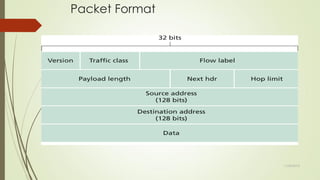
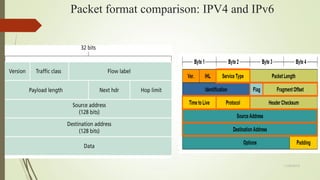
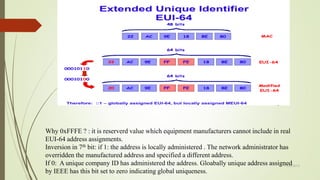
IPv6 is the latest version of the Internet Protocol that provides identification and location for computers on networks. It was developed to address the problem of IPv4 address exhaustion, as IPv4 addresses were running out. IPv6 is intended to eventually replace IPv4 and provides a vastly larger 128-bit address space compared to IPv4's 32-bit addresses. Key features of IPv6 include new header format, large address space, built-in security, prioritized traffic delivery, autoconfiguration, and mobility support.