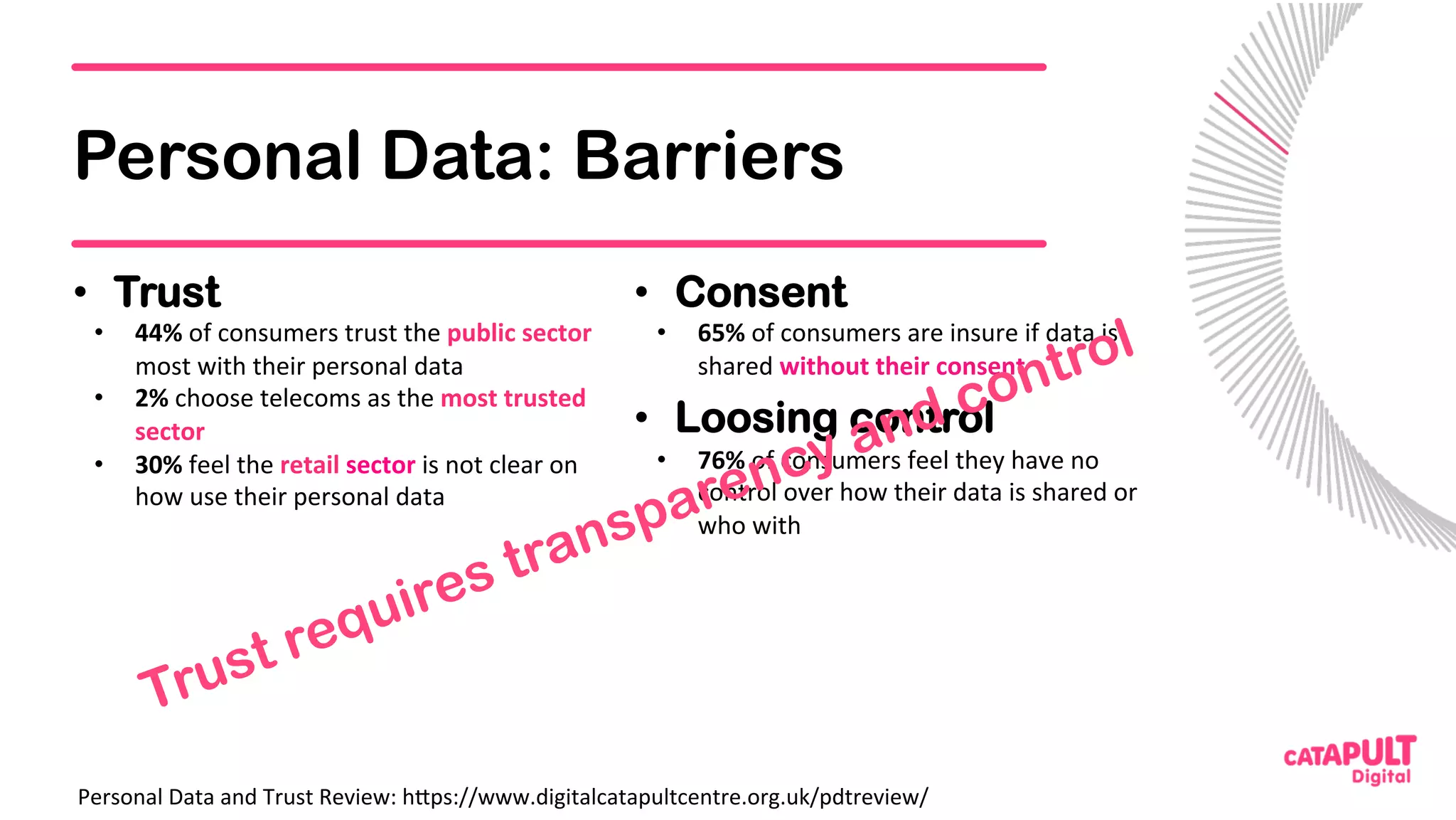
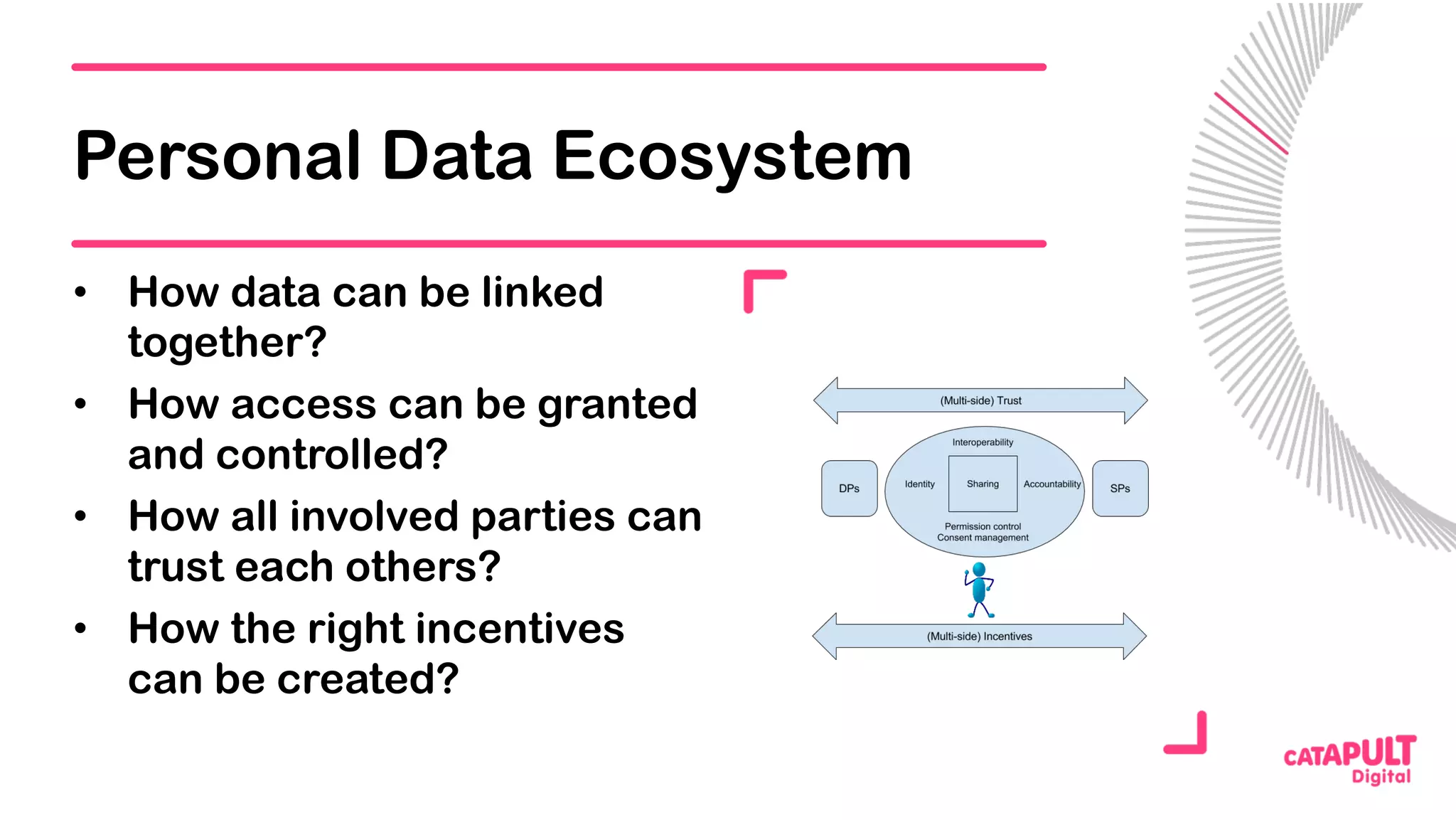
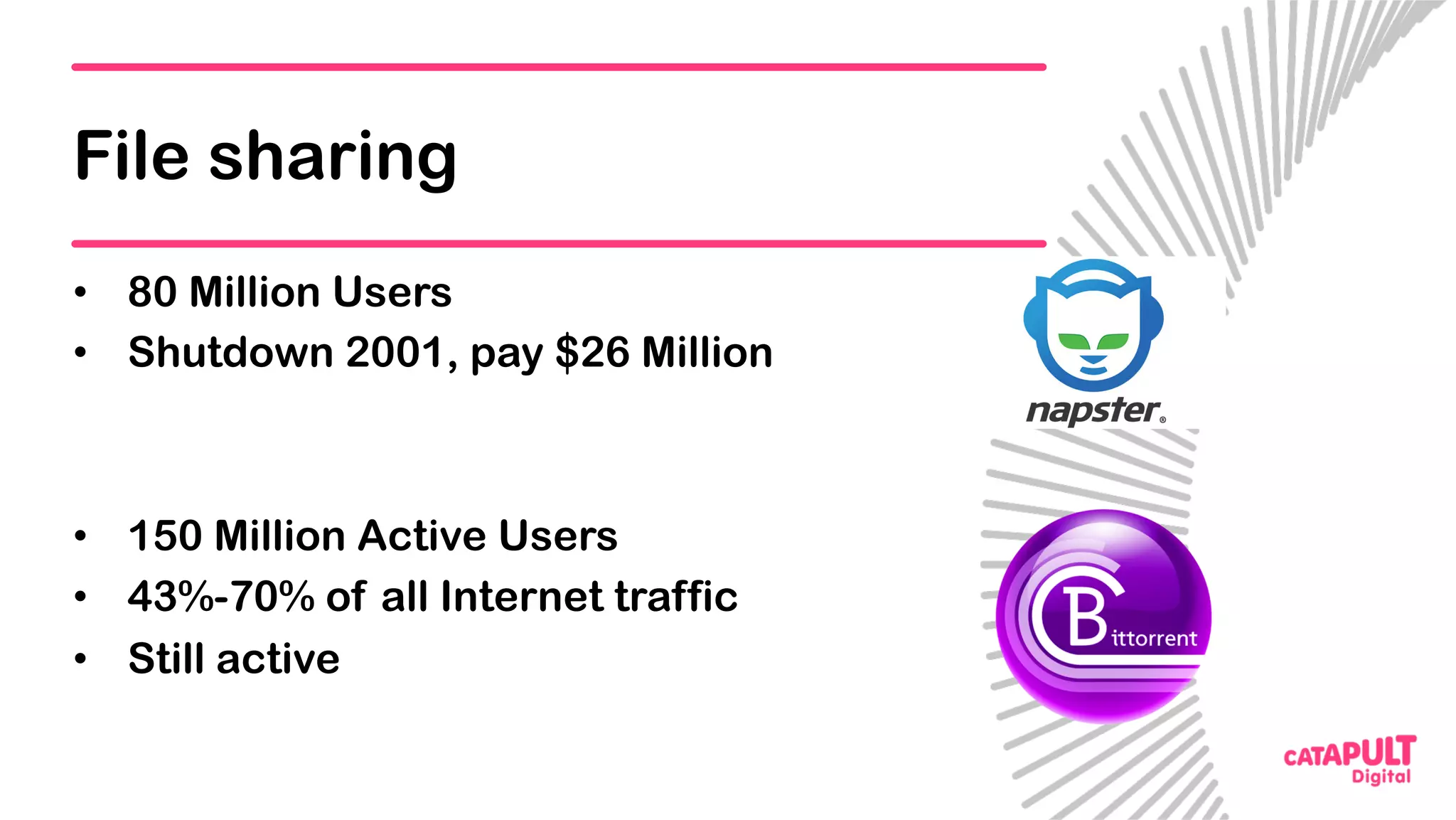
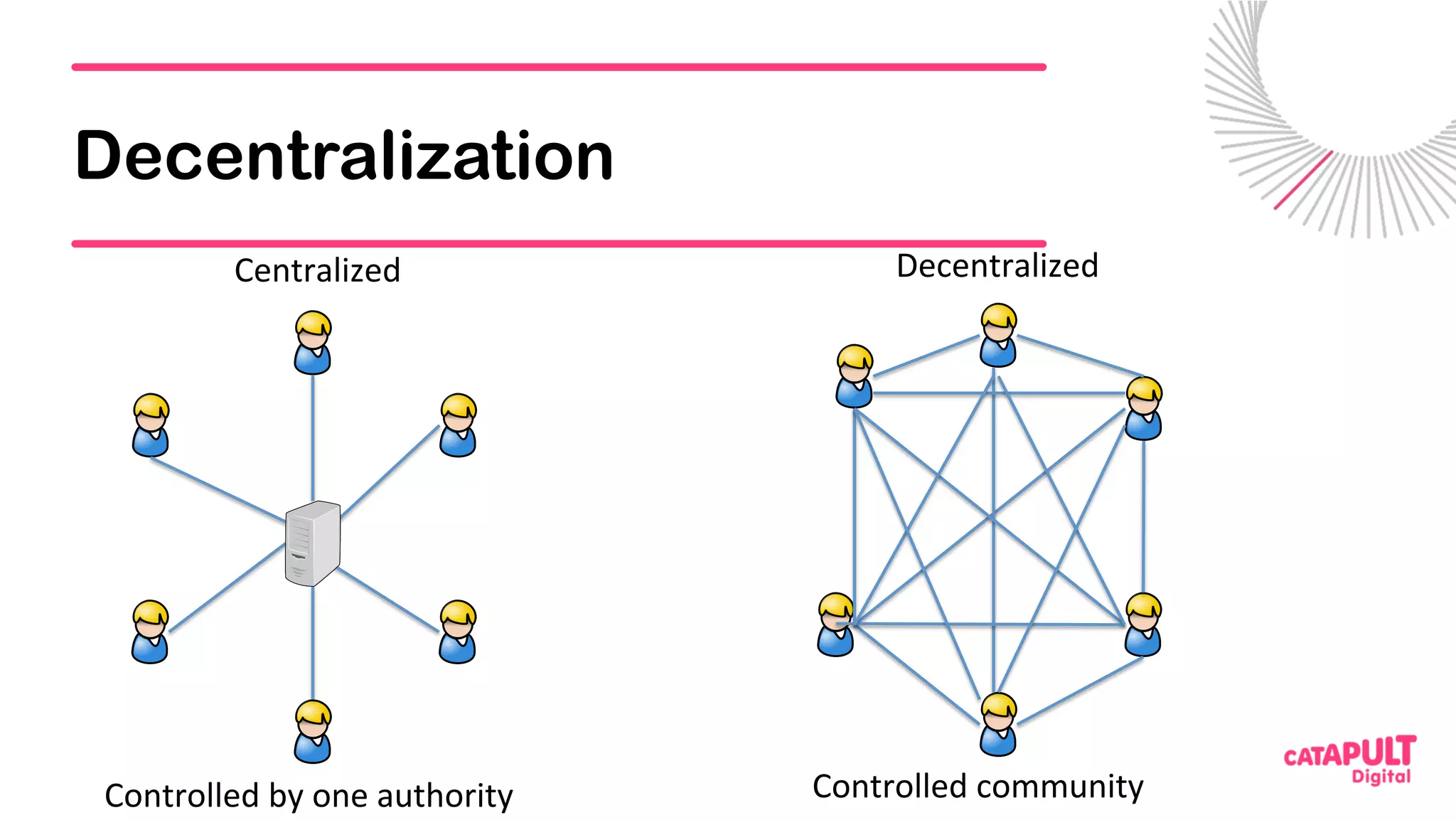
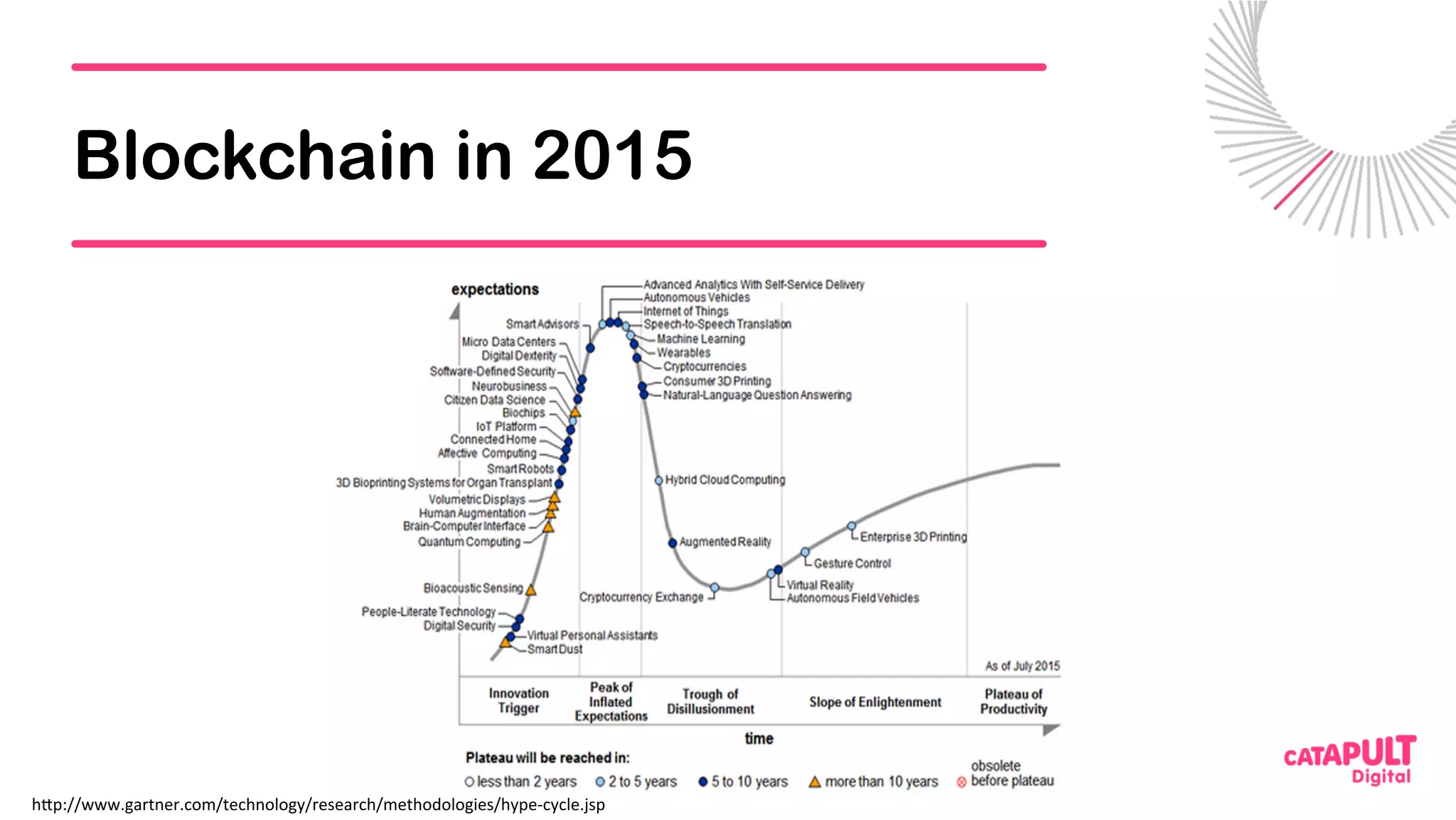
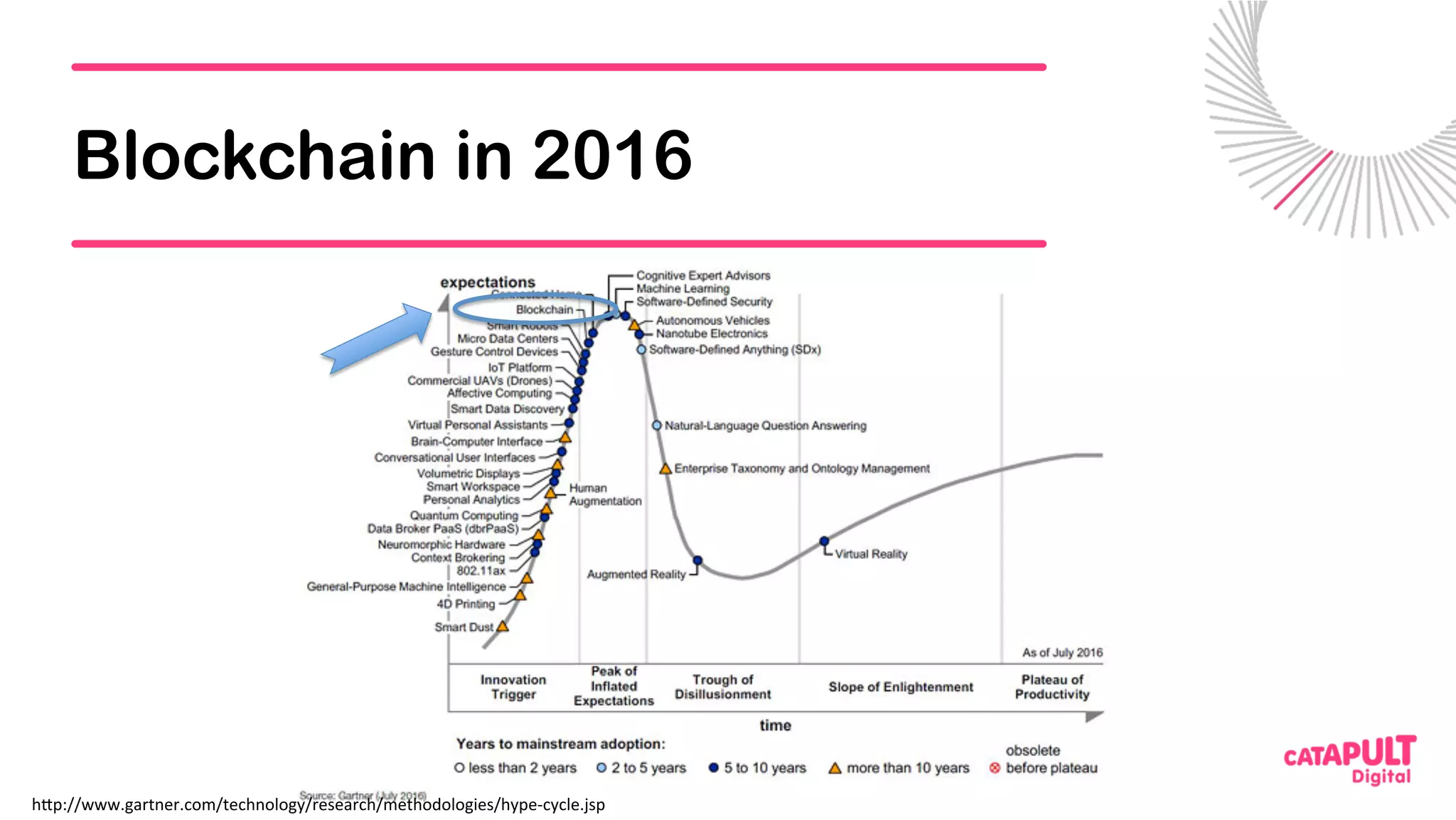
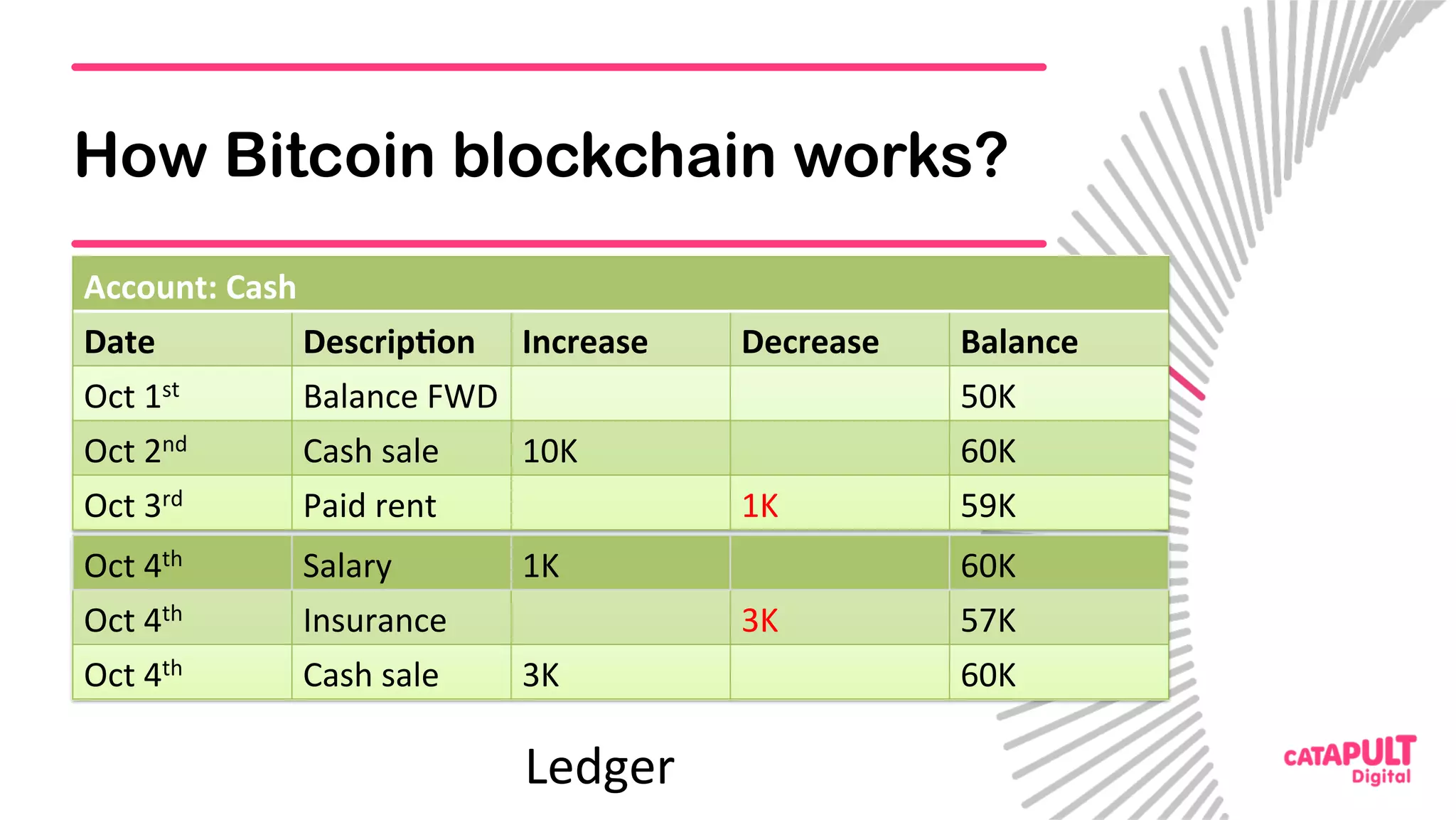
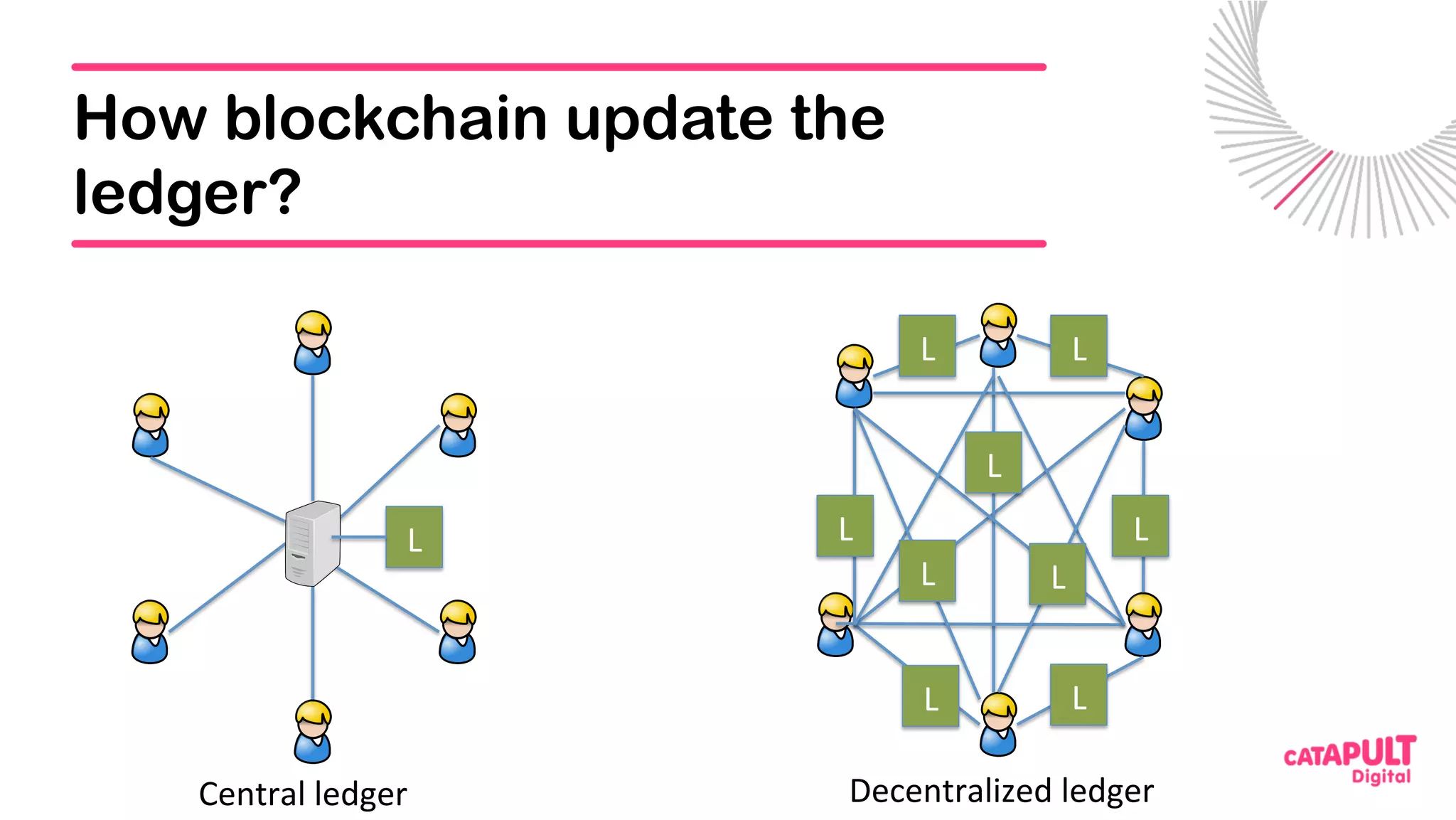
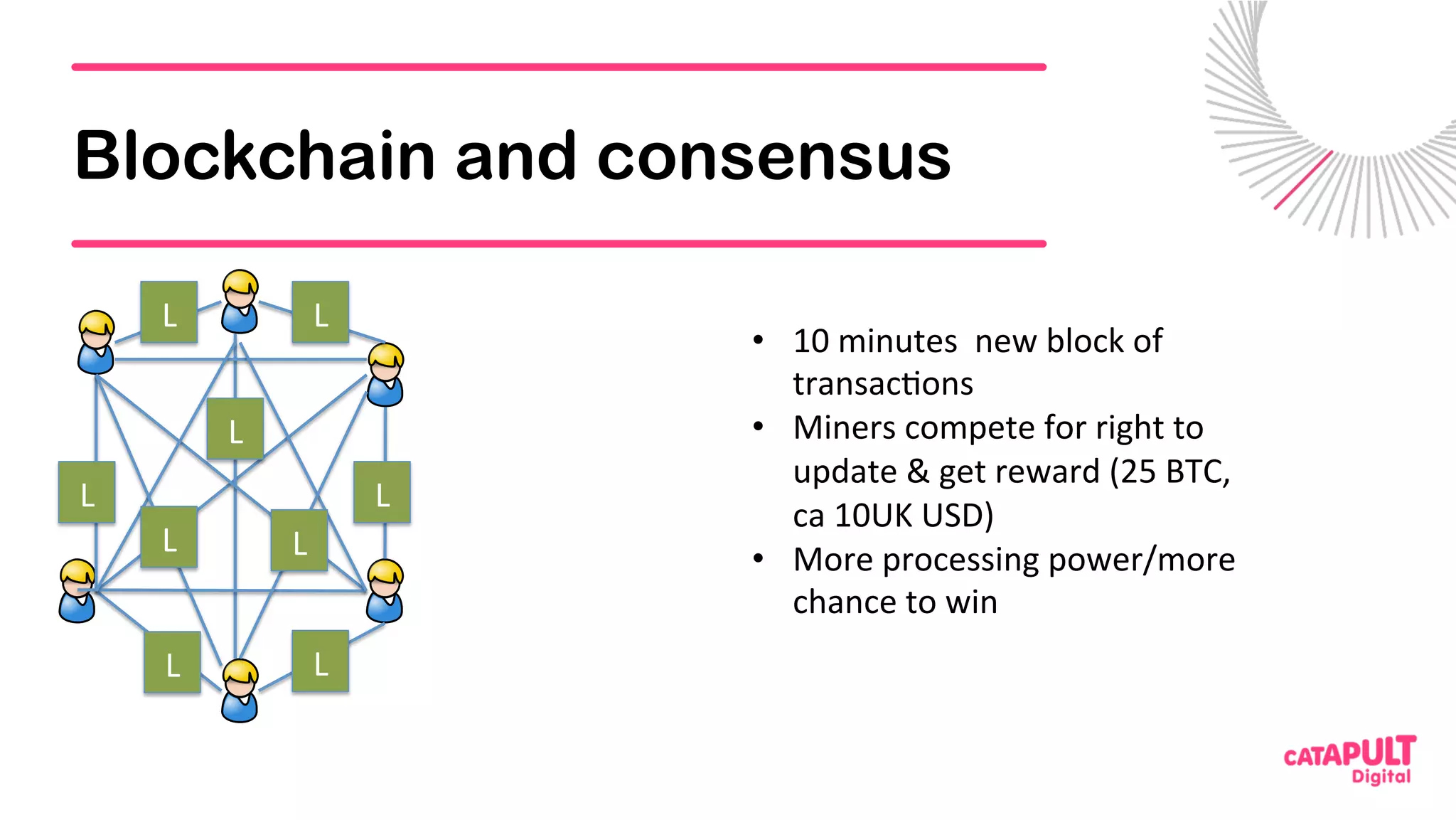
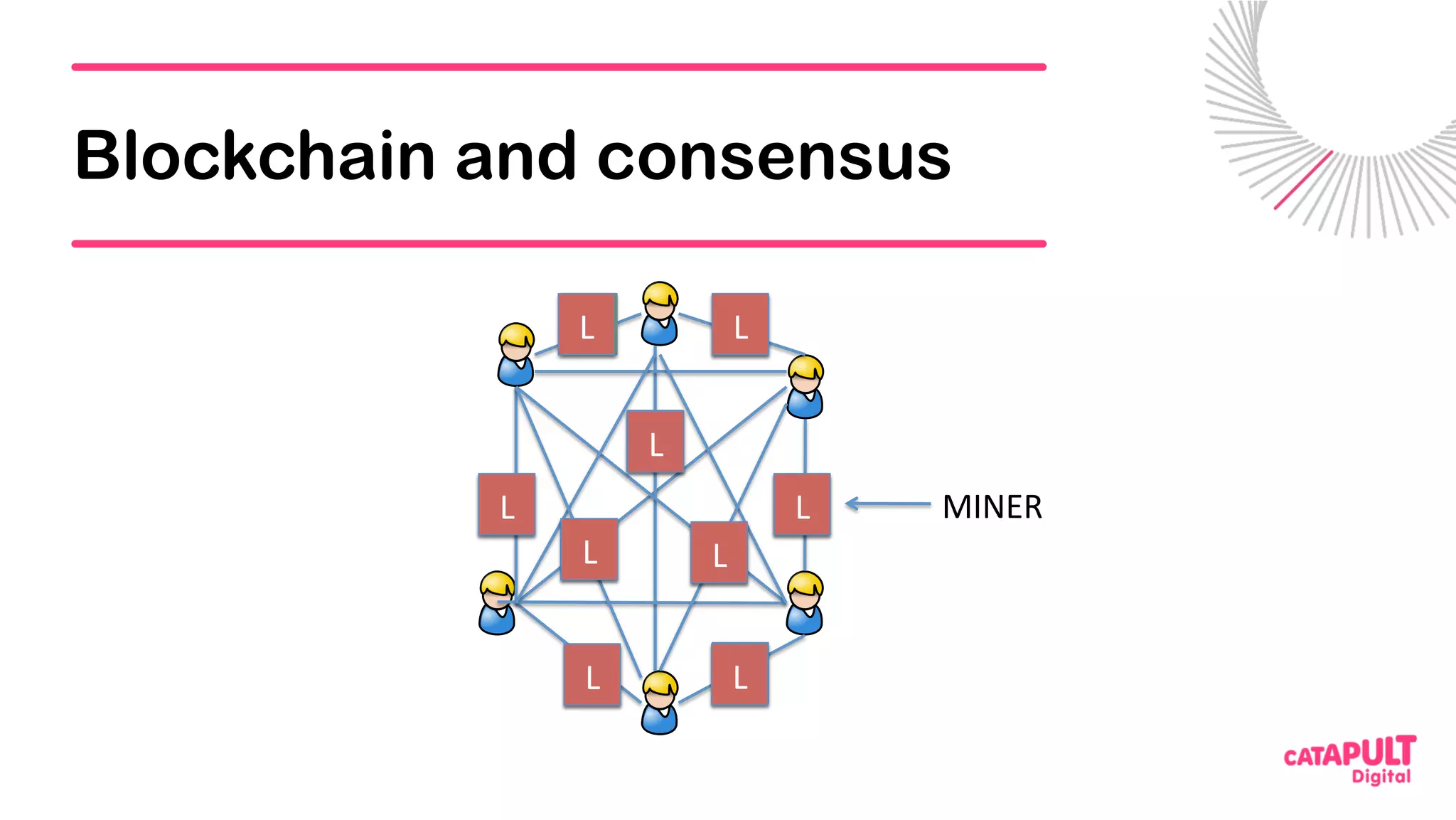
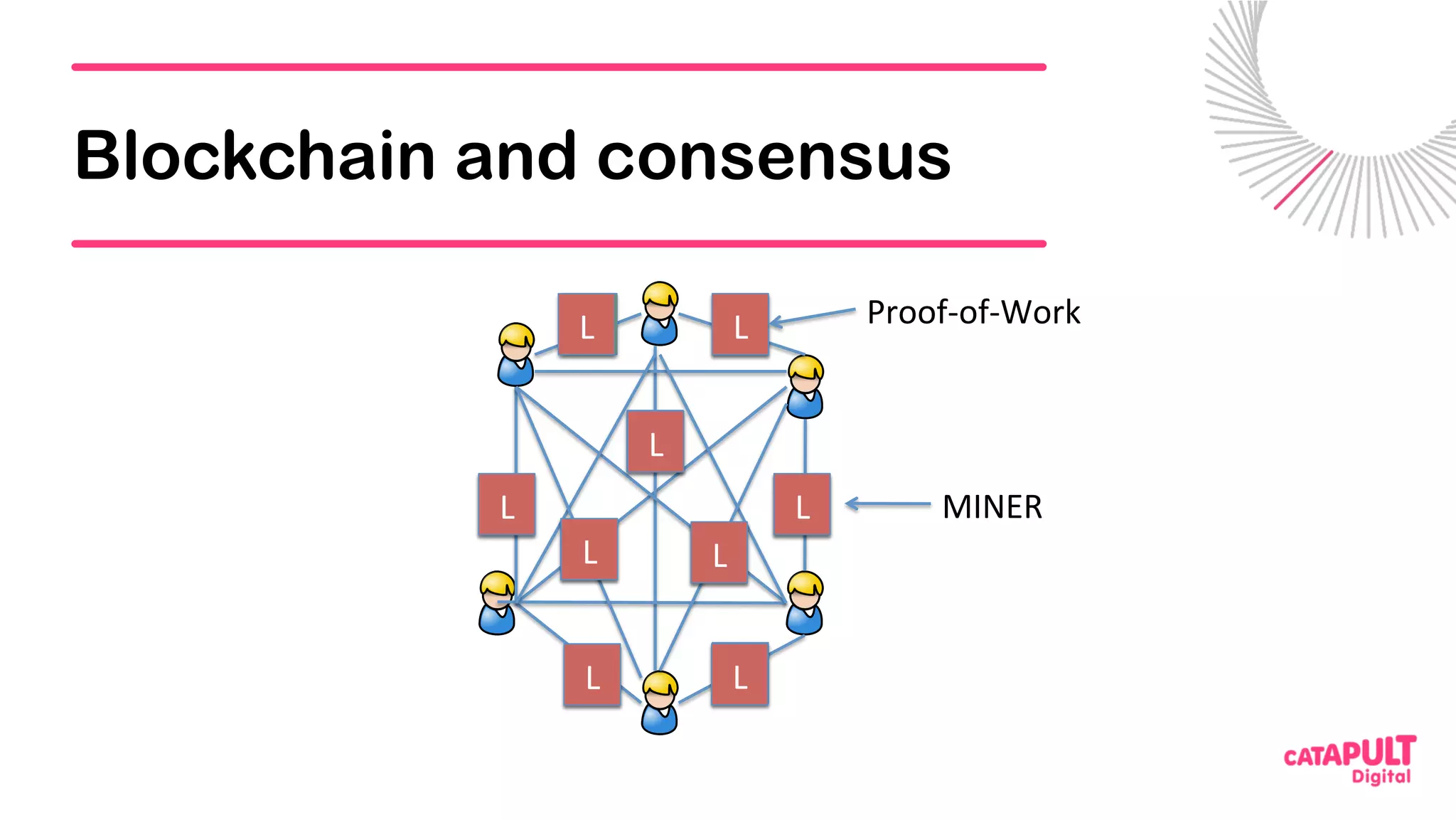
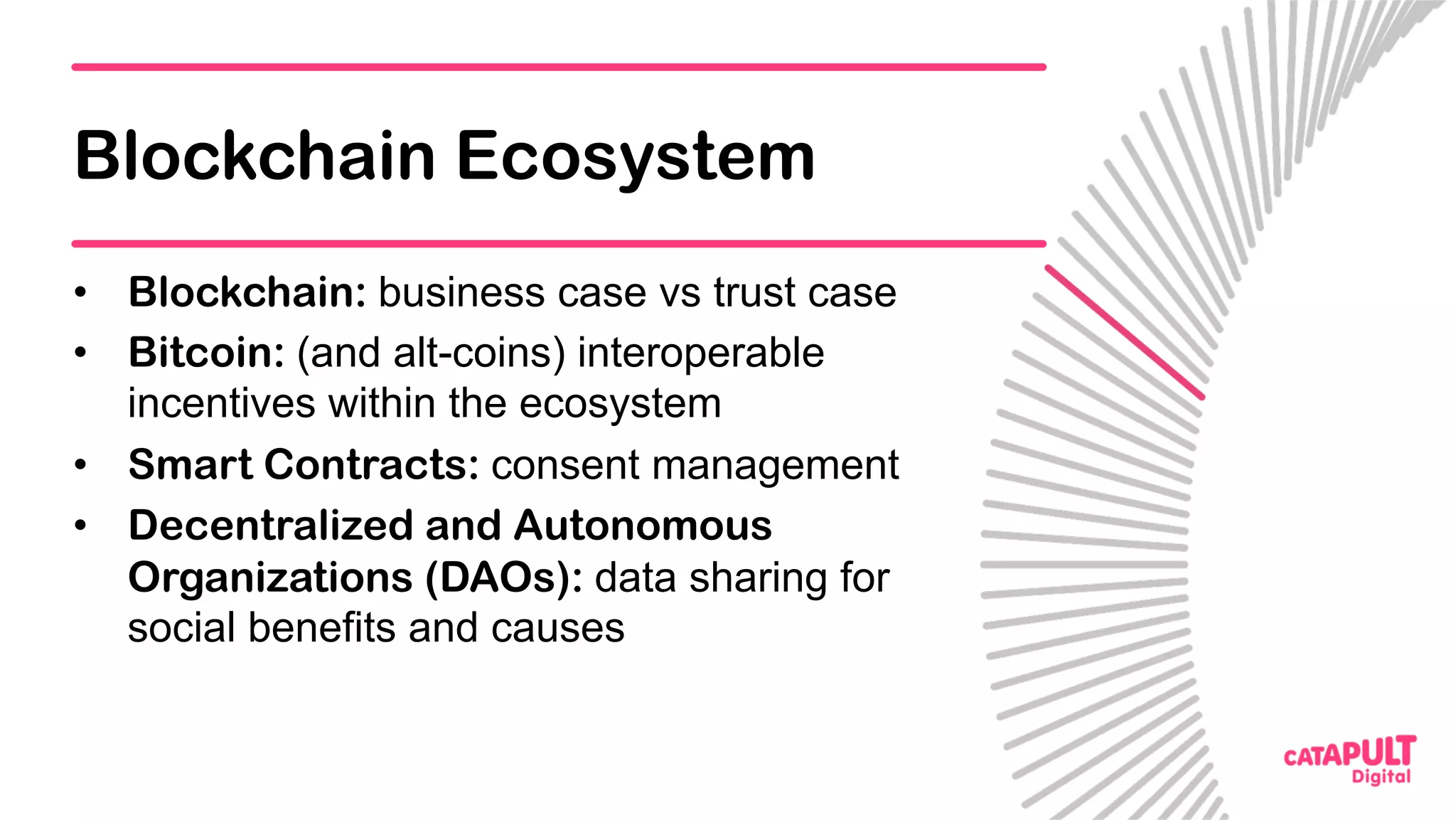
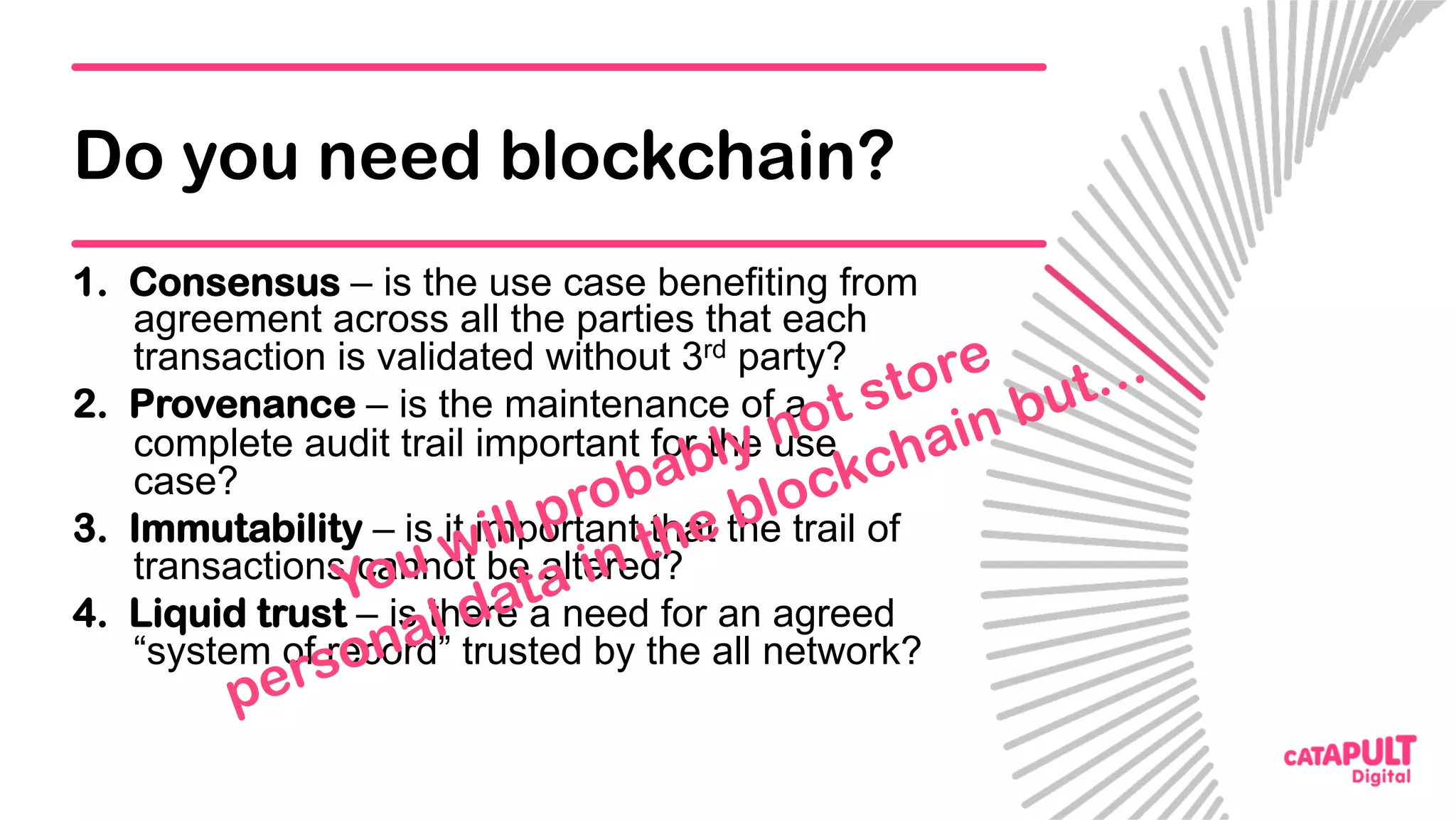
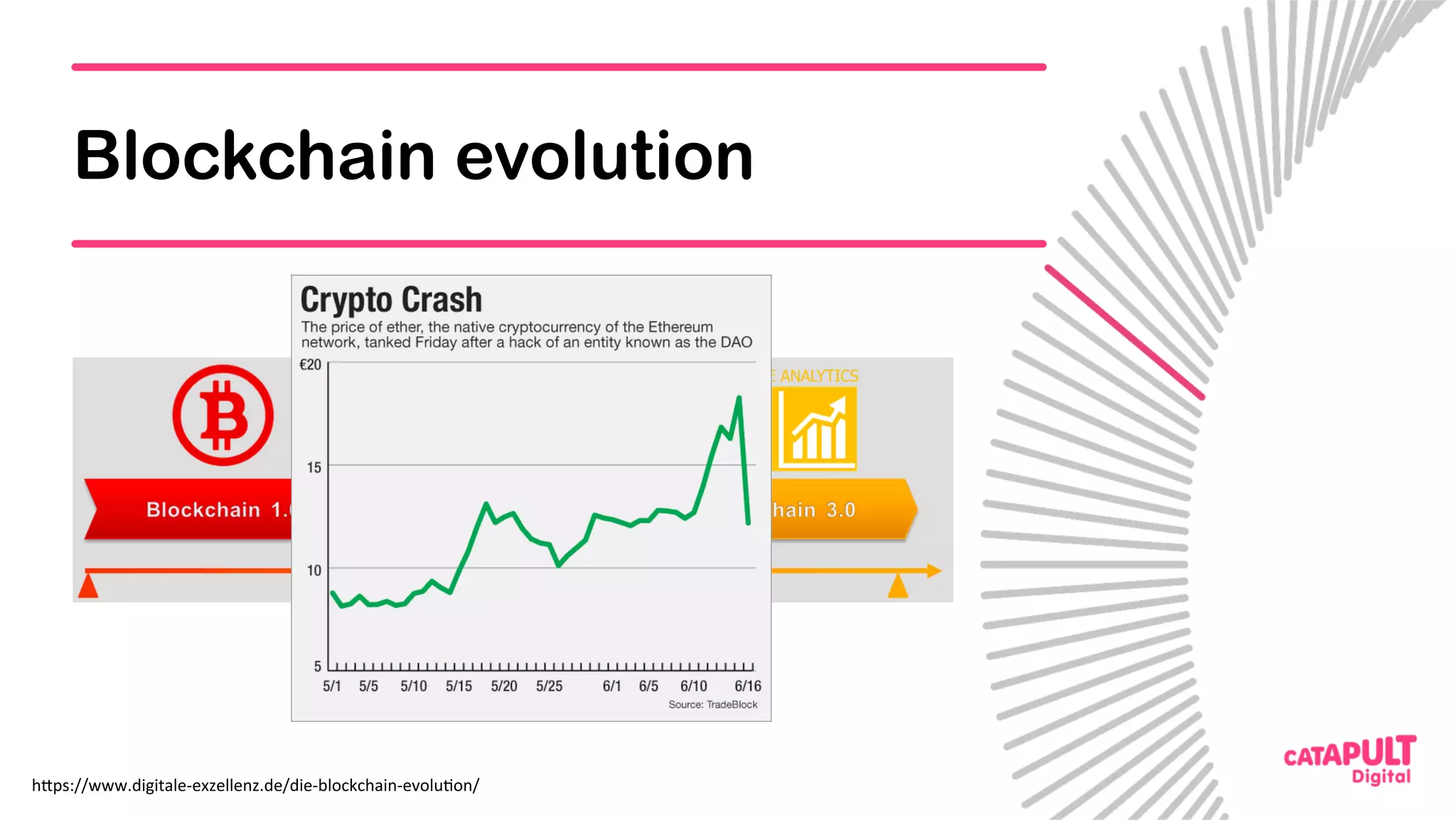
This document summarizes a presentation on personal data and blockchain. It discusses opportunities for personal data sharing, such as financial benefits and incentives, but also barriers like lack of trust and control over data. Blockchain is presented as a potential solution by providing decentralized control and transparency. Examples are given of how blockchain could be used for identity management and benefit distribution tracking for personal data. Challenges like privacy and governance of decentralized systems are also addressed.