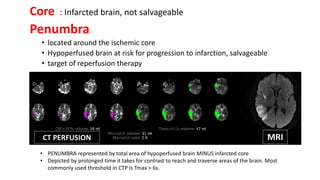
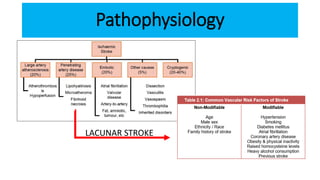
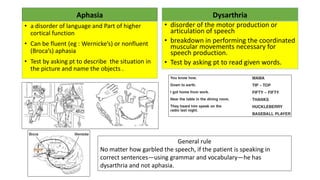
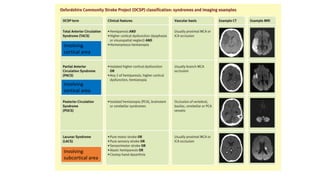
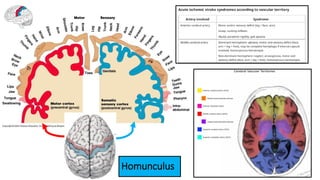
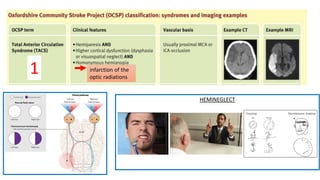
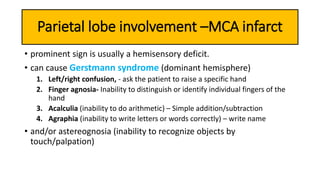
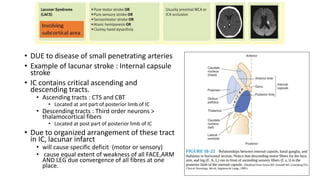
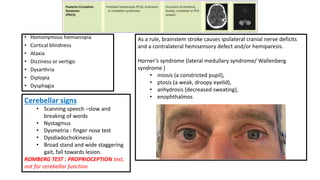
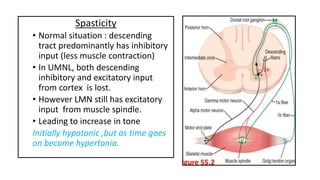
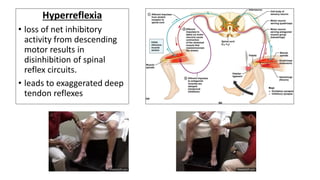
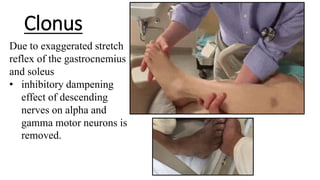
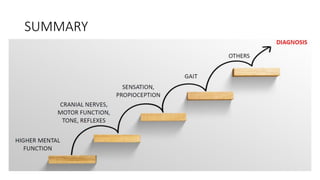
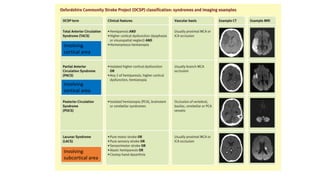
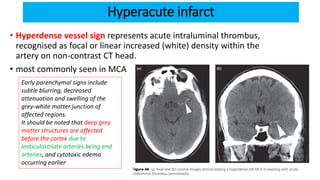
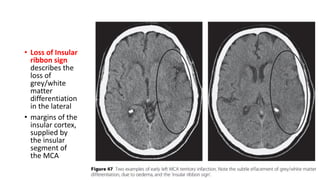
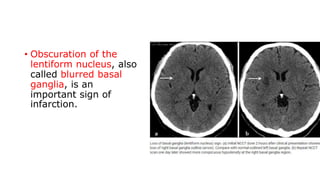
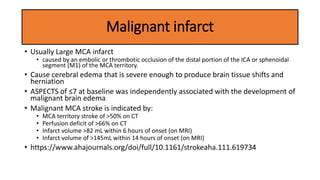
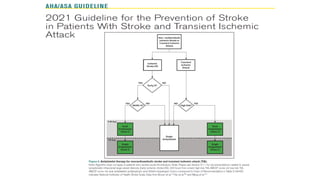
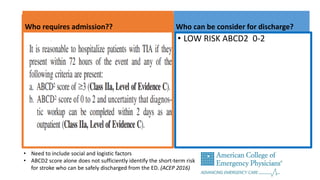
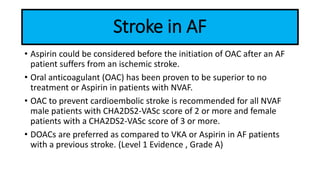
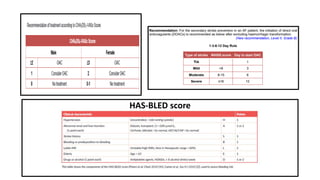
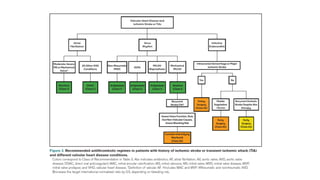
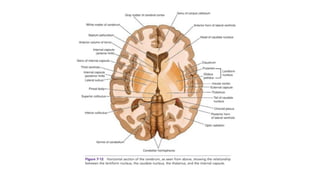
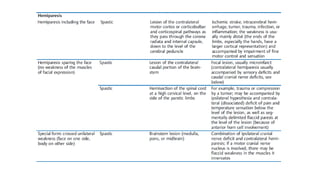
This document provides information on ischemic stroke. Some key points:
- Ischemic stroke occurs when blood flow to the brain is blocked, typically by a clot. It accounts for 80% of strokes.
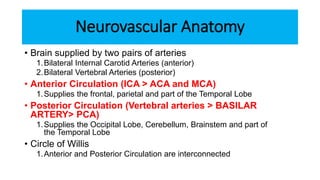
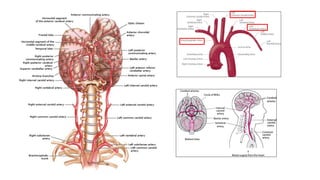
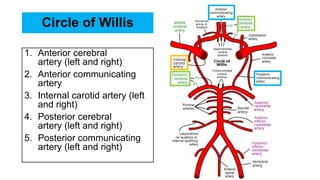
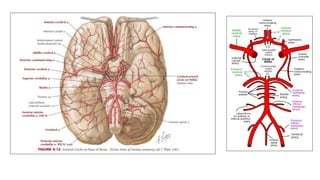
- The brain receives blood supply from two pairs of arteries: the internal carotid arteries and vertebral arteries. Strokes can occur in the anterior or posterior circulation territories.
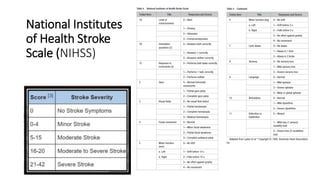
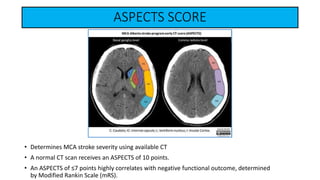
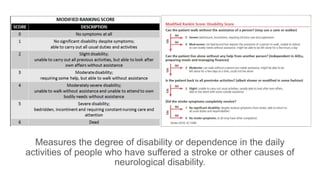
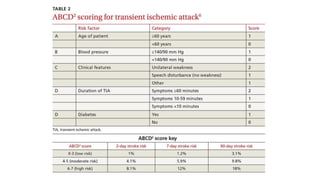
- Clinical assessment involves determining the neurological deficits, their onset, and ruling out "stroke mimics". Scoring systems like NIHSS and ASPECTS are used to evaluate severity.
- Management involves supporting vital functions, controlling risk factors like blood pressure, preventing complications, and in some cases reperfusion therapies like thrombol