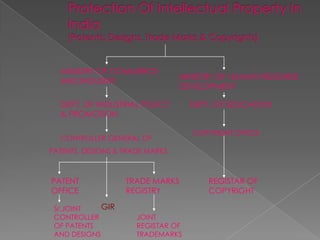
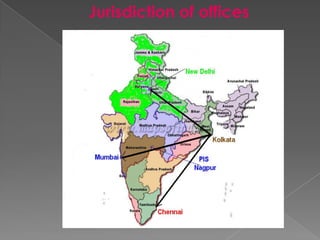
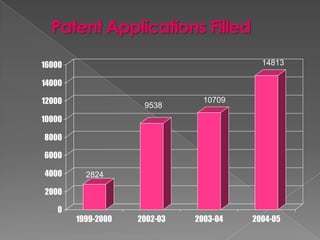
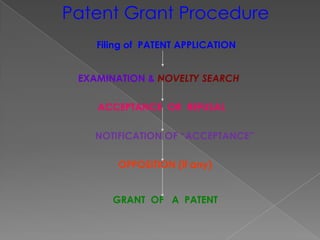
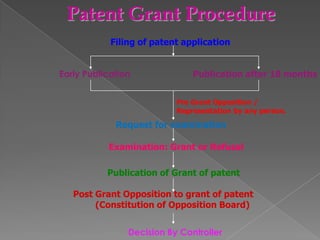
The document discusses intellectual property rights (IPR) and related concepts. It defines intellectual property and intellectual property rights. It then discusses different types of IPRs like patents, designs, trademarks, copyright etc. It provides details on patent filing procedures in India. It also introduces international agreements related to IPR - GATT and TRIPS. It defines GATT as the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade and TRIPS as the Trade Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights agreement under the World Trade Organization (WTO). The key objectives and principles of TRIPS are also summarized.