The document discusses security considerations for IoT devices. It provides an overview of IoTivity, an open source project that implements the OIC standard to define security mechanisms for IoT. IoTivity addresses IoT security issues like device onboarding, provisioning, access control and privacy through features such as secure connectivity, hardware hardening and an access manager. The document also outlines threats to IoT devices from a physical, software and network perspective.

![3Samsung Open Source Group
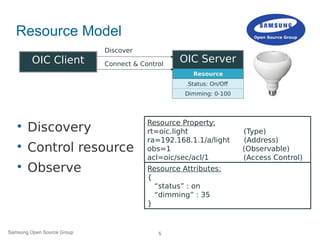
Need for IoT Security
IoT device to be around 26 billion by 2020 [1]
Increase in IoT device require strong security.
Lots of issues still in current IoT devices:[4]
– 80% of devices had privacy issues.
– 70% of devices used unencrypted network.
– 90% of device collected personal information.
– 70% of device along with their cloud enable
attacker to identify valid user account using
account renumeration.
Need for IoT devices to have device, network and
privacy concerns addressed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxconeu2015iotivitysecurity-151012152558-lva1-app6891/85/IoT-Meets-Security-3-320.jpg)





![12Samsung Open Source Group © SAMSUNG Electronics Co.
Ownership Transfer – Just Works
Onboarding Tool Enrolling DeviceOnboarding Tool
Ownership Transfer Start
GET /oic/sec/doxm?Owned=”False”
RSP [{“OxmType”: “oic.sec.doxm.jw”,
“DeviceId”: “UUID”}]
Discovery
Preparing for Ownership
transfer using Just Works
Set Ownership
transfer Method
PUT /oic/sec/doxm [{“OxmSel”:
“oic.sec.doxm.jw”}]
RSP 2.04
SRM enables
TLS_ECDH_anon_WITH_AES_12SHA256
cipher suite
DTLS Connection
PUT /oic/sec/doxm [{“Owned”: “T”,
“Owner”: “Admin0””}]
RSP 2.04
Ownership Transfer Stops](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxconeu2015iotivitysecurity-151012152558-lva1-app6891/85/IoT-Meets-Security-11-320.jpg)
![13Samsung Open Source Group © SAMSUNG Electronics Co.
Ownership Transfer – Random PIN
Onboarding Tool Enrolling DeviceOnboarding Tool
Ownership Transfer Start
GET /oic/sec/doxm?Owned=”False”
RSP [{“OxmType”: “oic.sec.doxm.rdp”,
“DeviceId”: “UUID”}]
Discovery
Preparing for Ownership
transfer using Random PIN
Set Ownership
transfer Method
PUT /oic/sec/doxm [{“OxmSel”:
“oic.sec.doxm.rdp”}]
RSP 2.04
SRM enables
TLS_ECDHE_PSK_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SH
A256 cipher suite
DTLS Connection
PUT /oic/sec/doxm [{“Owned”: “T”,
“Owner”: “Admin0””}]
RSP 2.04
Ownership Transfer Stops](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxconeu2015iotivitysecurity-151012152558-lva1-app6891/85/IoT-Meets-Security-12-320.jpg)

![15Samsung Open Source Group © SAMSUNG Electronics Co.
8
Onboarding Tool Enrolling DeviceOnboarding Tool
Ownership Transfer Start
GET /oic/sec/doxm?Owned=”False”
RSP [{“OxmType”: “oic.sec.doxm.mfgcert”,
“DeviceId”: “UUID”}]
Discovery
Preparing for Ownership
transfer using Certificate
Set Ownership
transfer Method
PUT /oic/sec/doxm [{“OxmSel”:
“oic.sec.doxm.mfgcert”}]
RSP 2.04
SRM enables
TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CCM_
8_SHA256 cipher suite
DTLS Connection
POST /oic/sec/doxm [{“credid”: “..”, “sub”: “..”,
“credType”: “8”, “pdbdata”: “device and CA in
base 64”, “pvdata”: {“x”: “x position of elliptic
curve in base 64”, “y”: “y position of elliptic
curve in base 64”, “ownrs”: “” }}]
RSP 2.04
Ownership Transfer Stops
Owner transfer protocol
- Asymmetric certificate](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxconeu2015iotivitysecurity-151012152558-lva1-app6891/85/IoT-Meets-Security-14-320.jpg)

![17Samsung Open Source Group © SAMSUNG Electronics Co.
Provisioning
8
Onboarding Tool Enrolling DeviceOnboarding Tool
ACL Provisioning Start
GET /oic/sec/pstat
RSP [{“IsOp”: “False”, “Sm”: “0x11”}]
Status
Client Mode PUT /oic/sec/pstat [{“Om”: “0x11”}]
RSP 2.04
RSP 2.04
ACL Provisioning Stop
DTLS with Owner PSK
RSP 2.04
RSP 2.04](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxconeu2015iotivitysecurity-151012152558-lva1-app6891/85/IoT-Meets-Security-16-320.jpg)
![18Samsung Open Source Group © SAMSUNG Electronics Co.
Secure Resource Manager (SRM)
Management of the secure virtual resource and ACL [3].
Secure Resource Manager Layer
Resource Manager (RM)
Persistent Storage
interface
Policy Engine (PE)
Connection Abstraction (CA) Layer
DTLS Module
Resource Introspection (RI) Layer
Application
Secure
Virtual
Resource
Database](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxconeu2015iotivitysecurity-151012152558-lva1-app6891/85/IoT-Meets-Security-17-320.jpg)



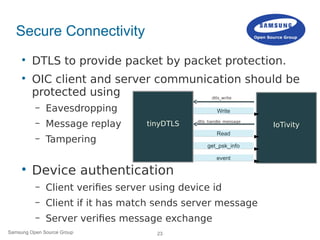




![29Samsung Open Source Group
Local Access Control
Is light open?
Request
Accept
Response
Turn Light Off
Request
Reject
Response
acl[0]
acl[0]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxconeu2015iotivitysecurity-151012152558-lva1-app6891/85/IoT-Meets-Security-28-320.jpg)
![30
Remote Access Control
Samsung Open Source Group
Is light open?
Request
Accept
Response
Turn Light Off
Request
Reject
Response
Request
amacl[0]
amacl[0]
Request
AMS1
AMS1
Response
Response](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxconeu2015iotivitysecurity-151012152558-lva1-app6891/85/IoT-Meets-Security-29-320.jpg)

![32Samsung Open Source Group © SAMSUNG Electronics Co.
References
[1] http://www.gartner.com/newsroom/id/2636073
[2] https://www.owasp.org/images/8/8e/Infographic-v1.jpg
[3] https://wiki.iotivity.org/iotivity_security
[4] http://www8.hp.com/h20195/V2/GetPDF.aspx/4AA5-4759ENW.pdf
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxconeu2015iotivitysecurity-151012152558-lva1-app6891/85/IoT-Meets-Security-31-320.jpg)
