Embed presentation
Downloaded 10 times





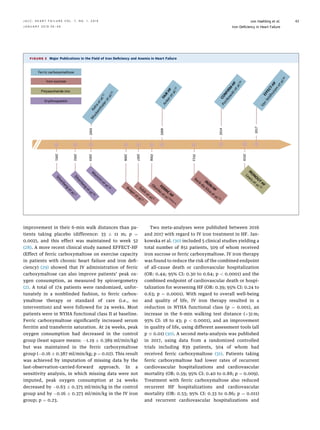
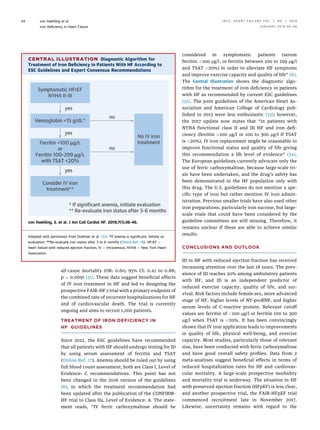



Iron deficiency is a prevalent comorbidity in heart failure patients, impacting exercise capacity and quality of life, with diagnostic criteria established as serum ferritin levels and transferrin saturation. Oral iron treatments are largely ineffective, leading to a preference for intravenous iron, particularly ferric carboxymaltose, which shows significant benefits in physical well-being and hospitalization rates. Current research is ongoing to further understand the impact of iron deficiency on morbidity and mortality in heart failure.










