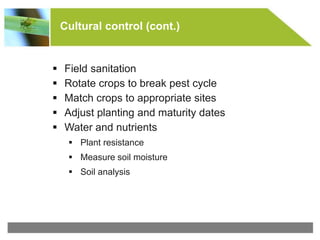
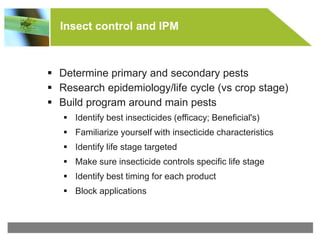
Integrated pest management (IPM) is a strategy that uses various pest control methods in conjunction to manage pests in an ecologically friendly way. It involves monitoring pest populations, using cultural practices, biological controls, and targeted use of pesticides only when necessary. The key components of an IPM program include host plant resistance, monitoring, cultural controls like crop rotation and sanitation, biological controls using beneficial organisms, and selective use of pesticides to control weeds, insects, and diseases. Monitoring is the first and most important step to identify pest thresholds and determine appropriate interventions.