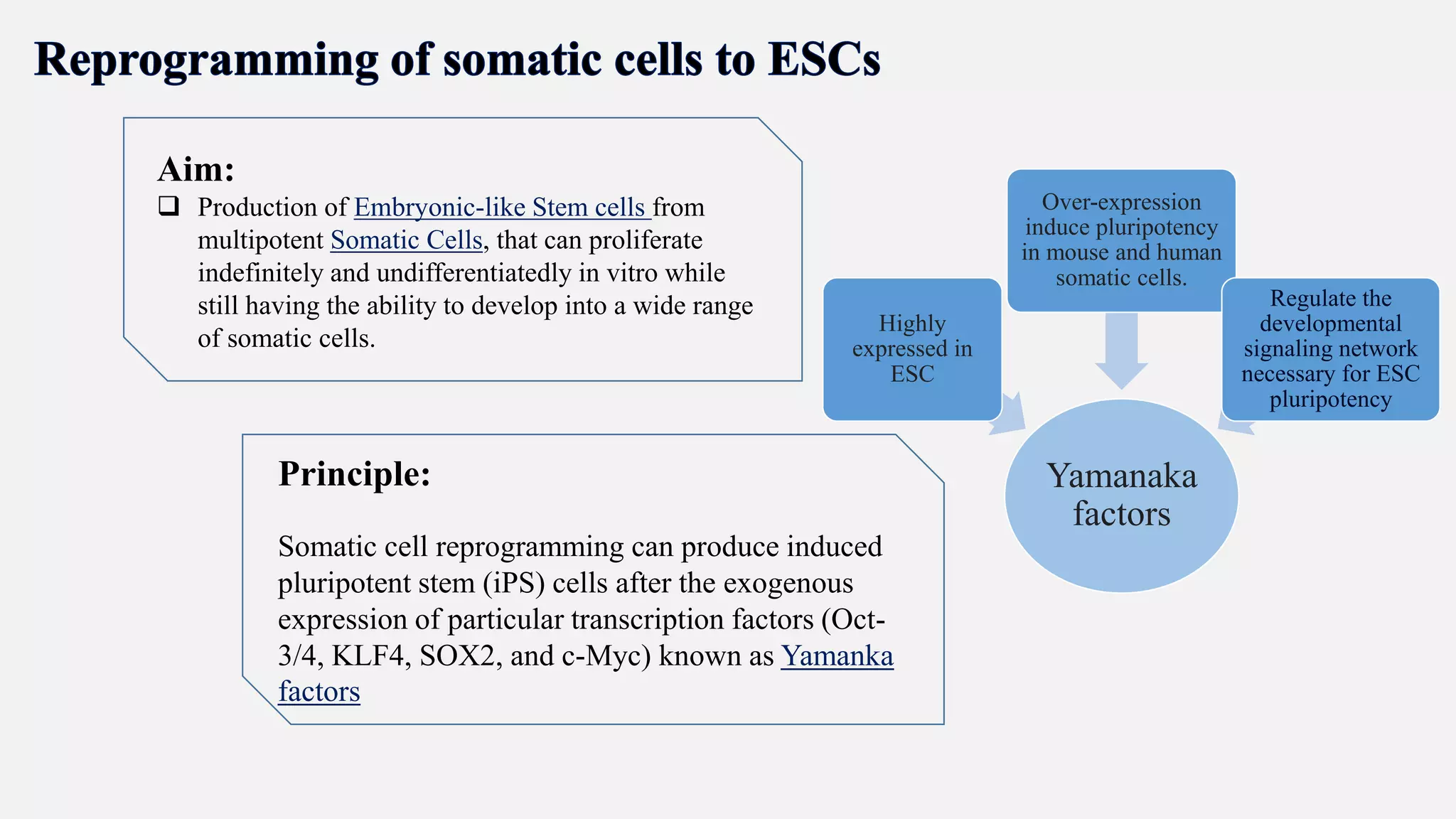
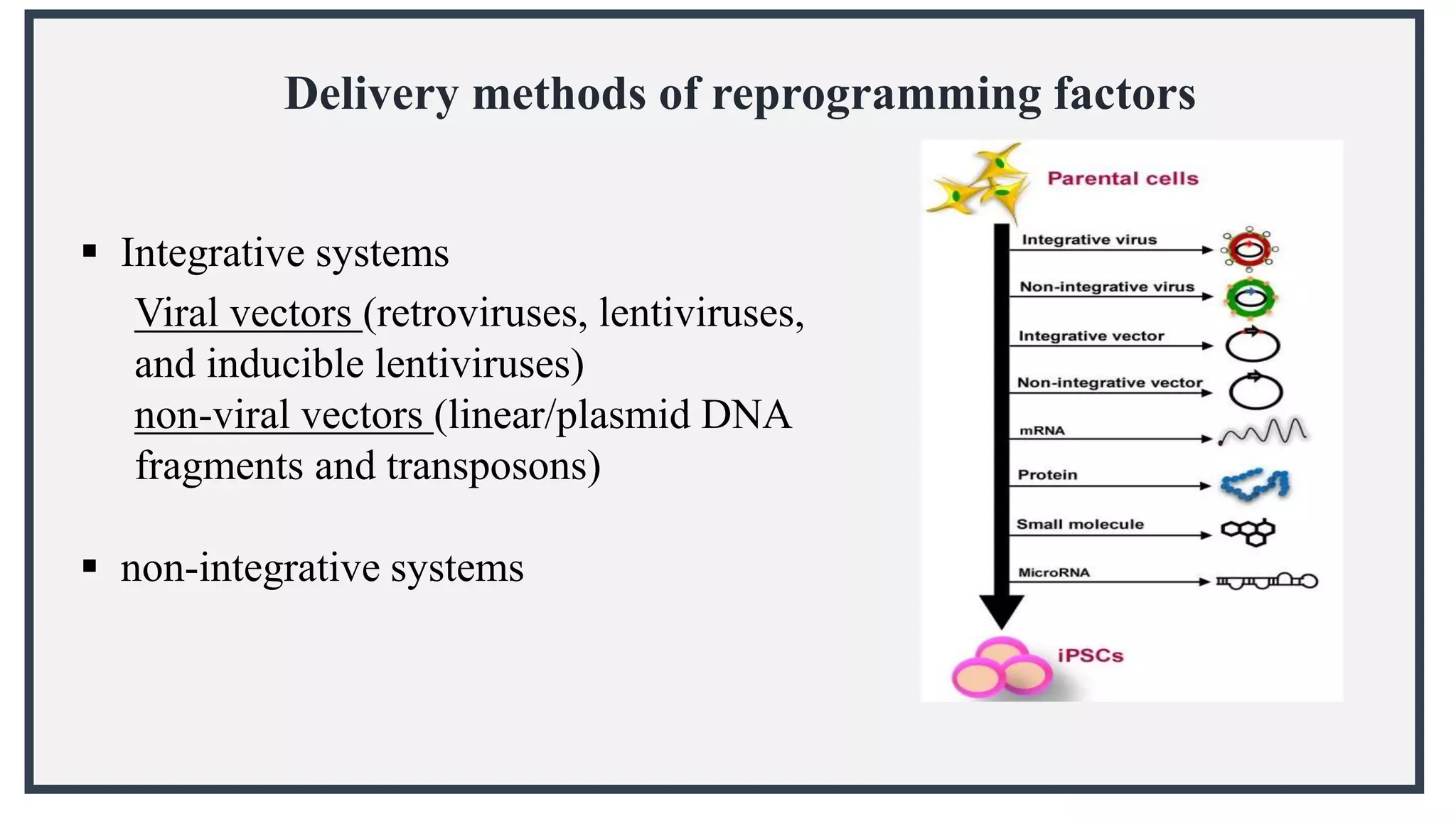
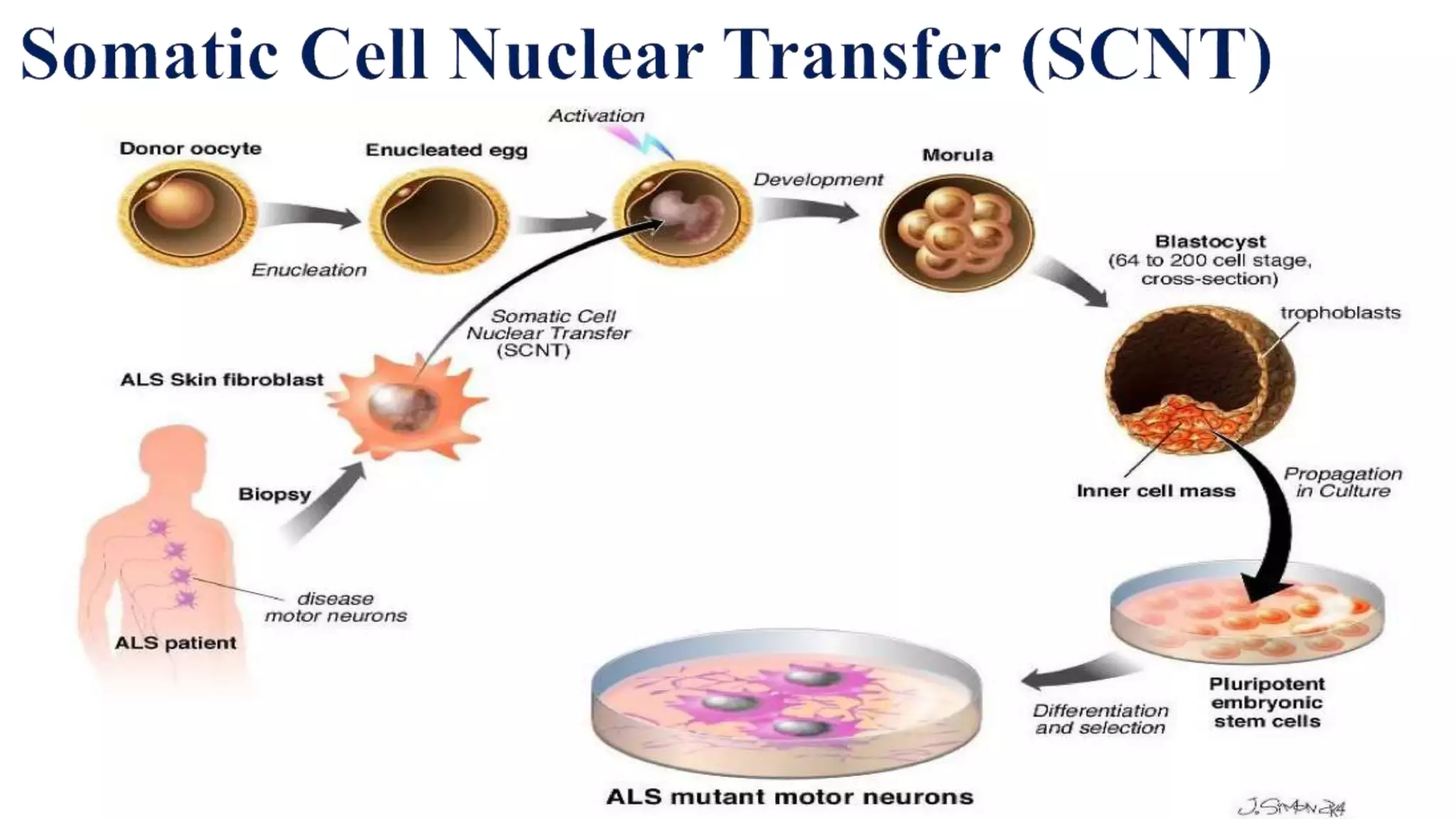
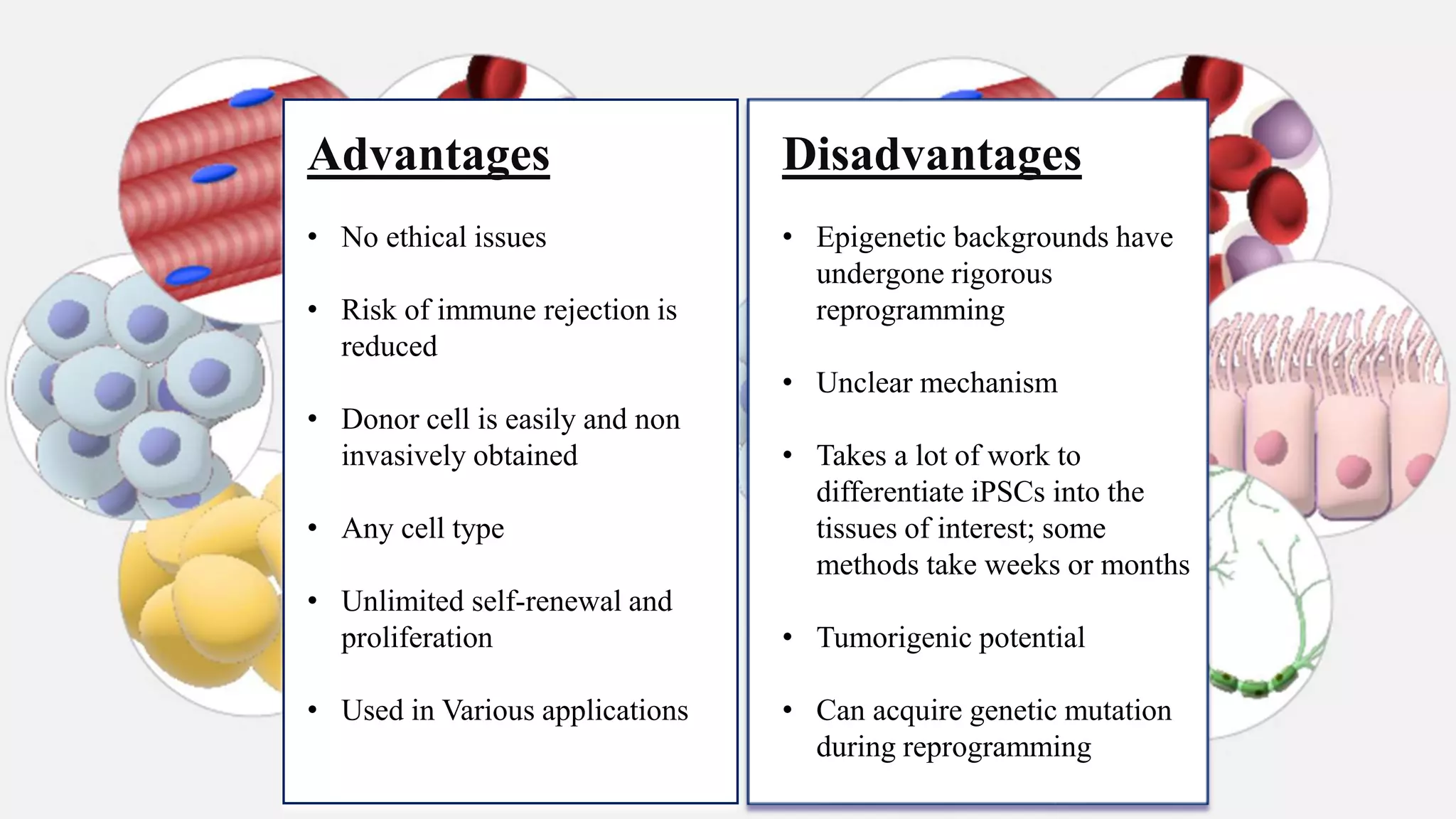
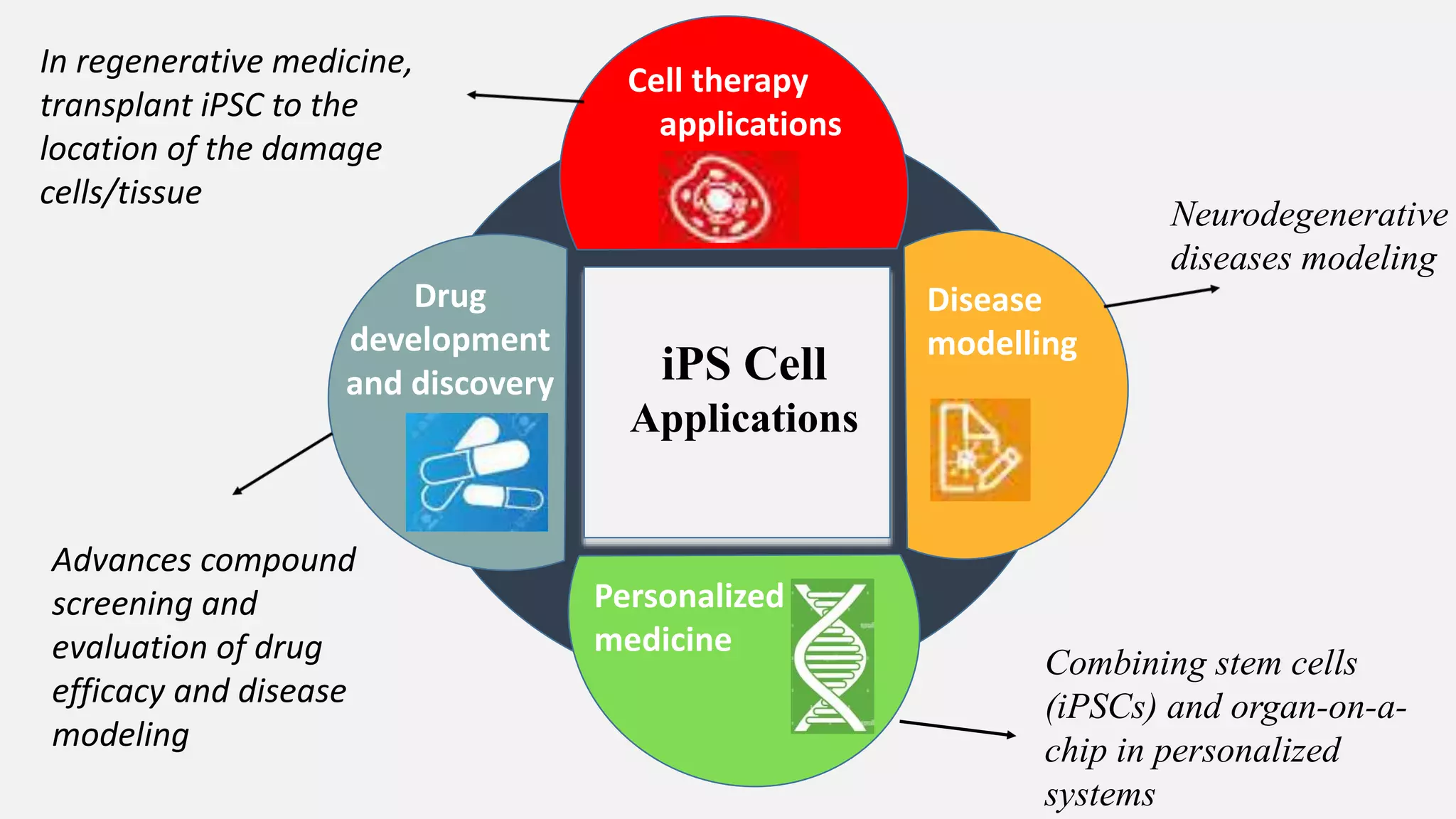
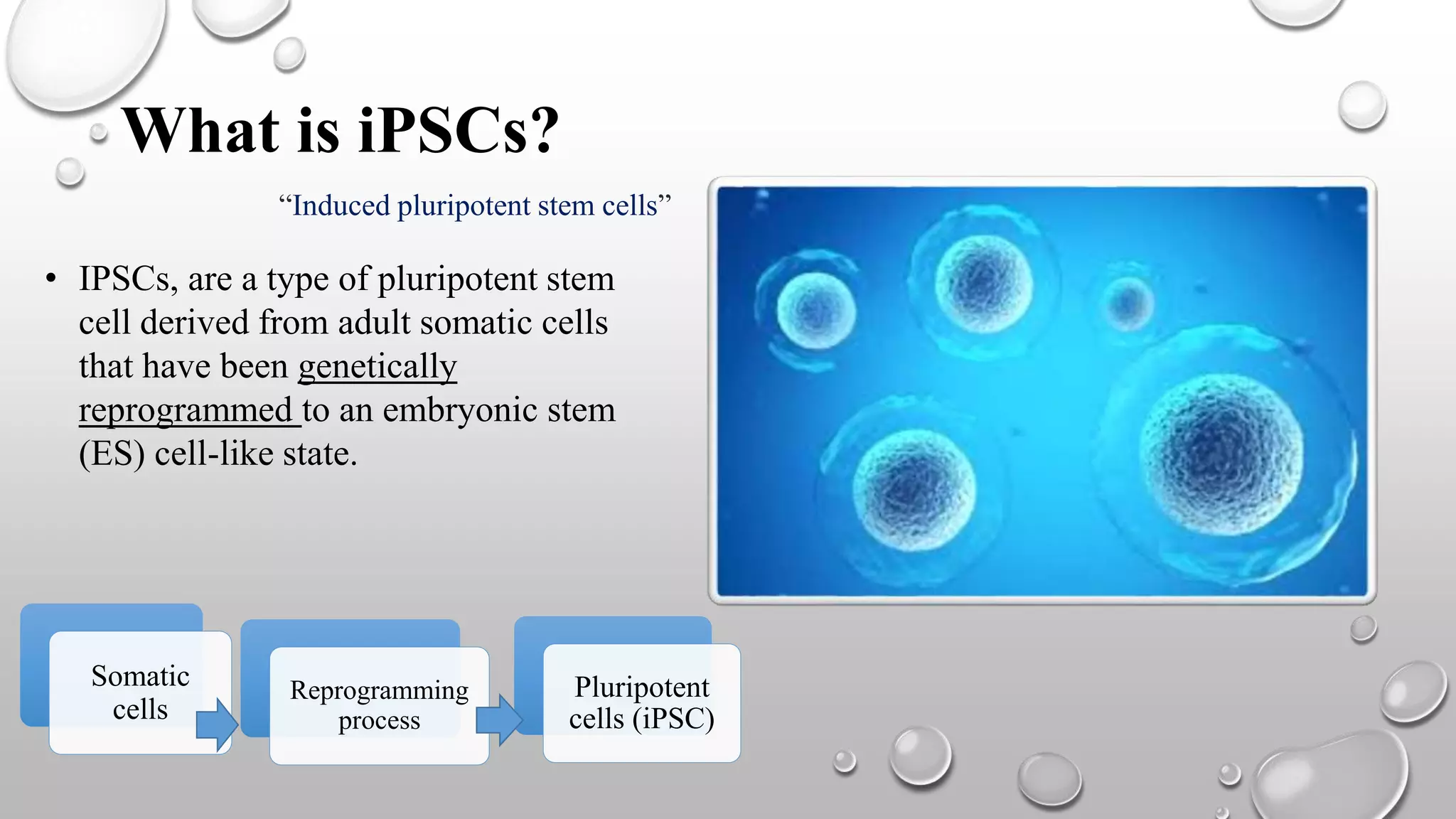
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are derived from adult somatic cells that have been genetically reprogrammed to an embryonic stem cell-like state. In 2006, Shinya Yamanaka and Kazutoshi Takahashi showed that the introduction of four transcription factors (Oct3/4, Sox2, c-Myc and Klf4) could convert somatic cells into iPSCs. iPSCs have similarities to embryonic stem cells in that they are pluripotent, can self-renew indefinitely, and can differentiate into various cell types. iPSCs hold promise for applications in regenerative medicine, disease modeling, drug discovery, and personalized medicine.

![Pre-implantation embryo-derived self-renewable cell lines were
developed by Sir Martin John Evans, Matthew H. Kaufman, and Gail R.
Martin
Seminal studies confirmed the existence of reprogramming agents that
might be used to manipulate the pluripotency of any cell.
In 2006
The iPSC technology was pioneered by Shinya Yamanaka and Kazutoshi
Takahashi in Kyoto, Japan, who together showed that the introduction of
four specific genes (named Myc, Oct3/4, Sox2 and Klf4) “Yamanaka
factors” encoding transcription factors could convert somatic cells
into pluripotent stem cells.[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ipscsppt-230409223726-61a5f3cc/75/Stem-Cells-iPSCs-3-2048.jpg)