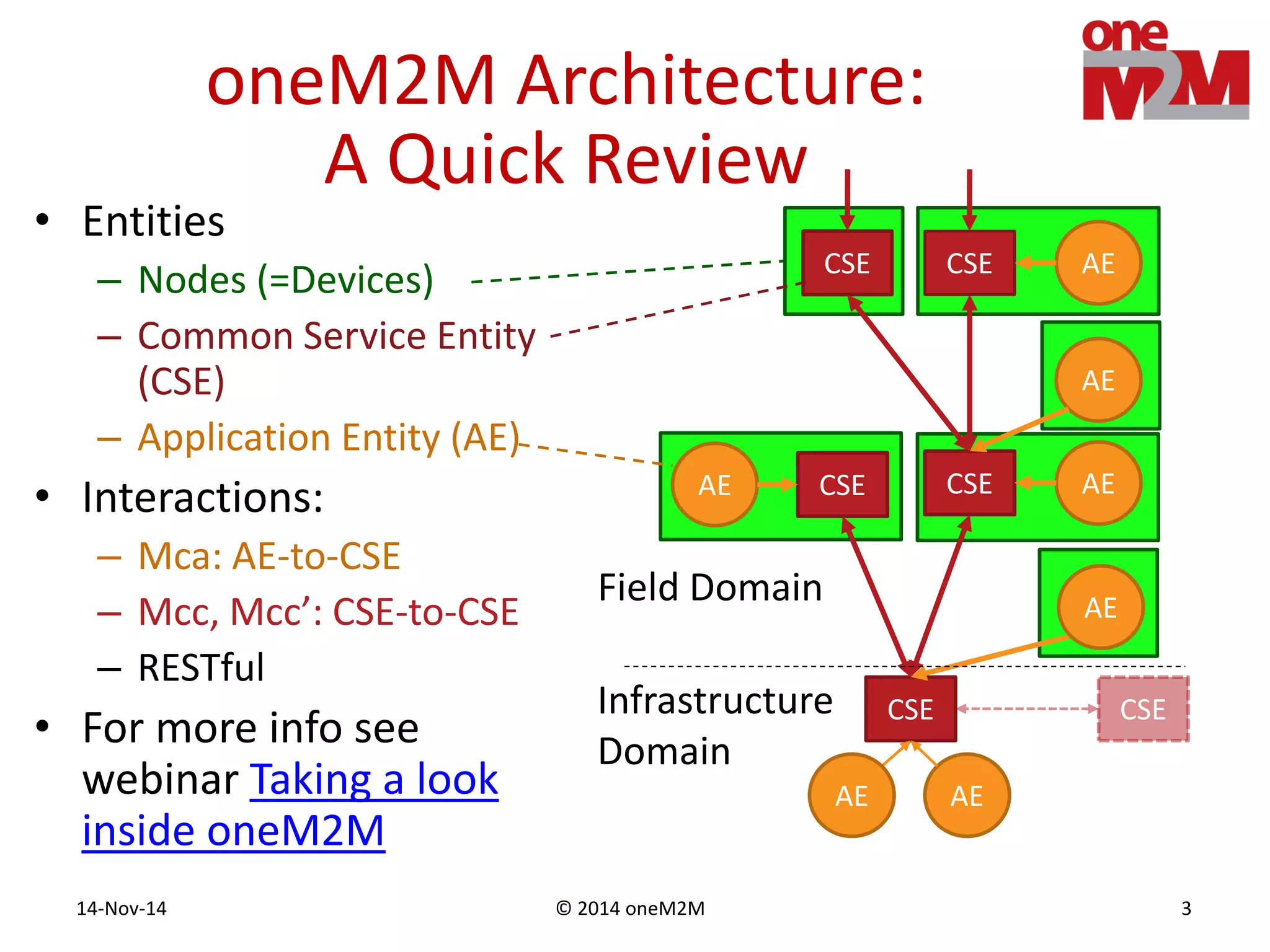
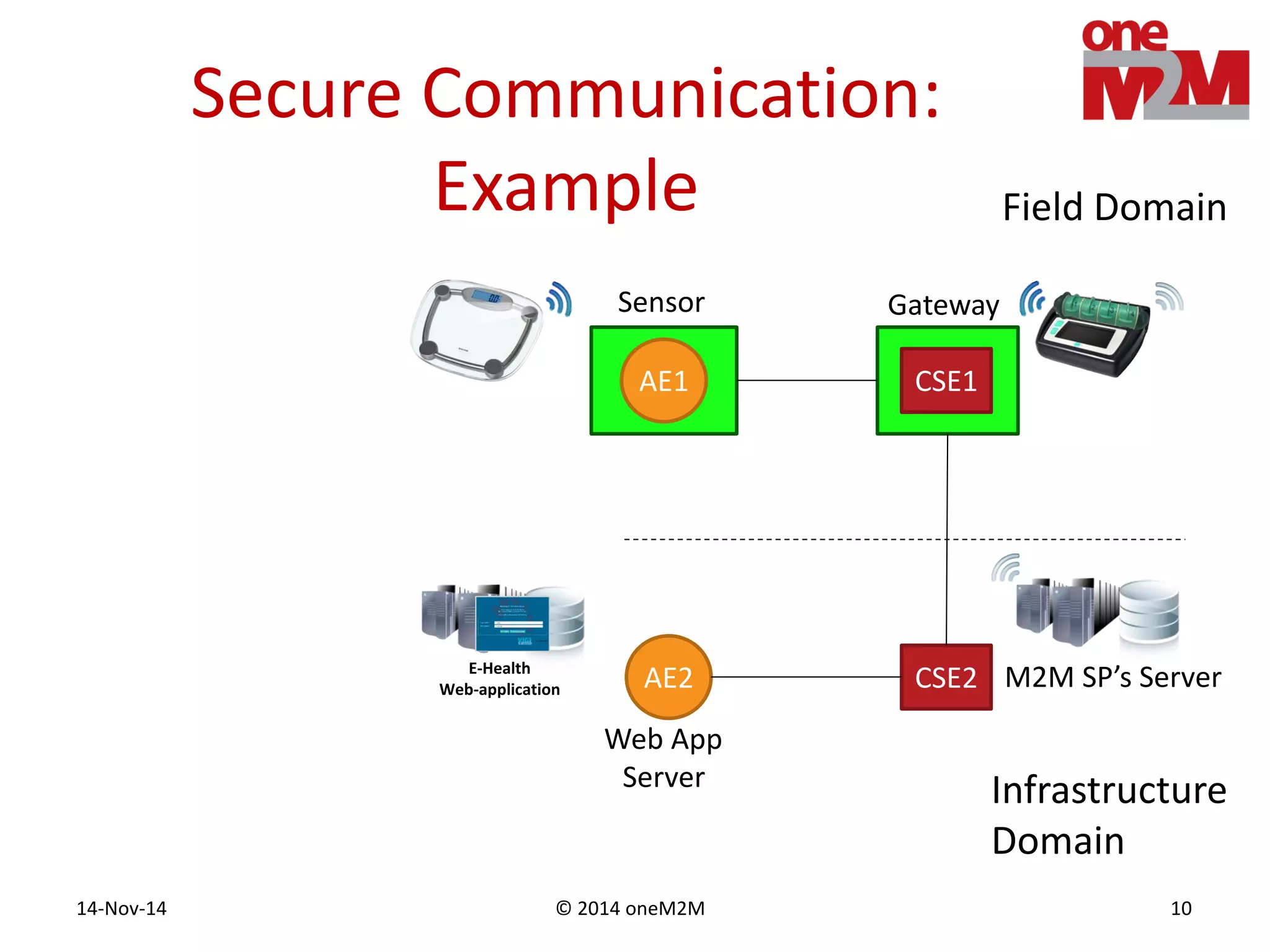
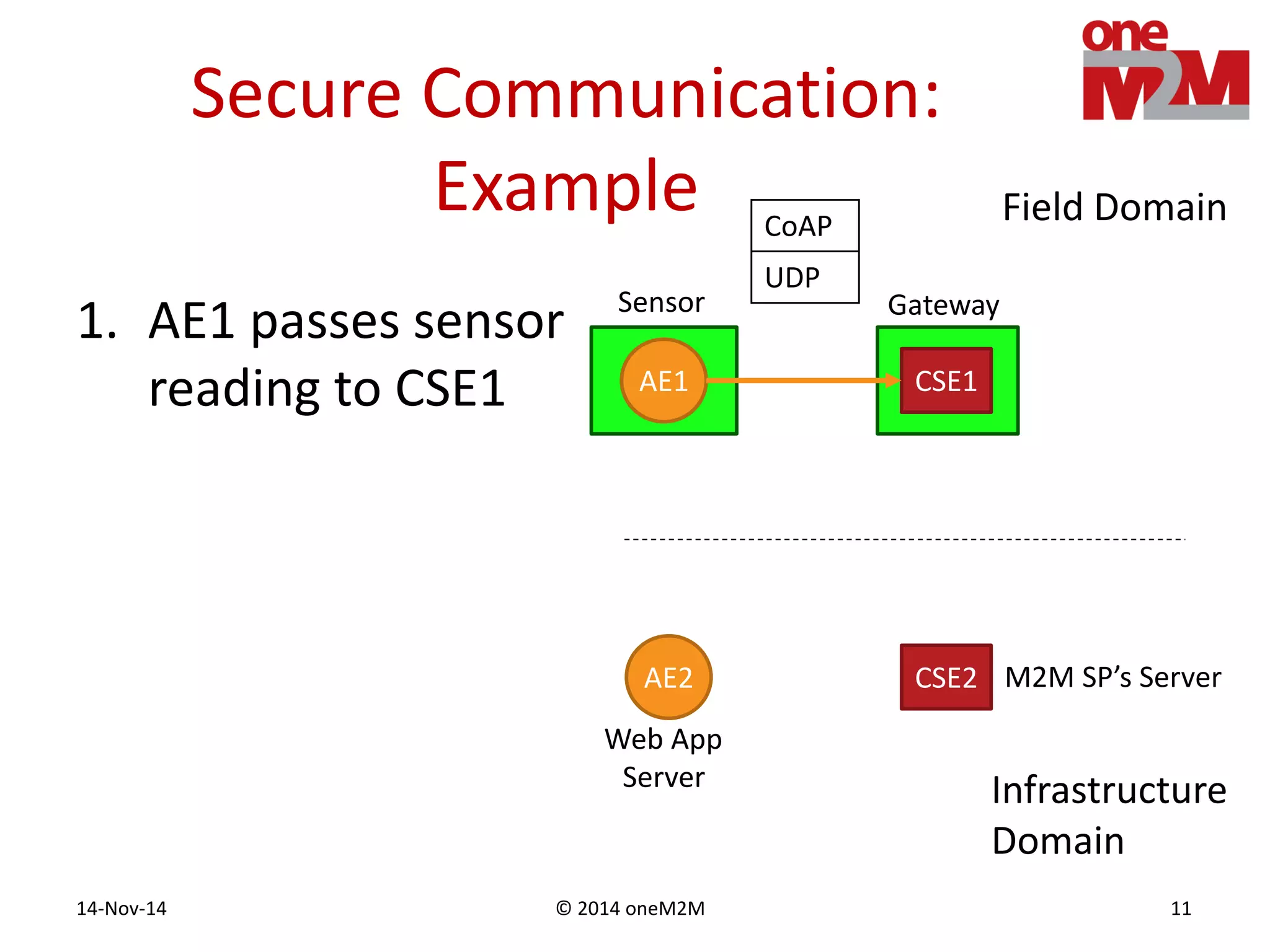
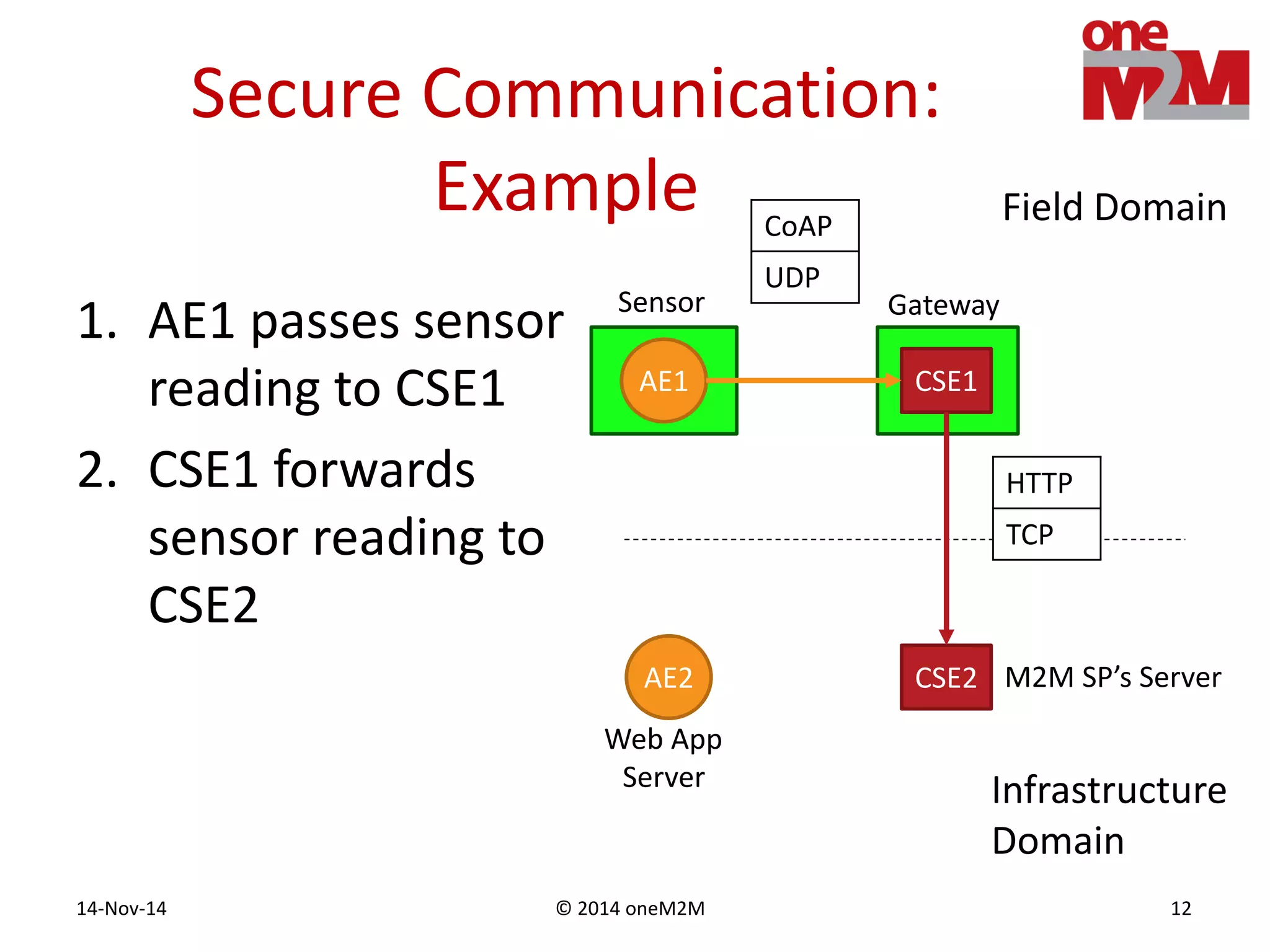
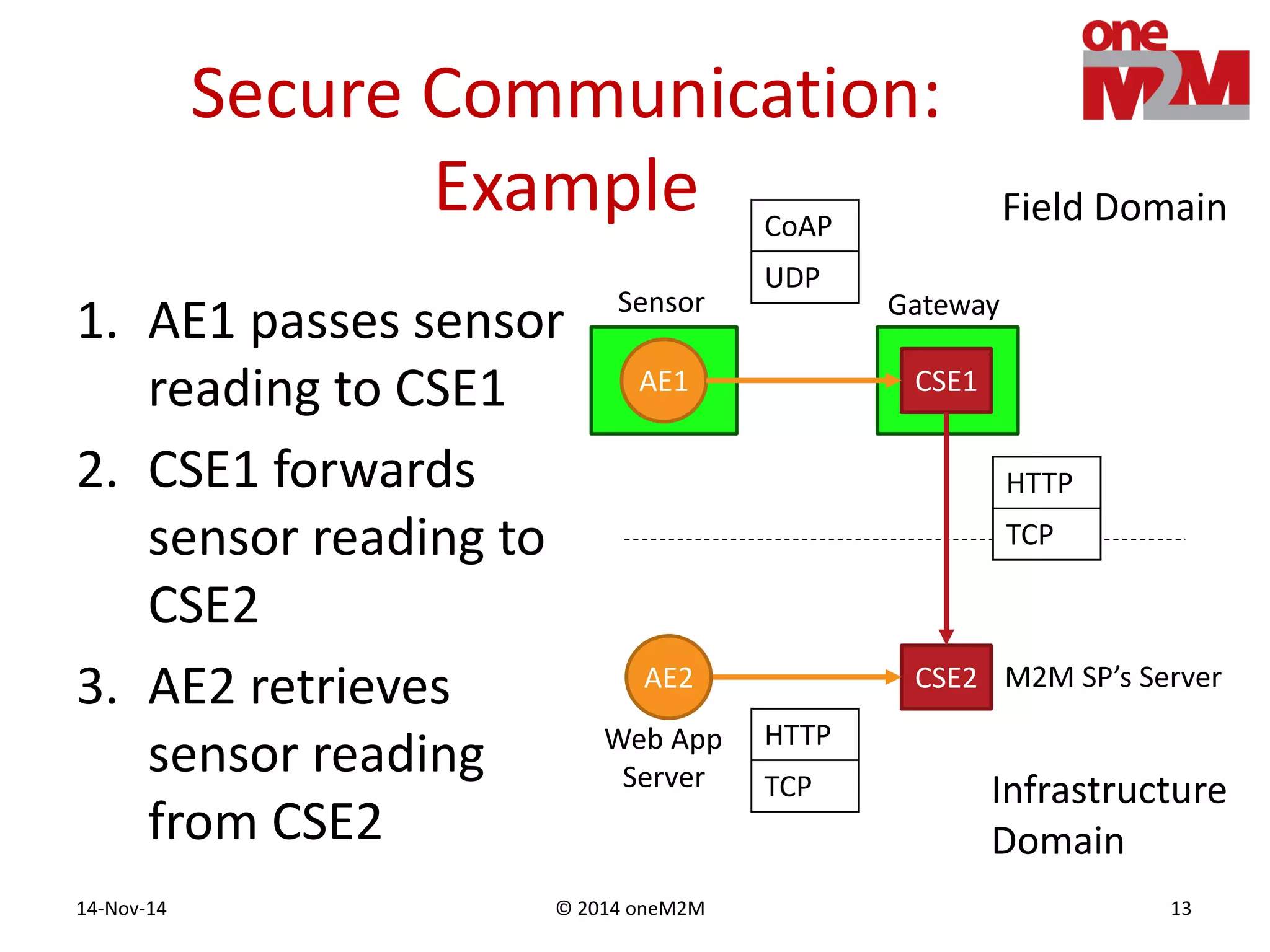
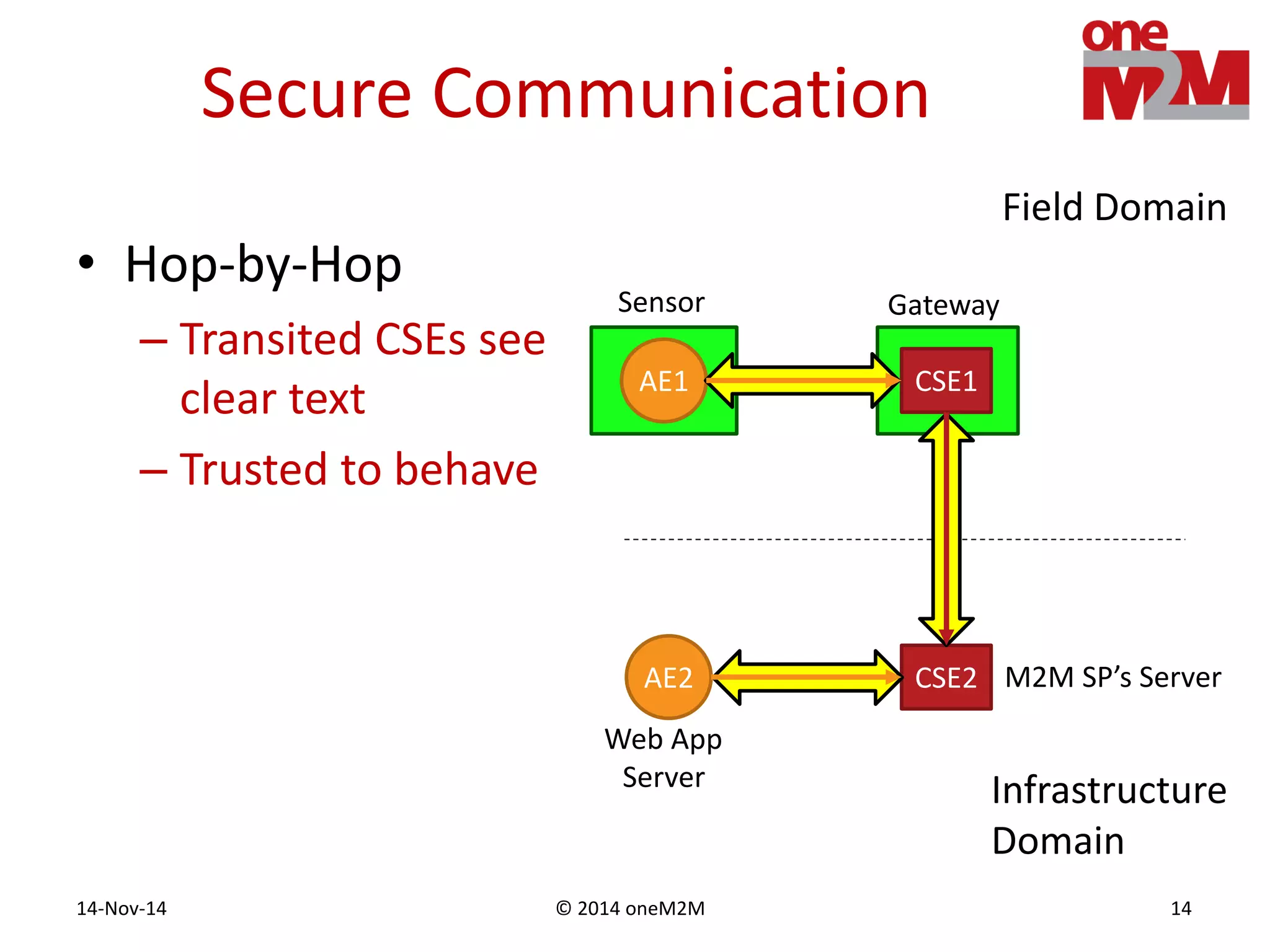
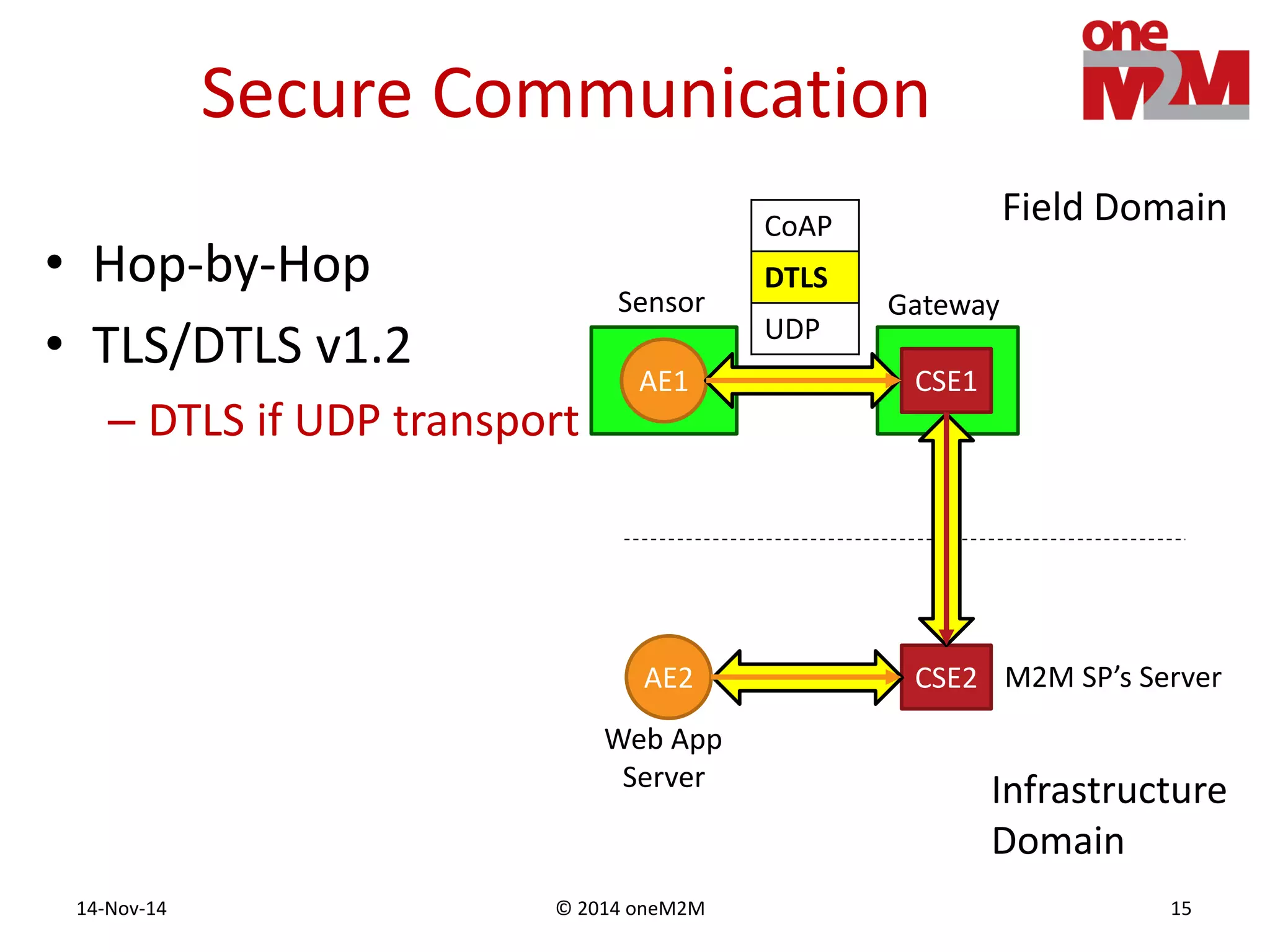
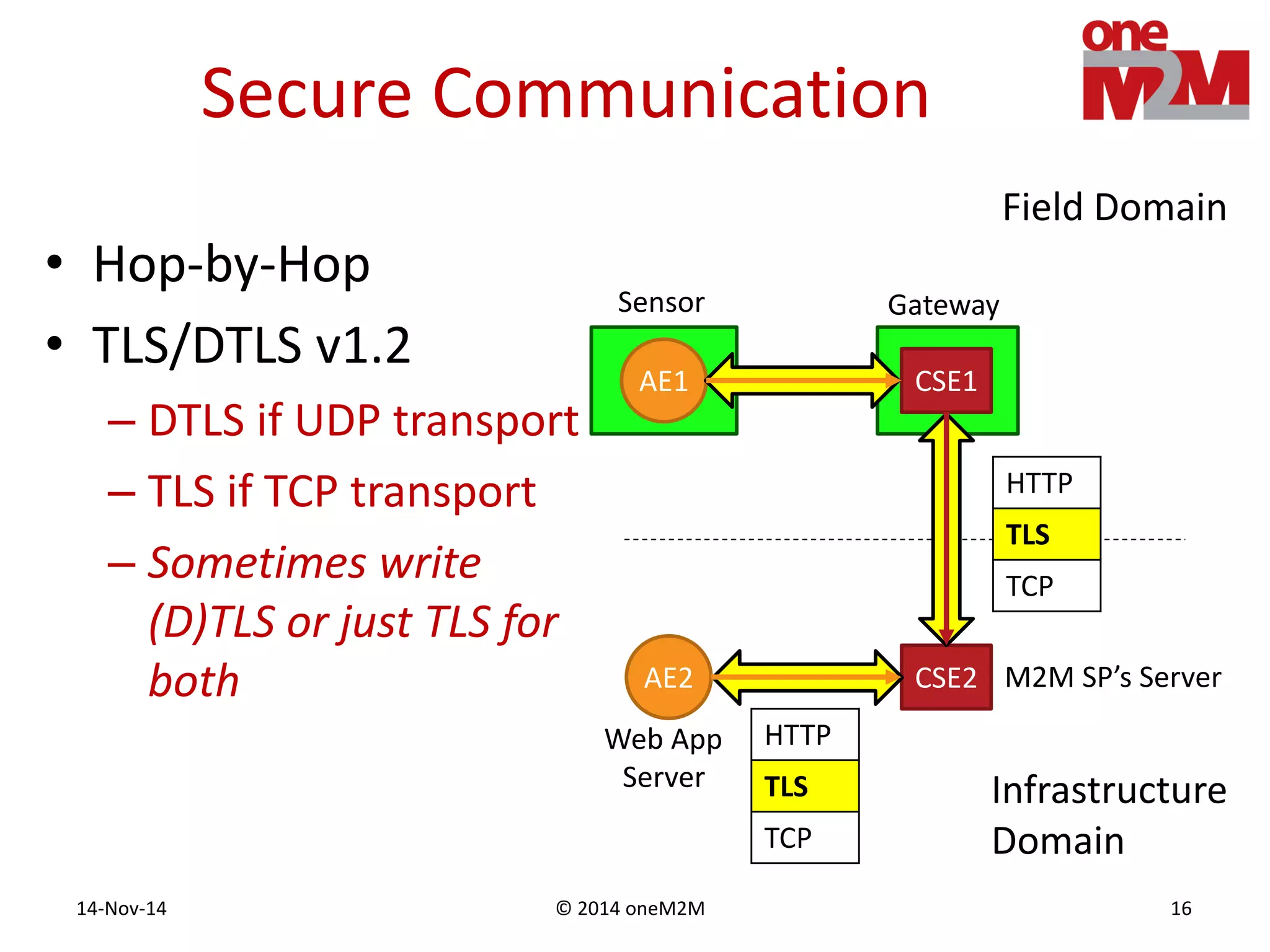
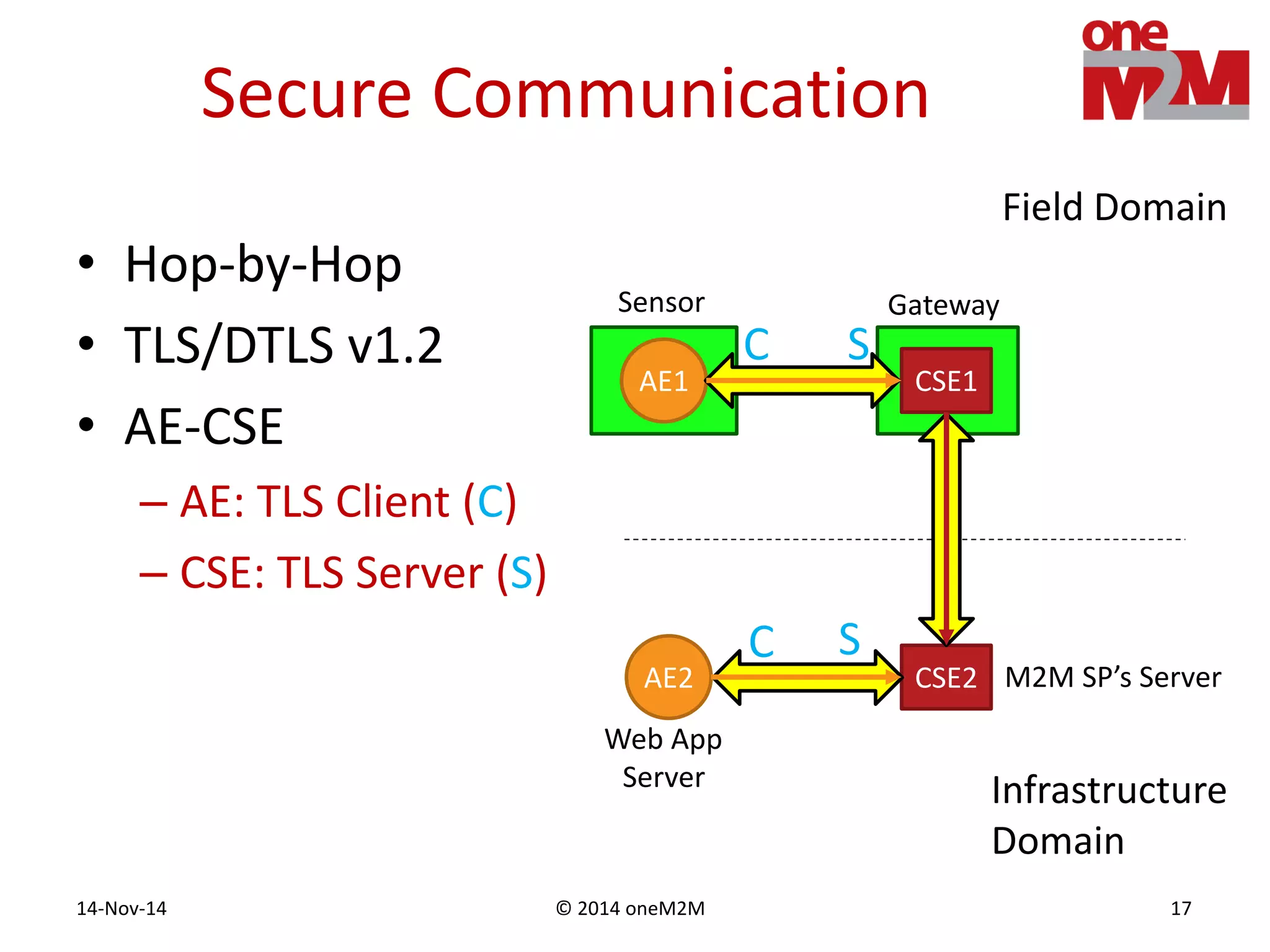
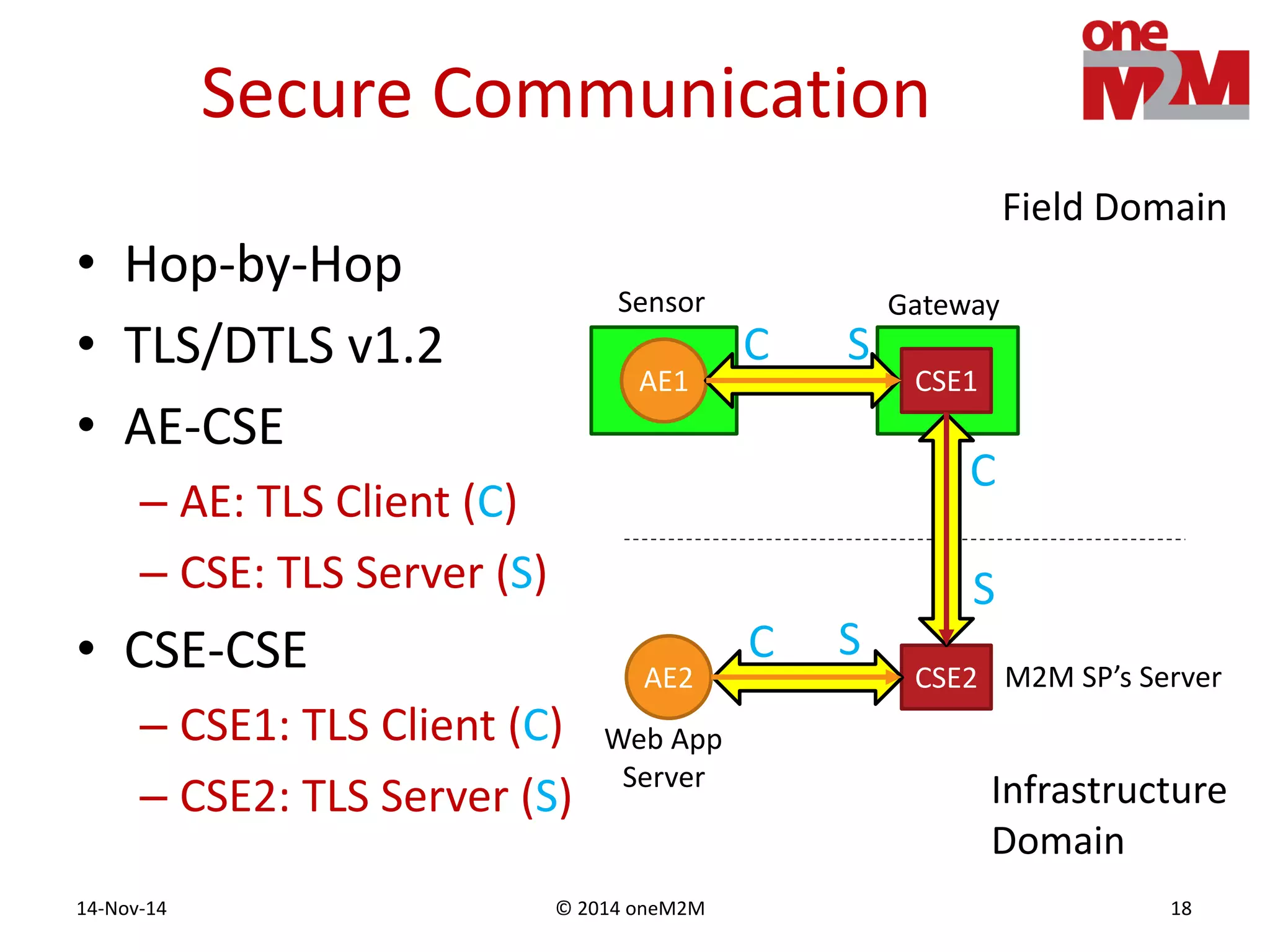
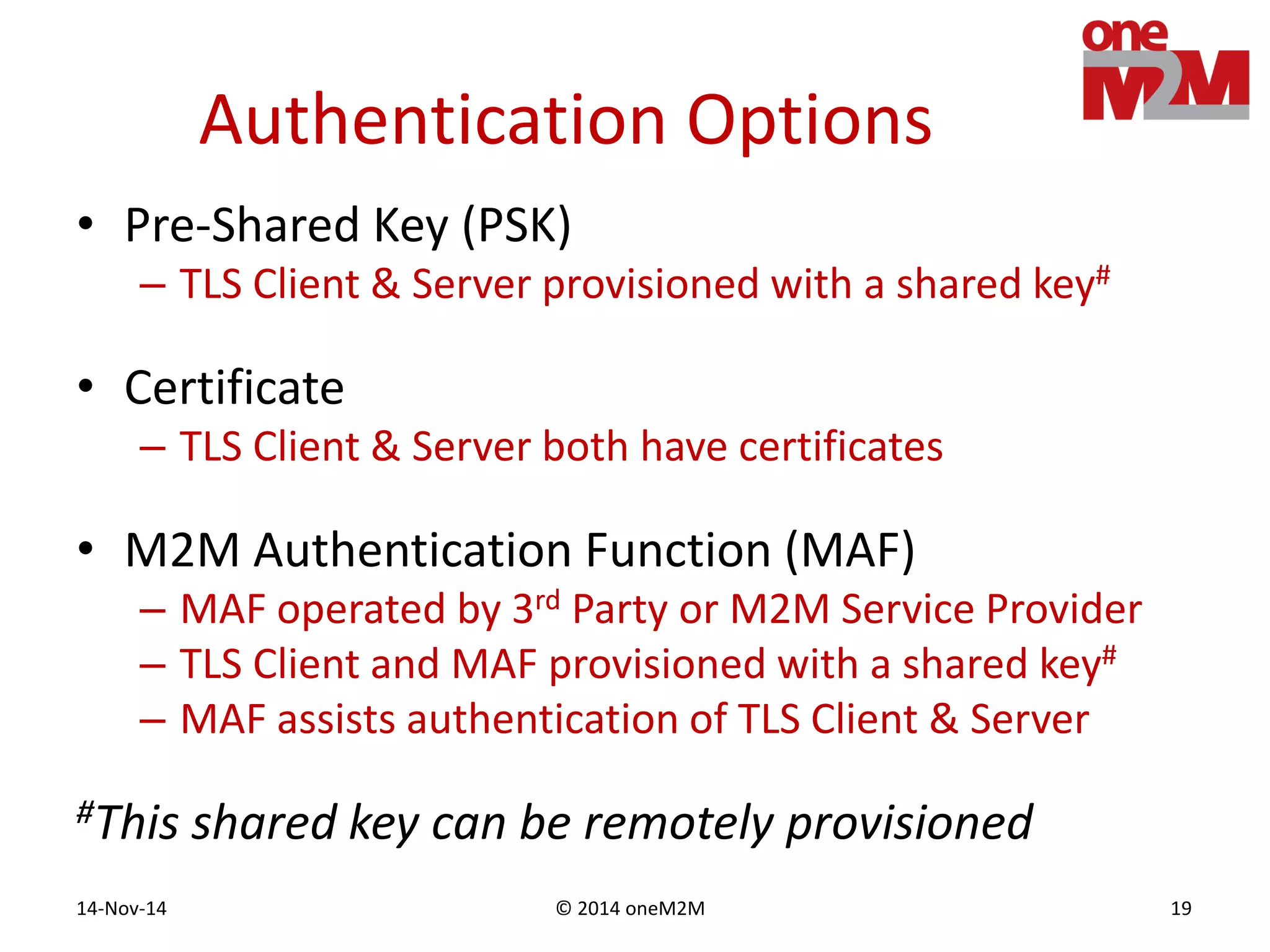
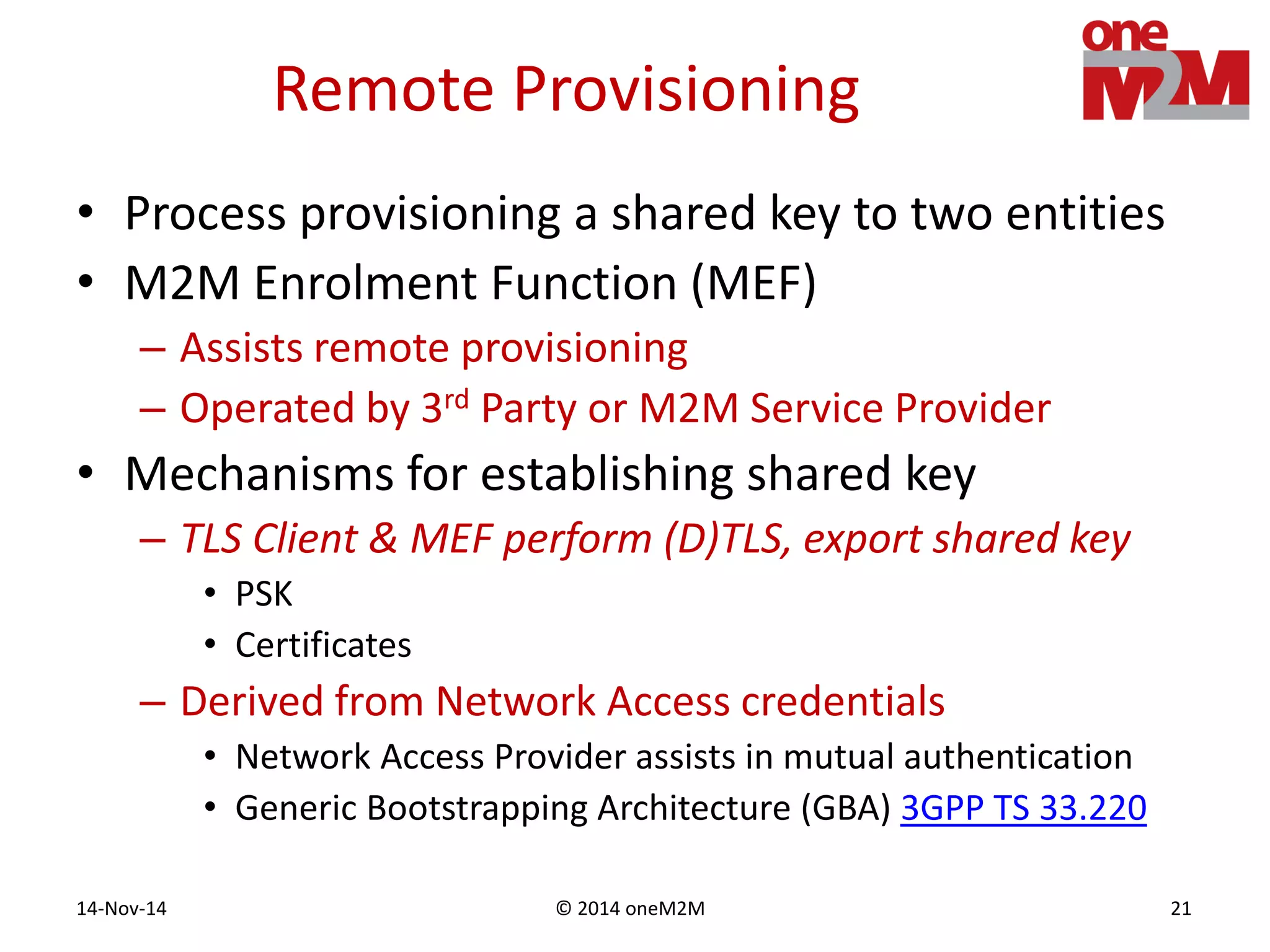
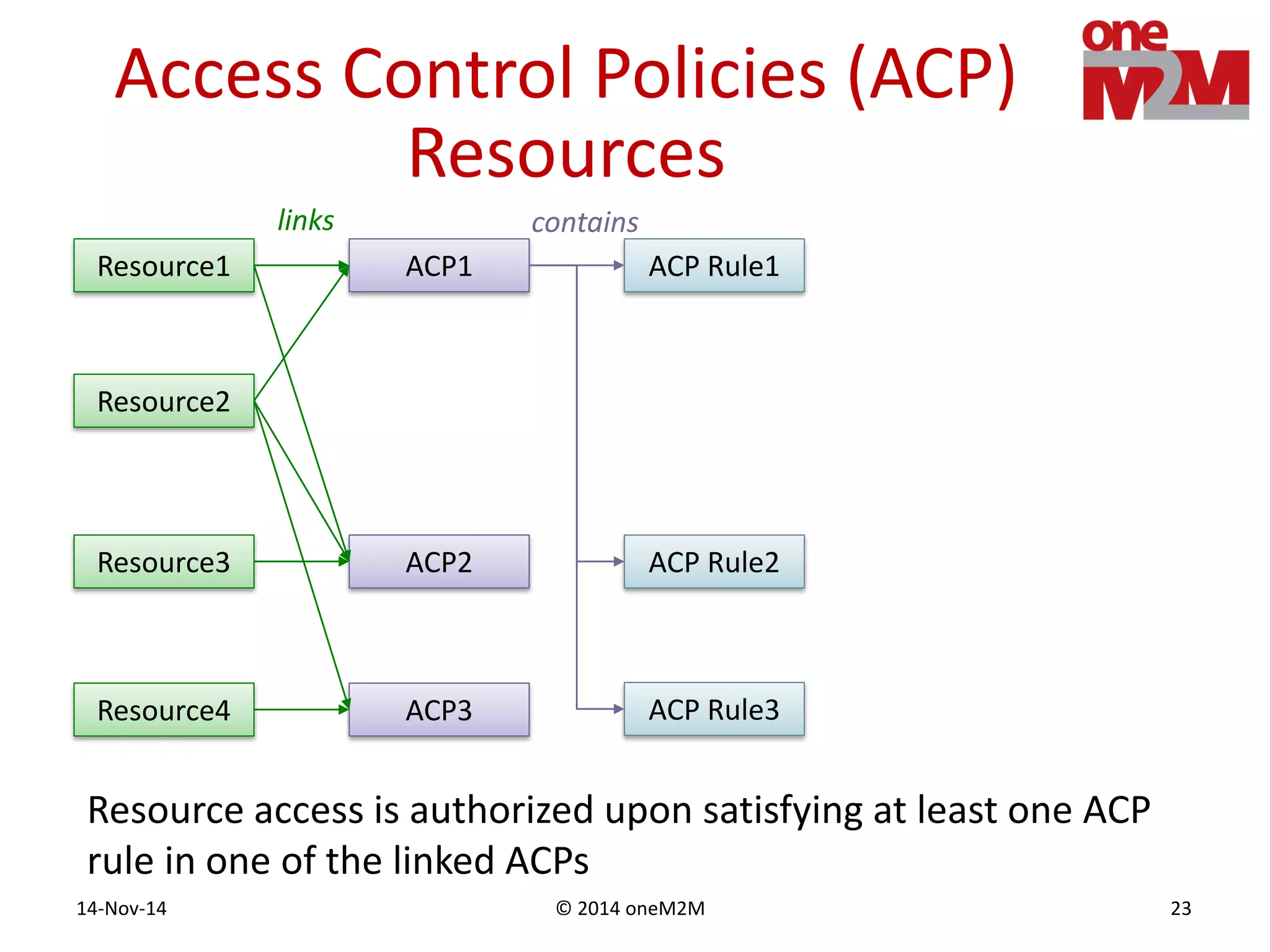
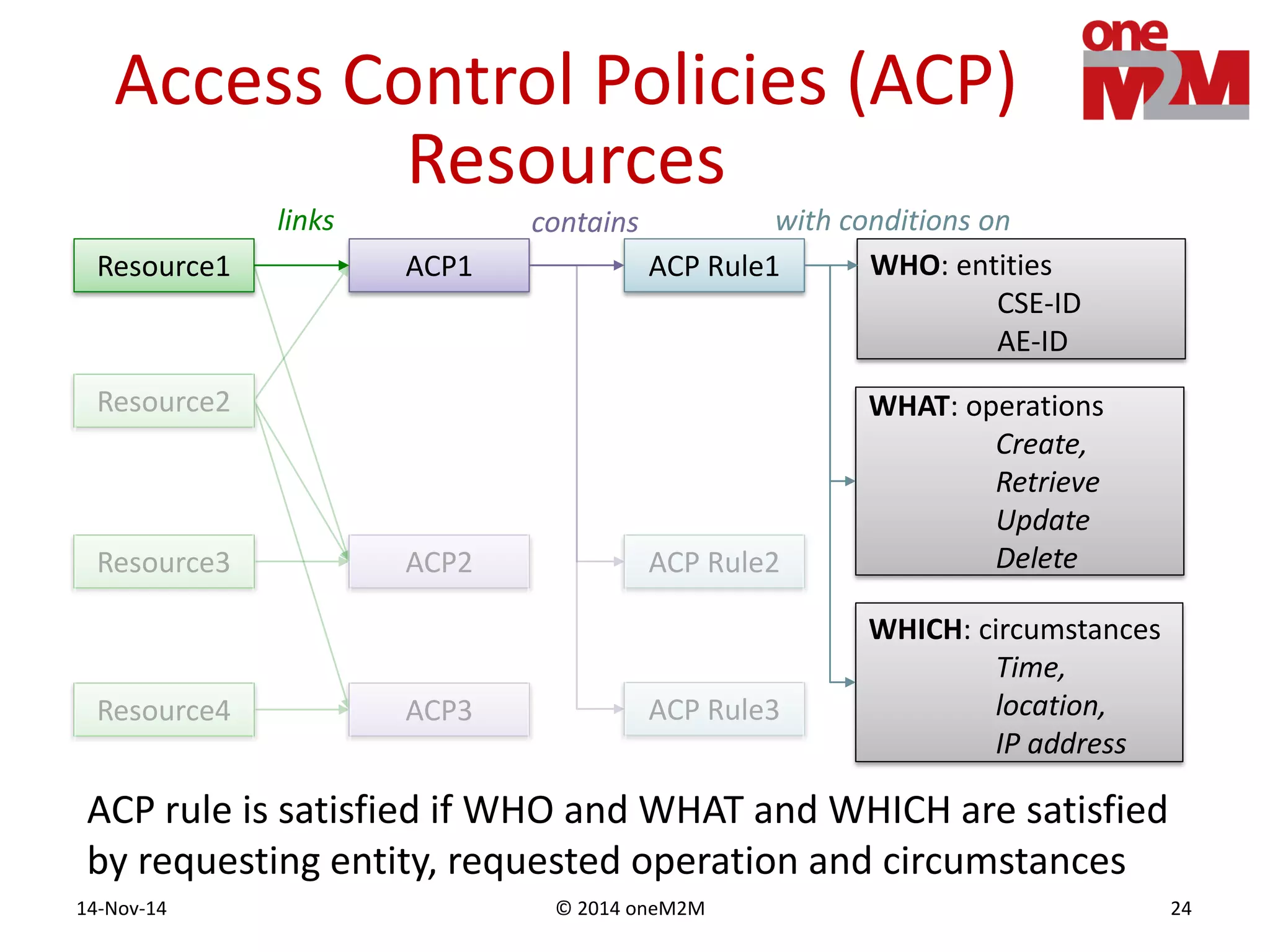
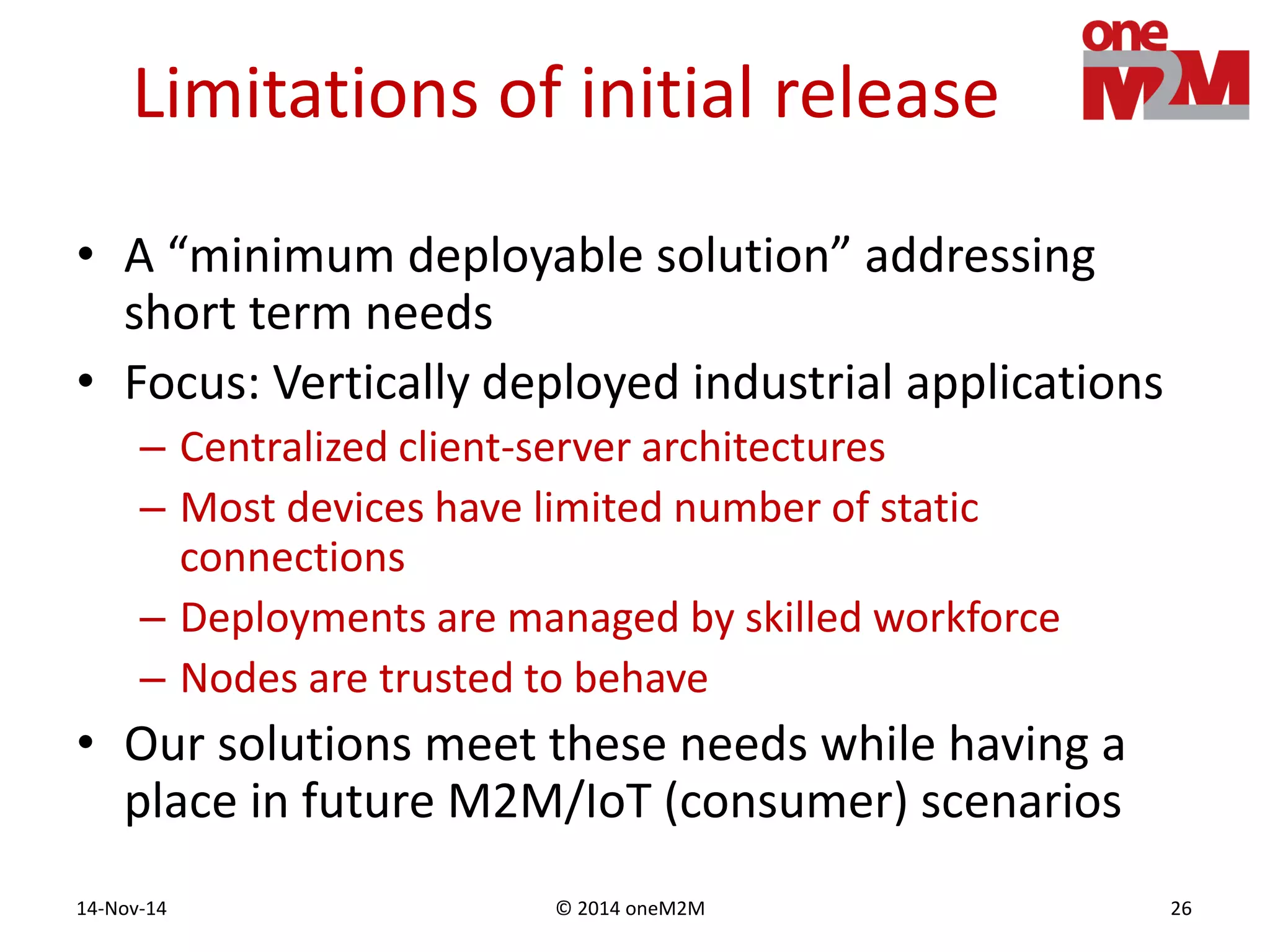
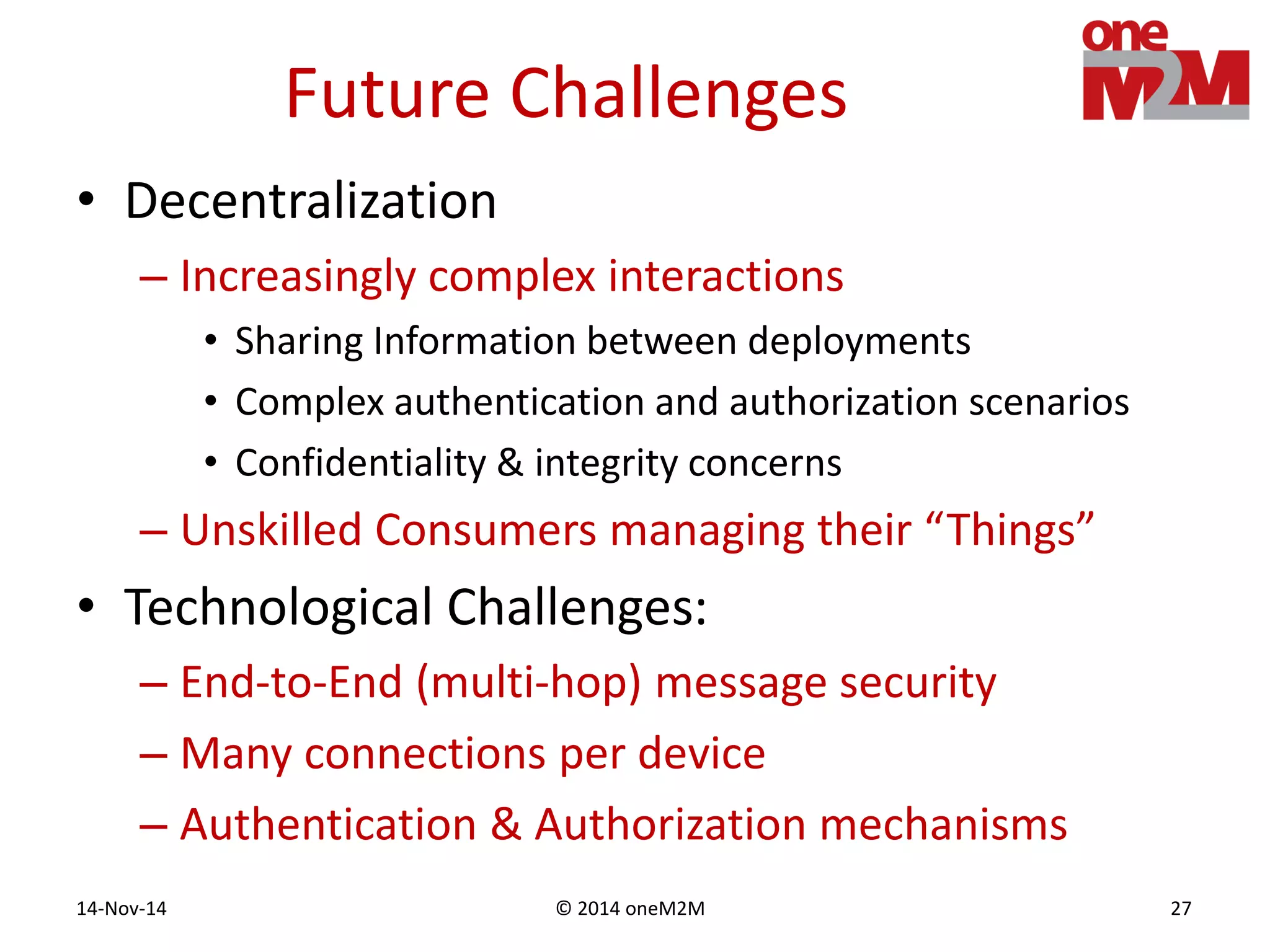
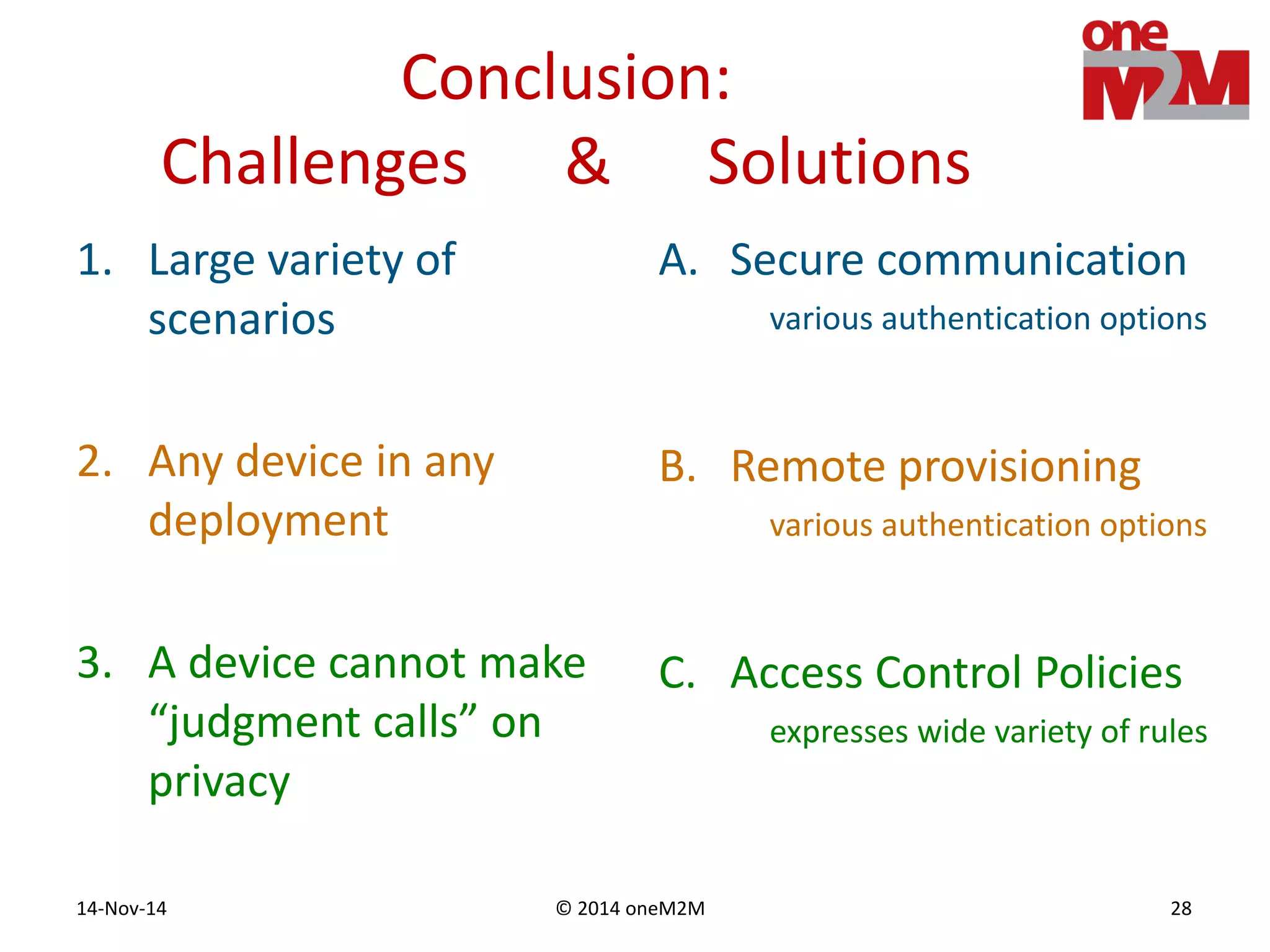
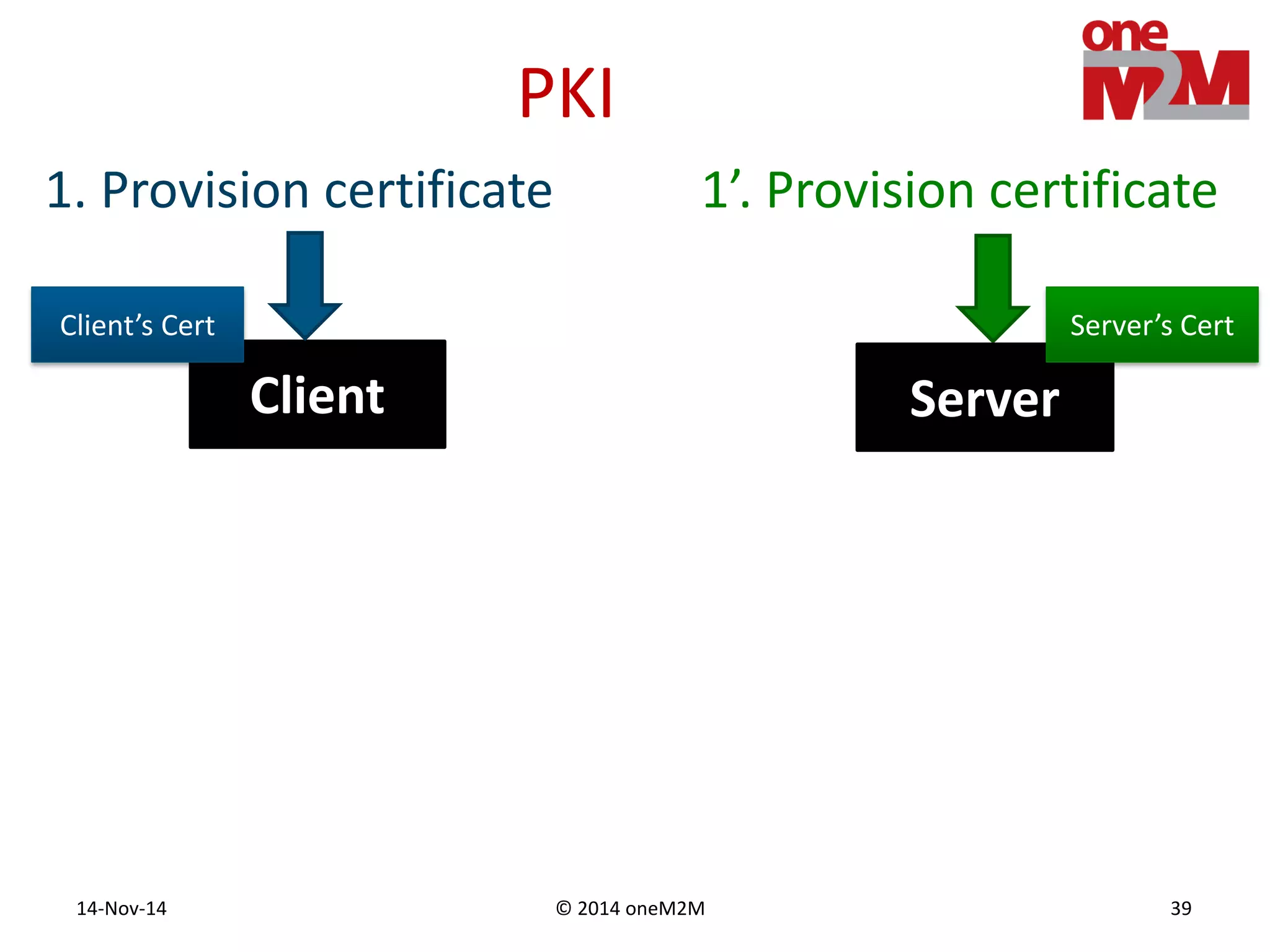
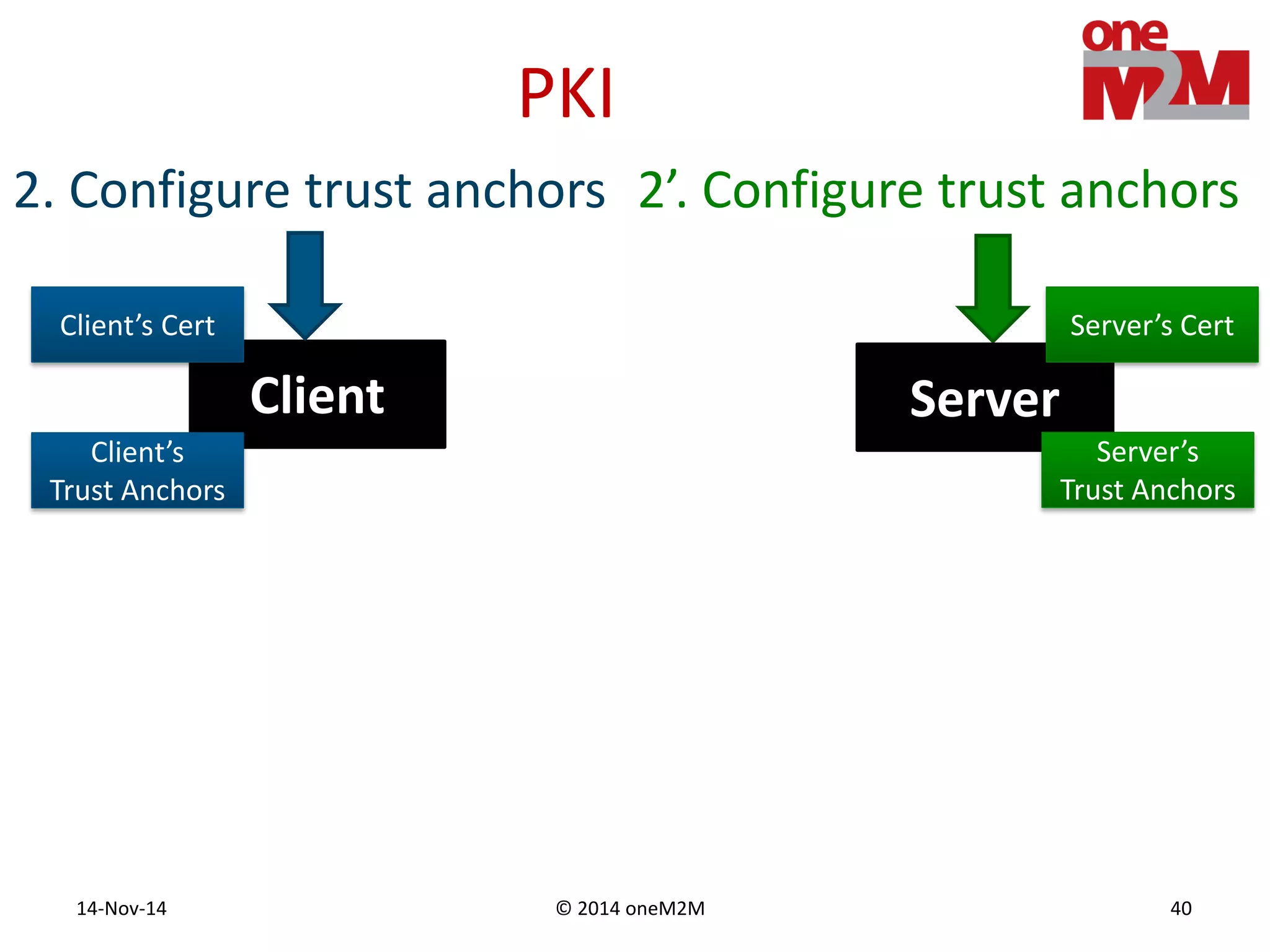
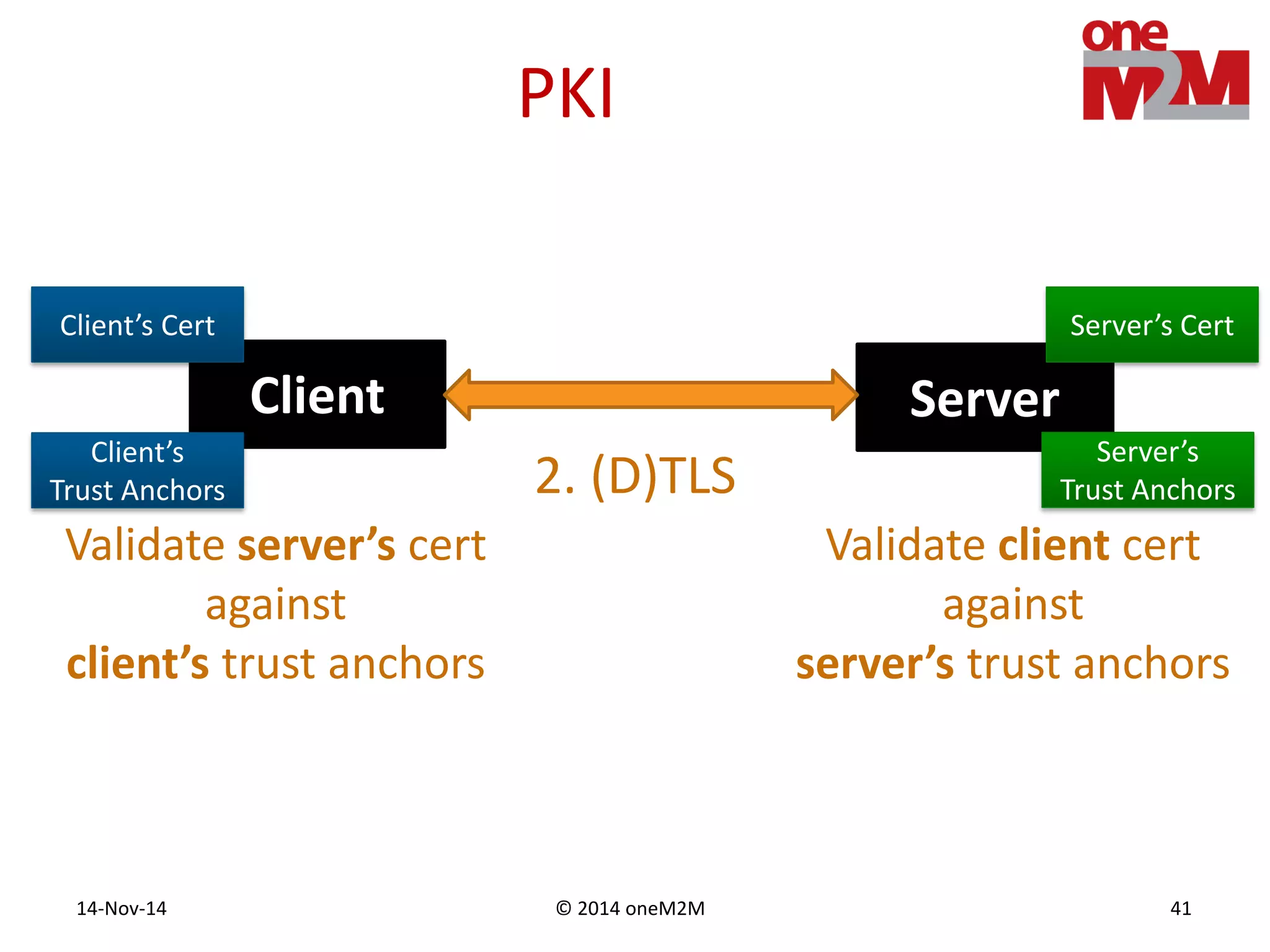
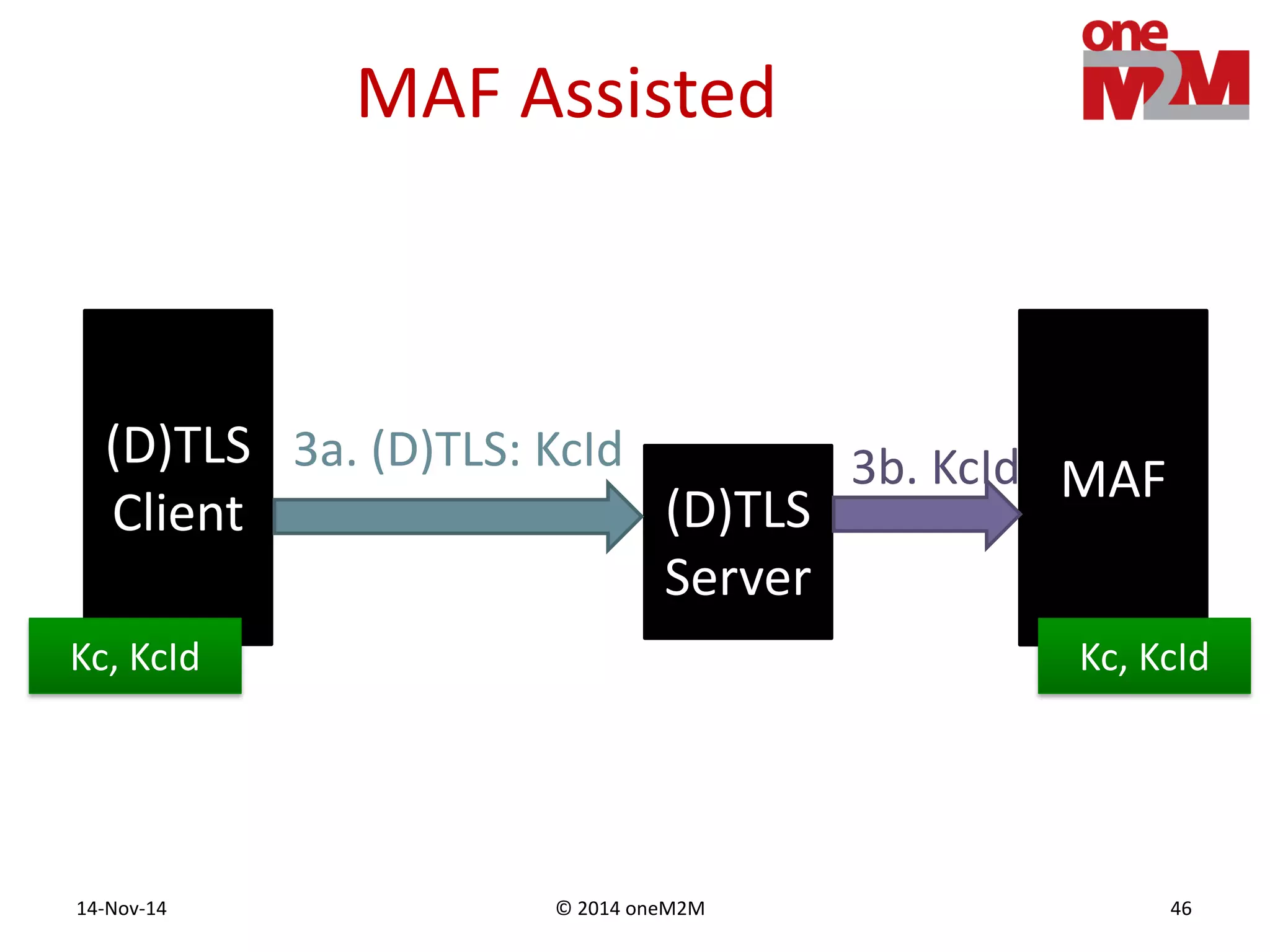
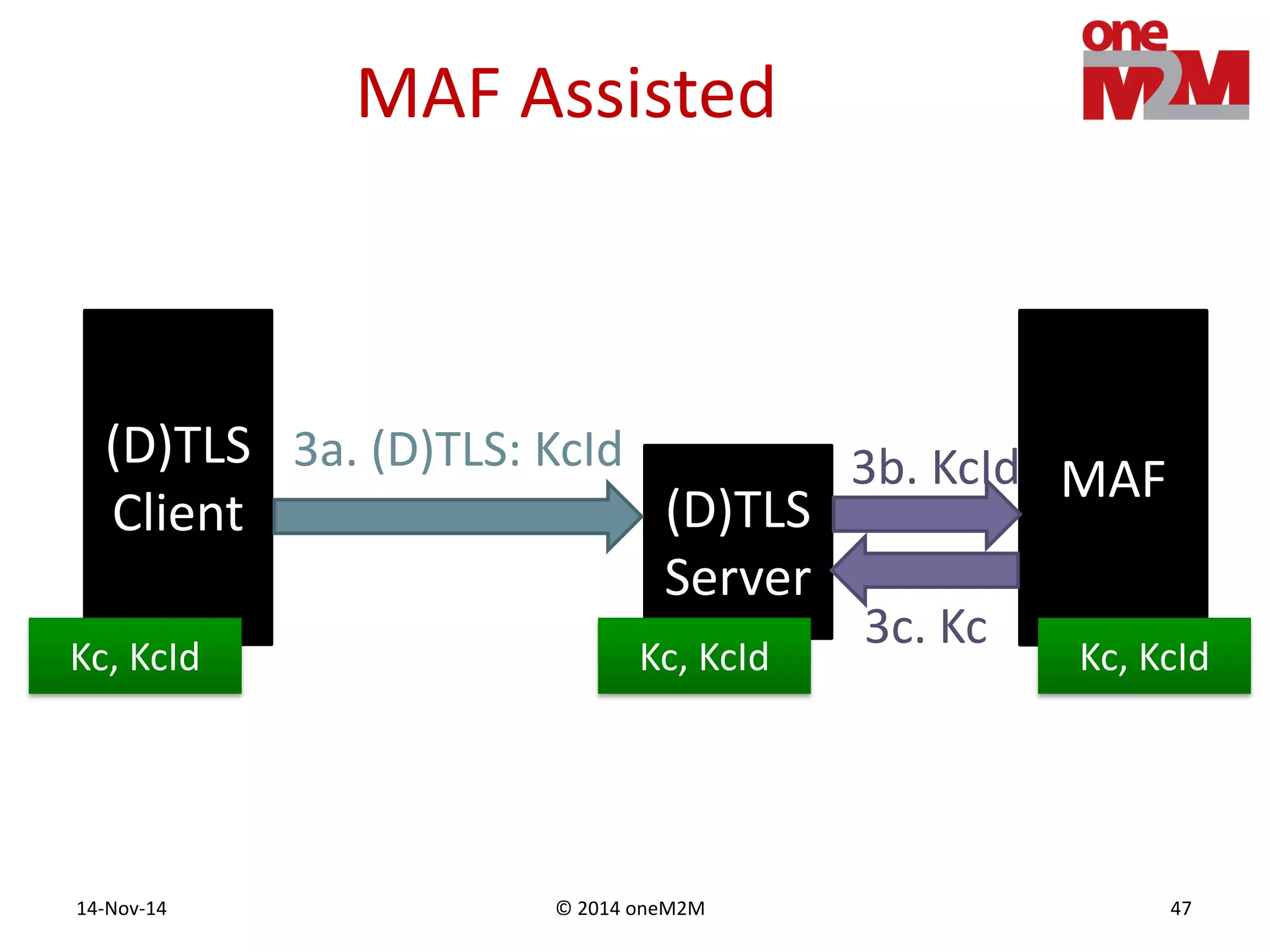
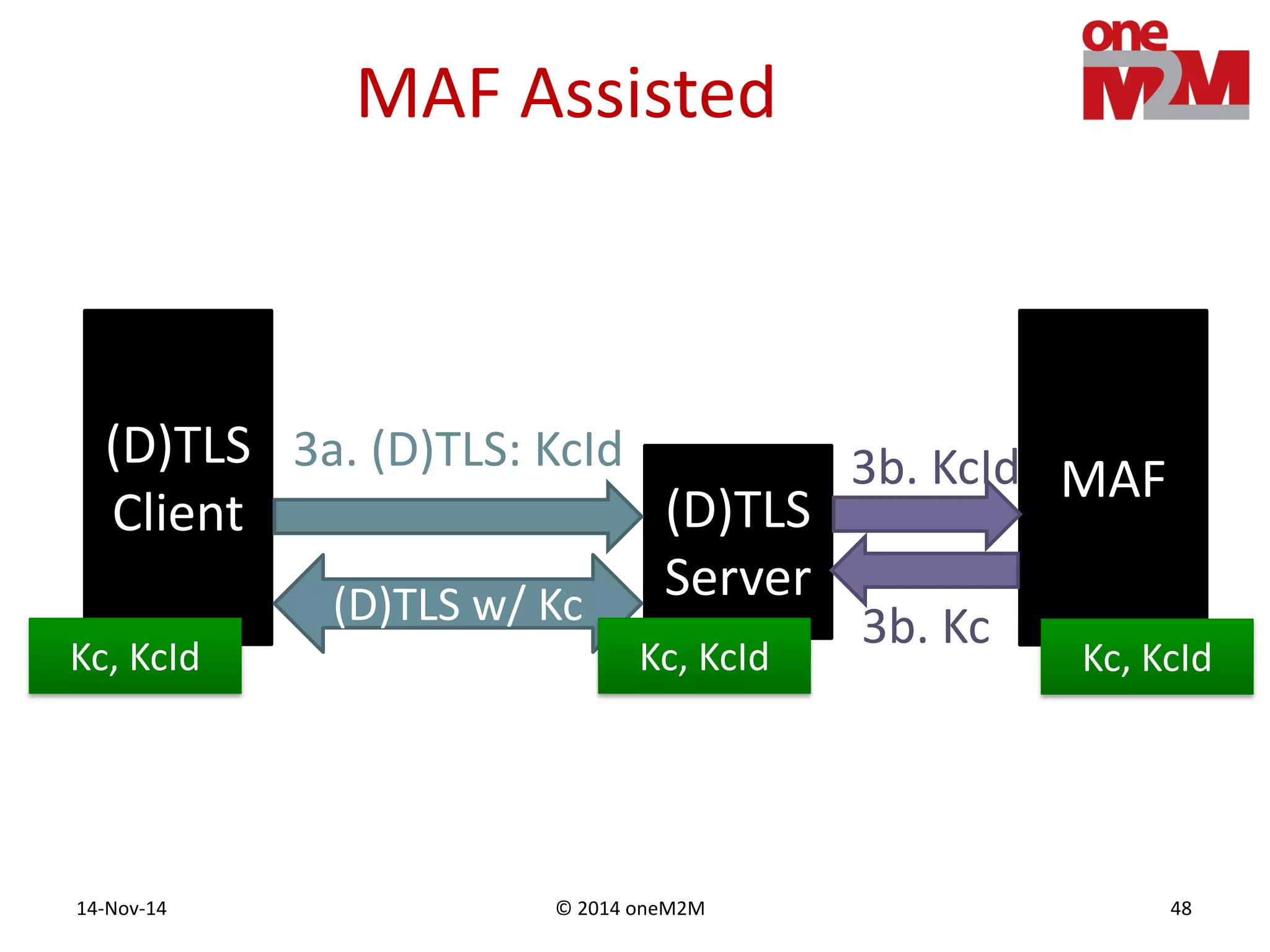
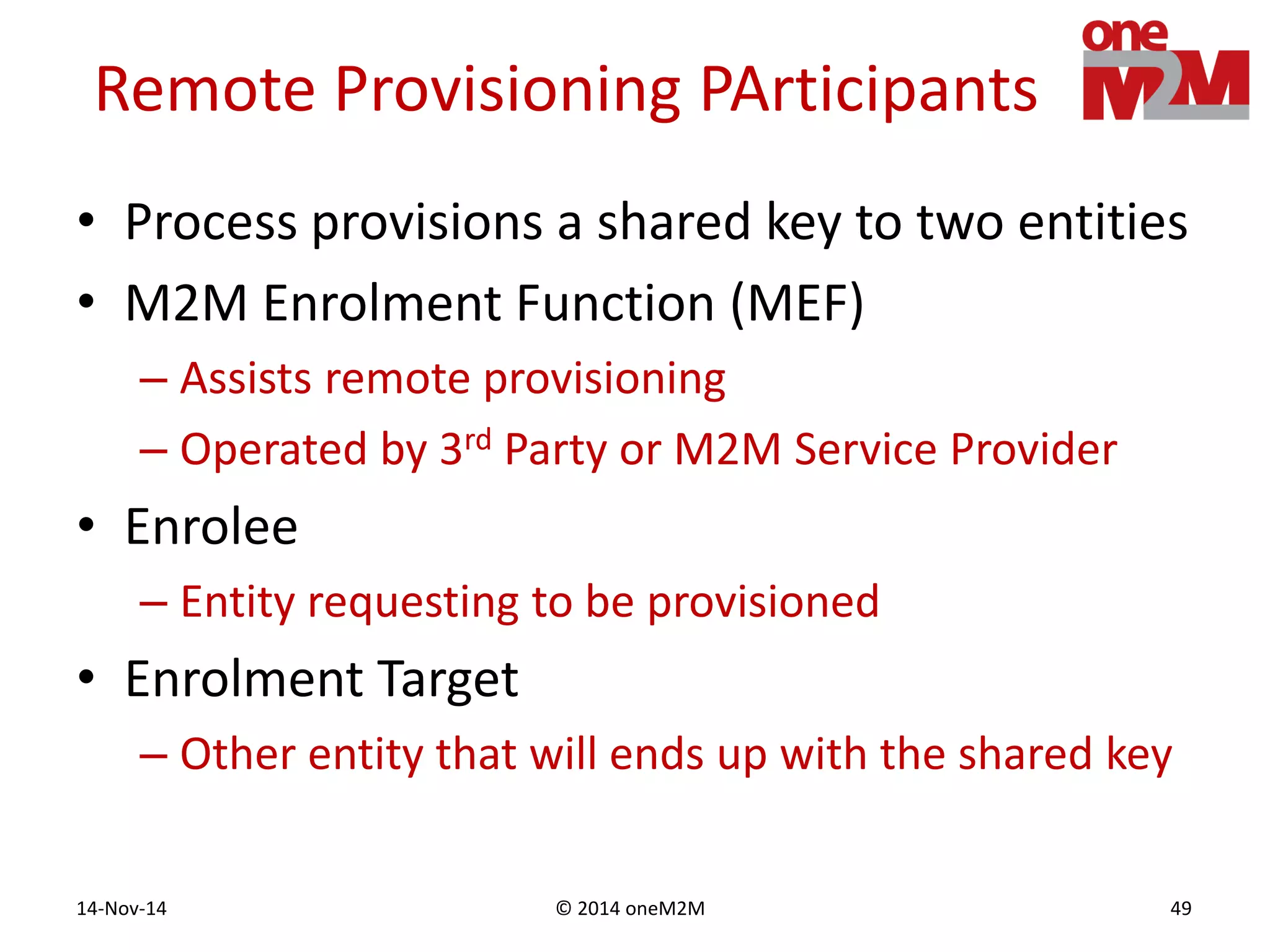
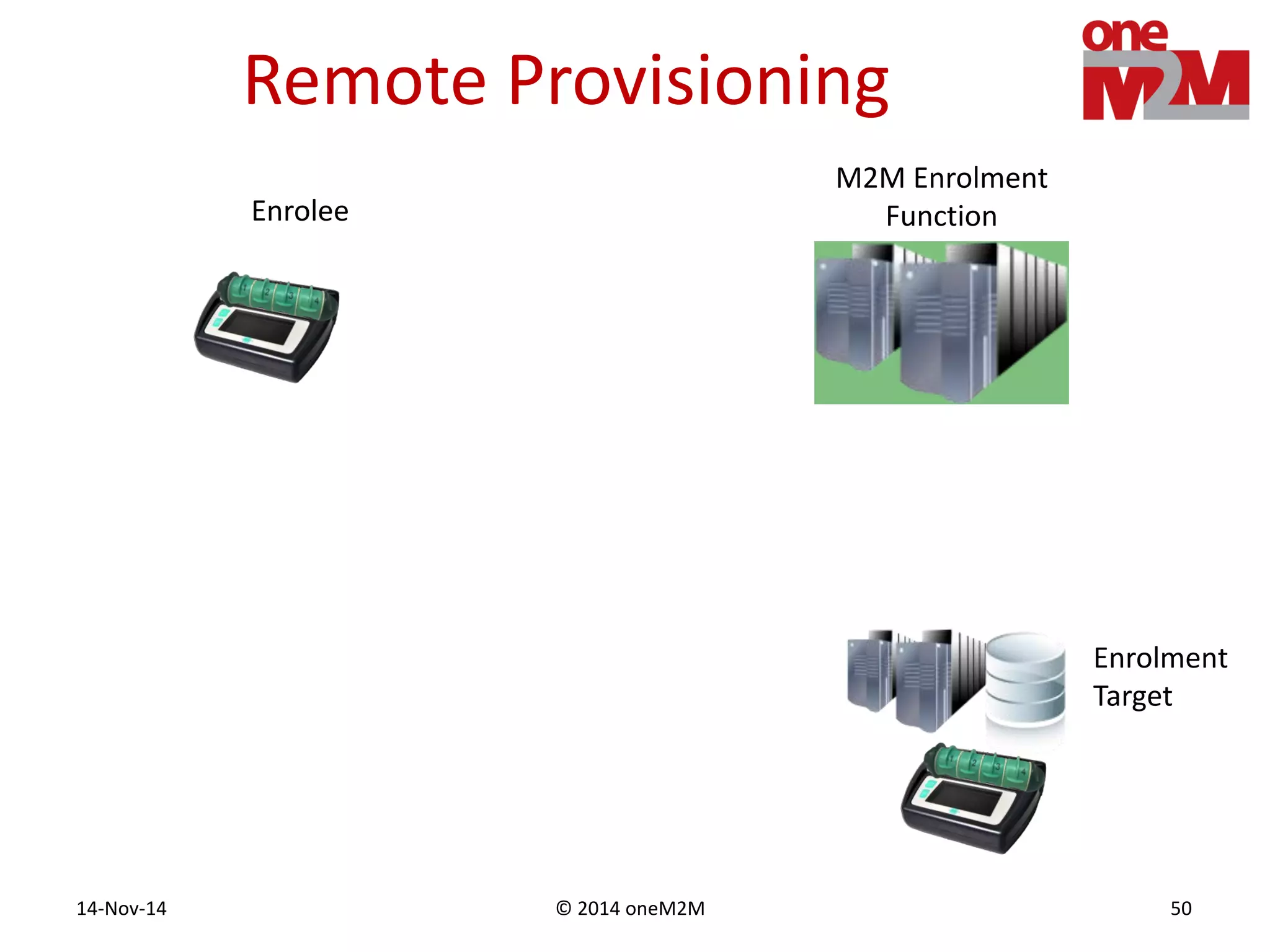
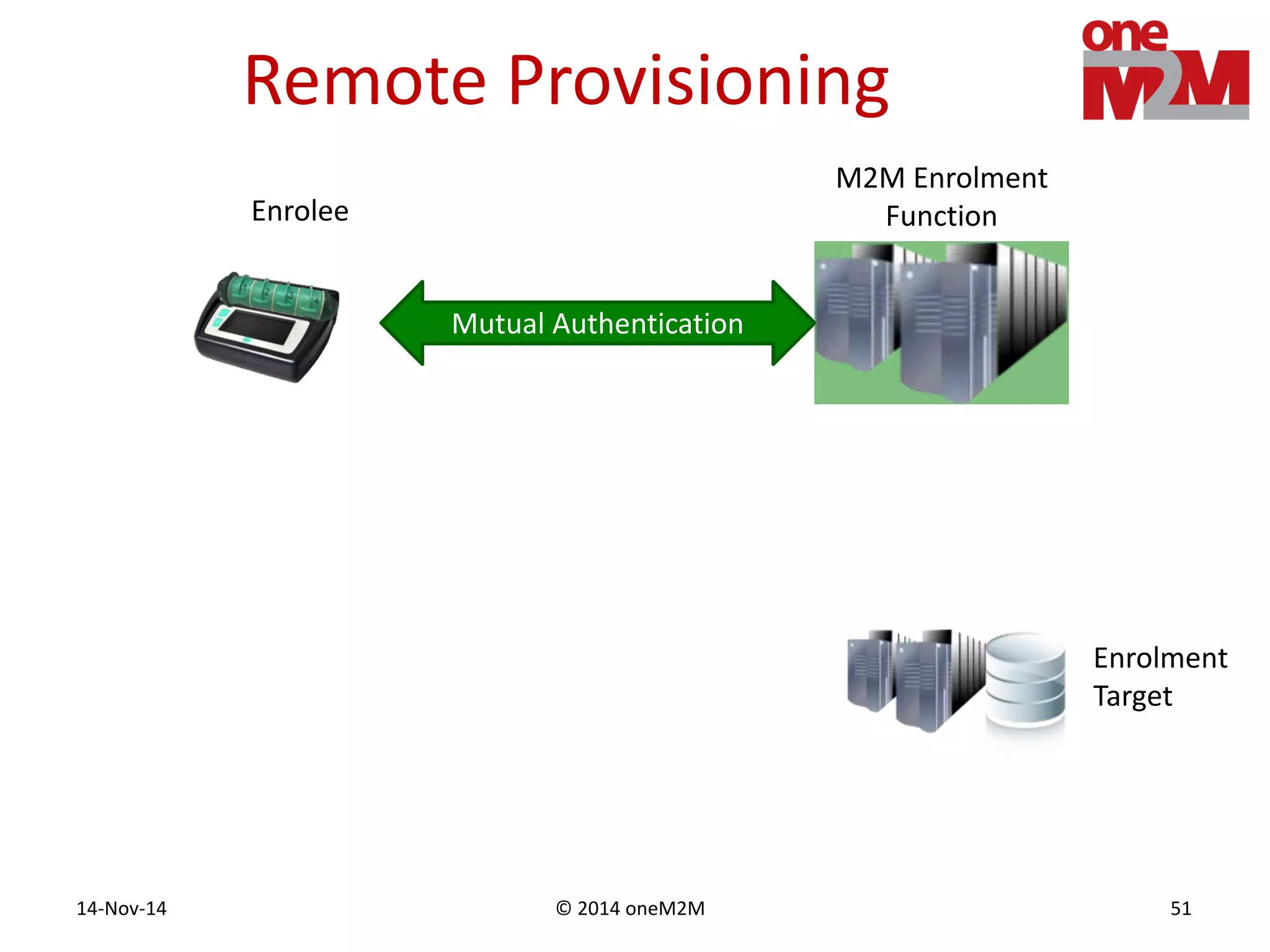
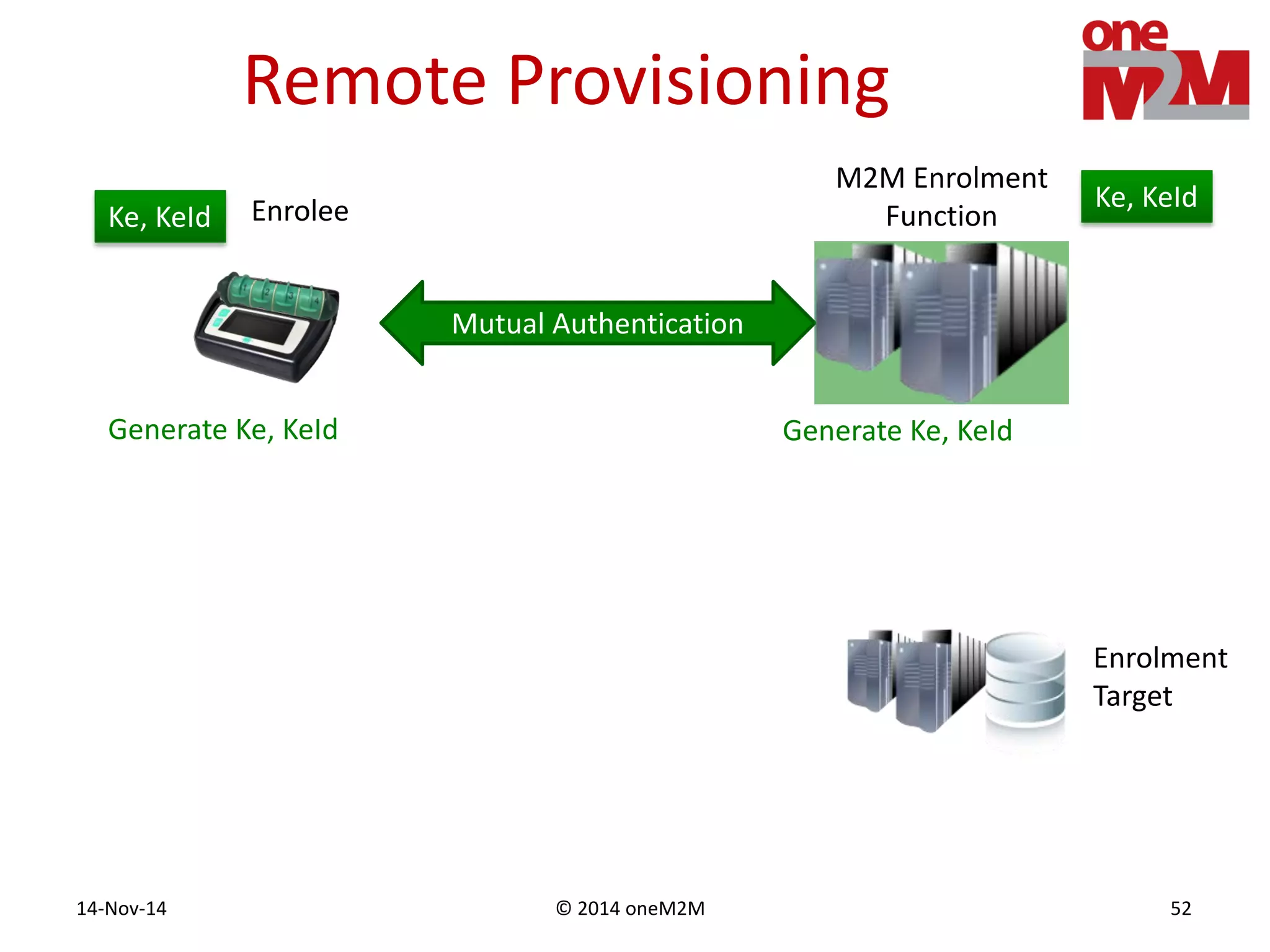
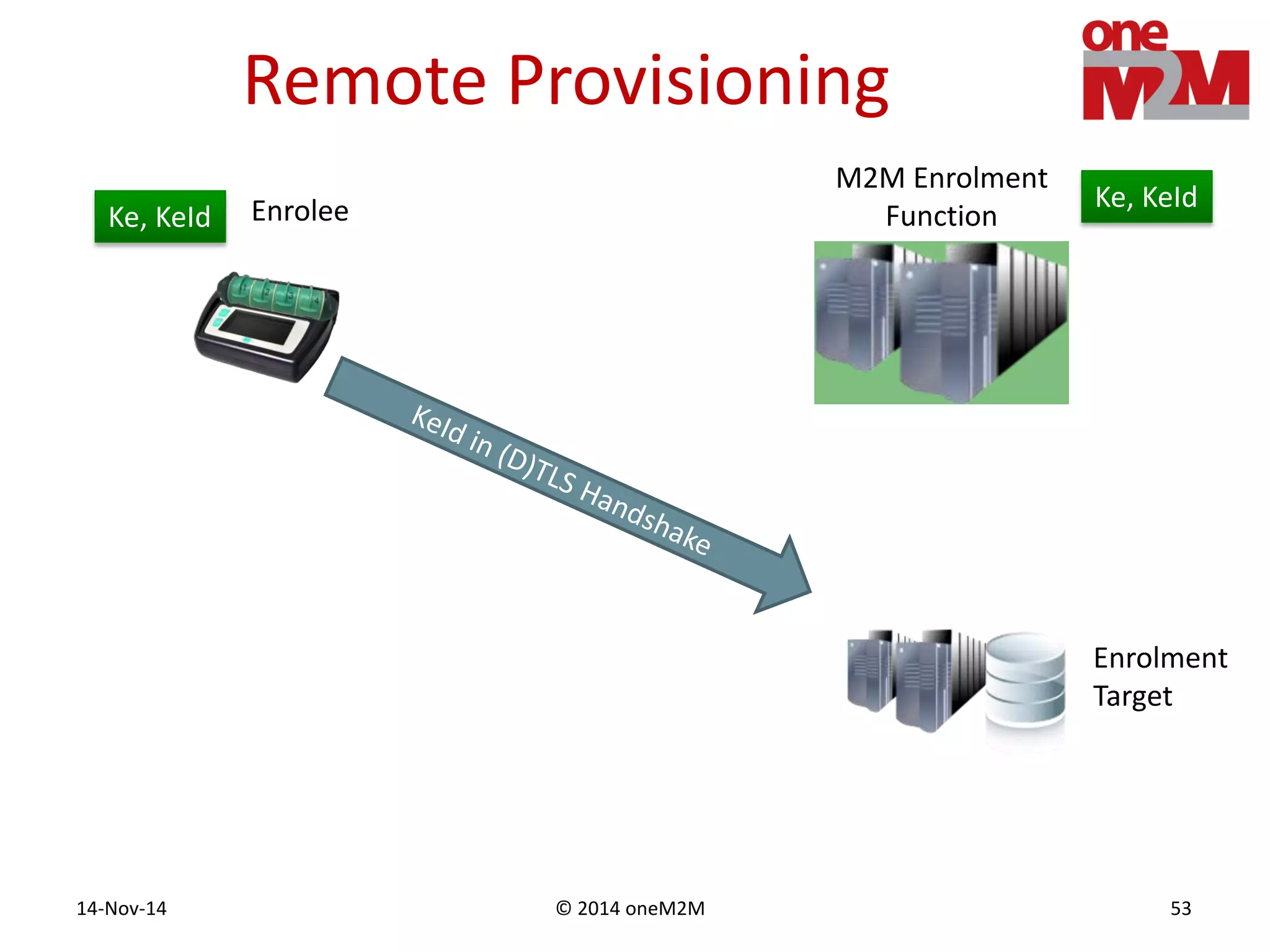
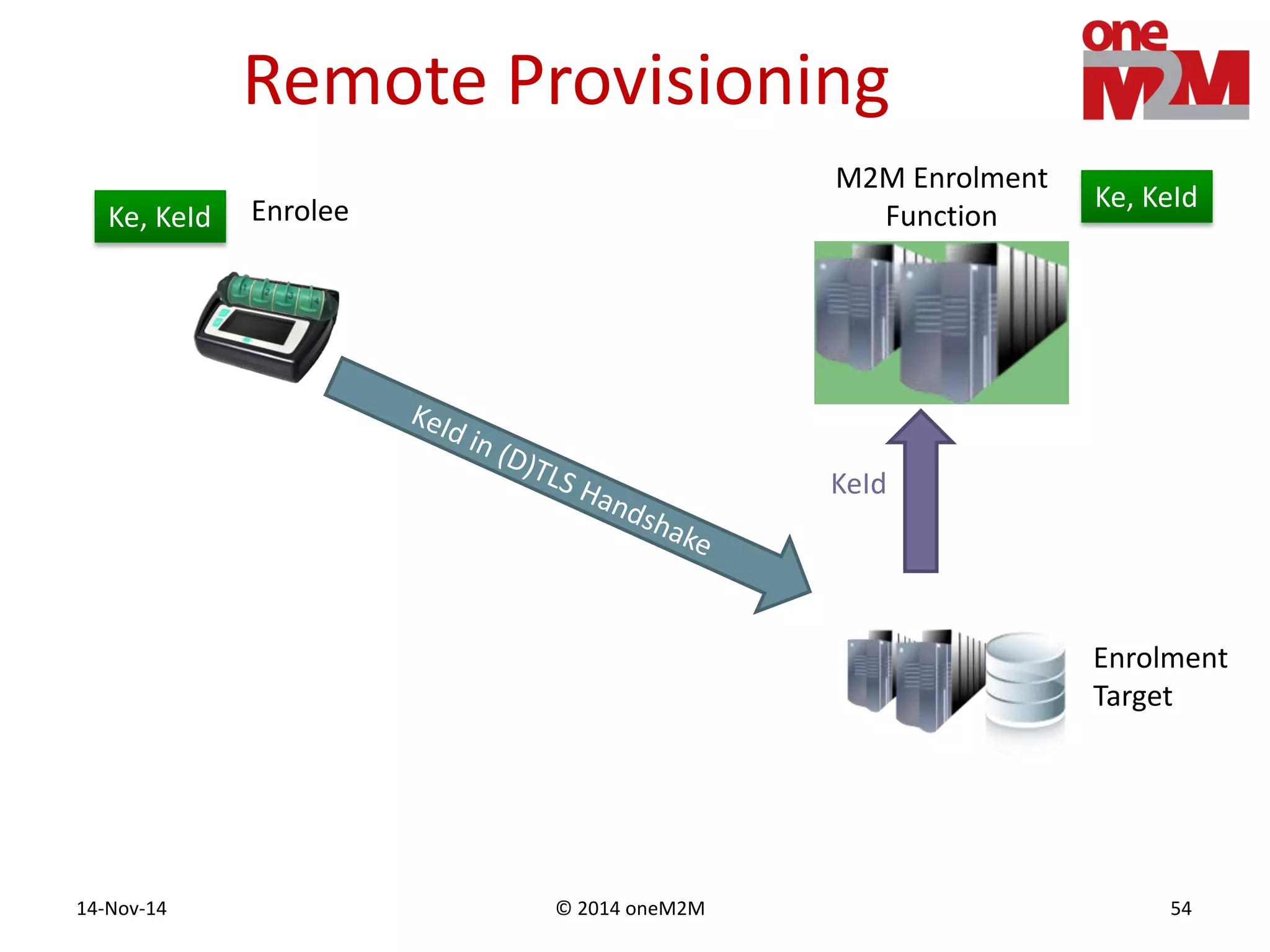
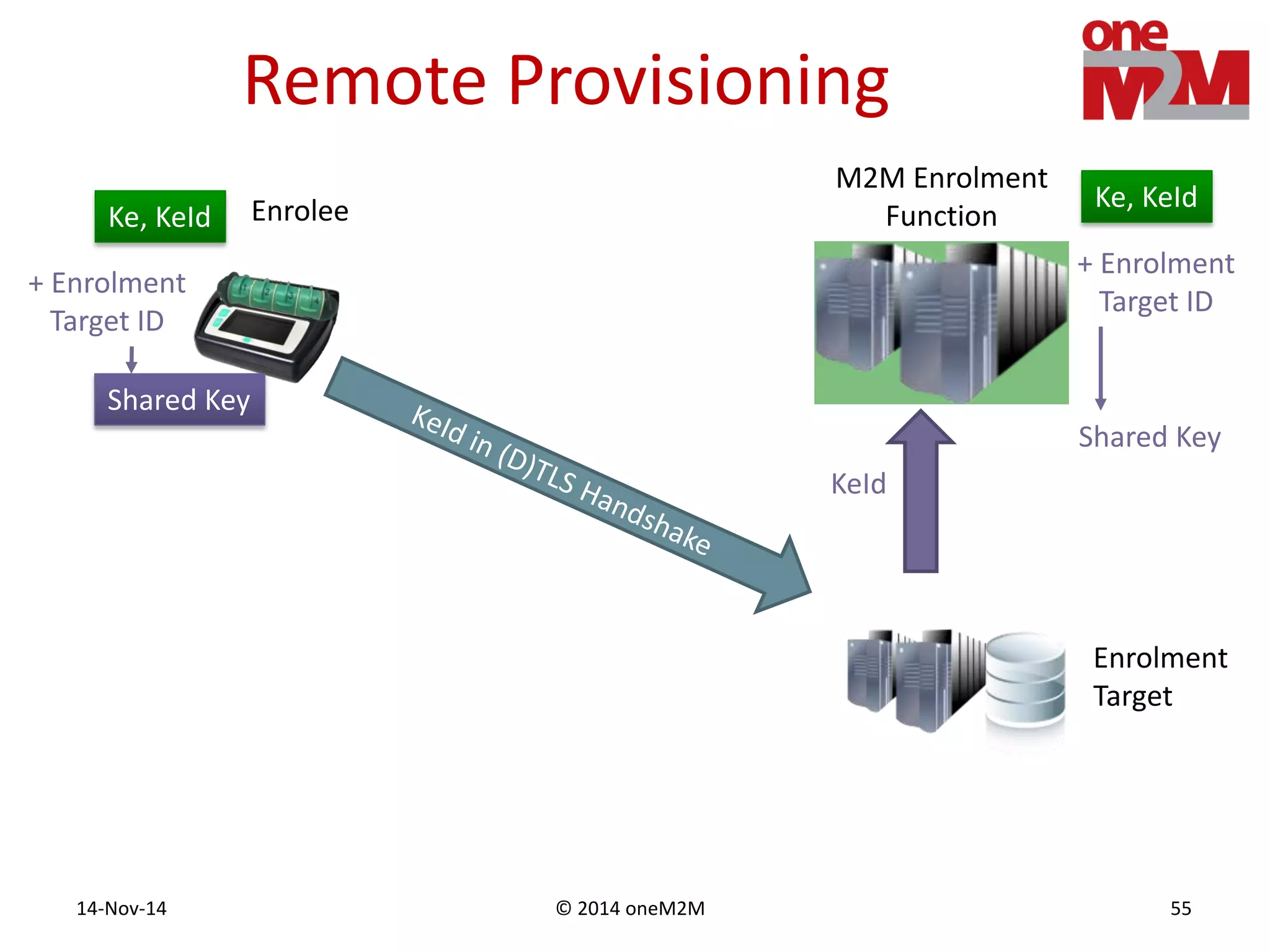
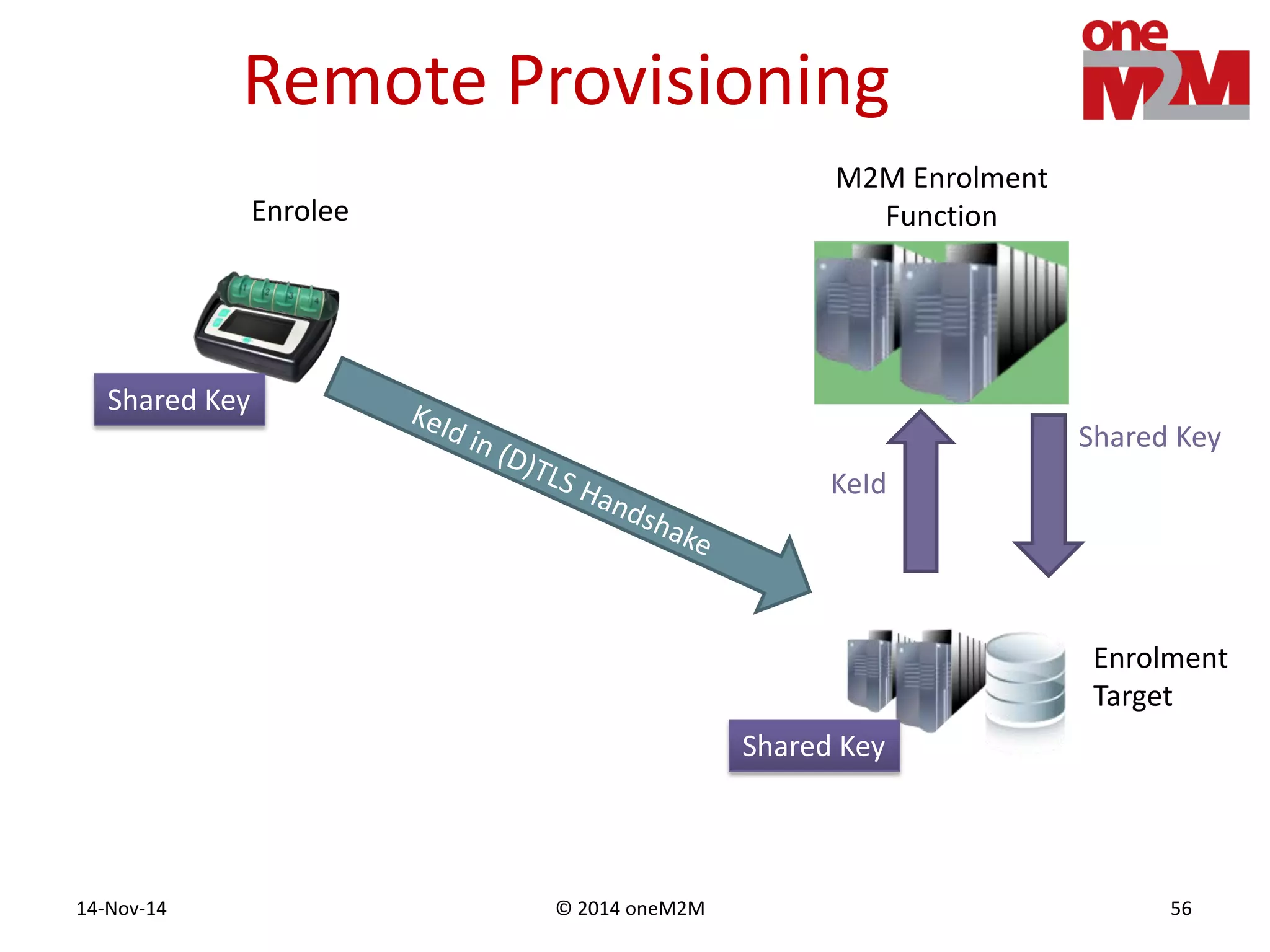
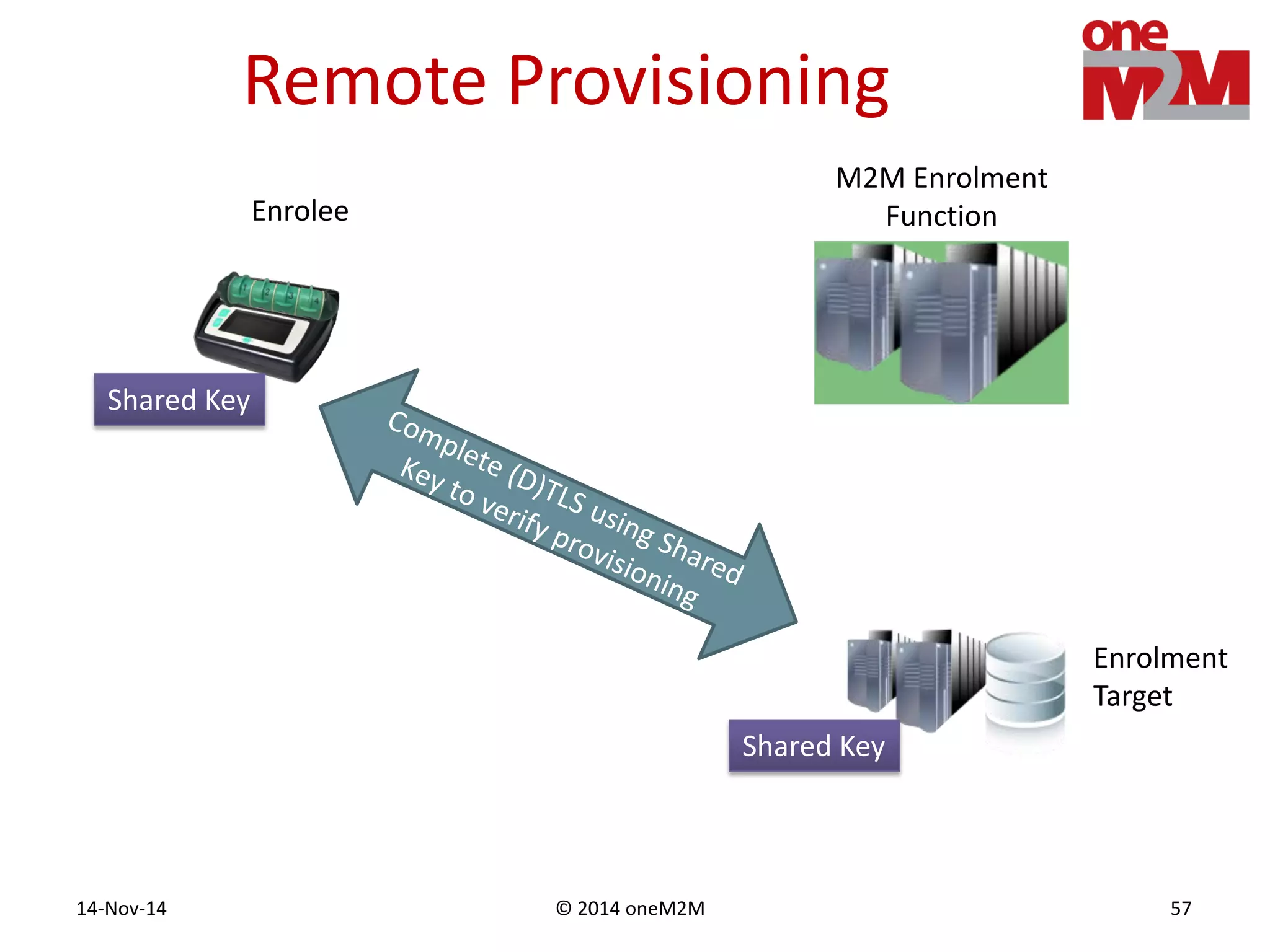
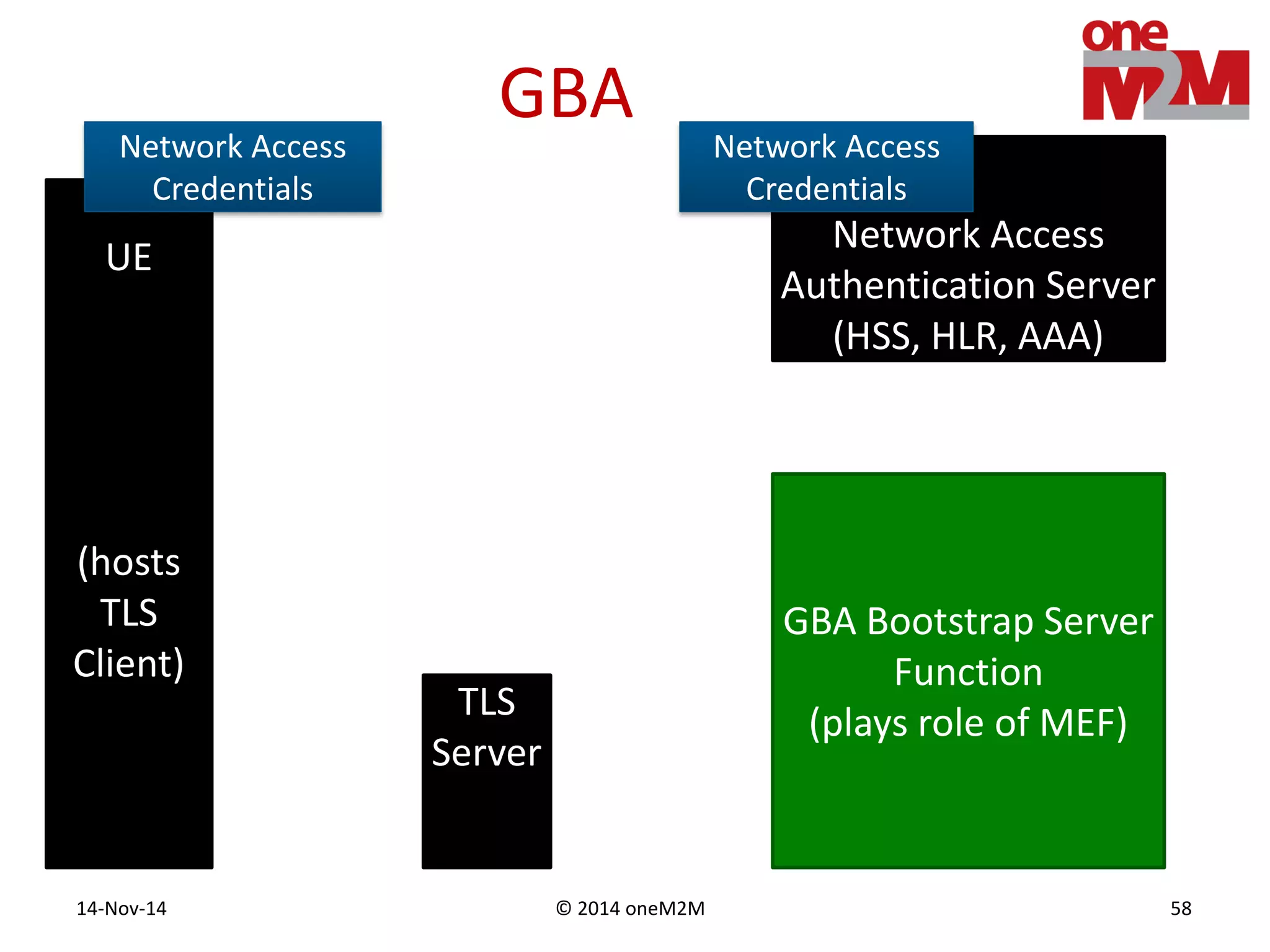
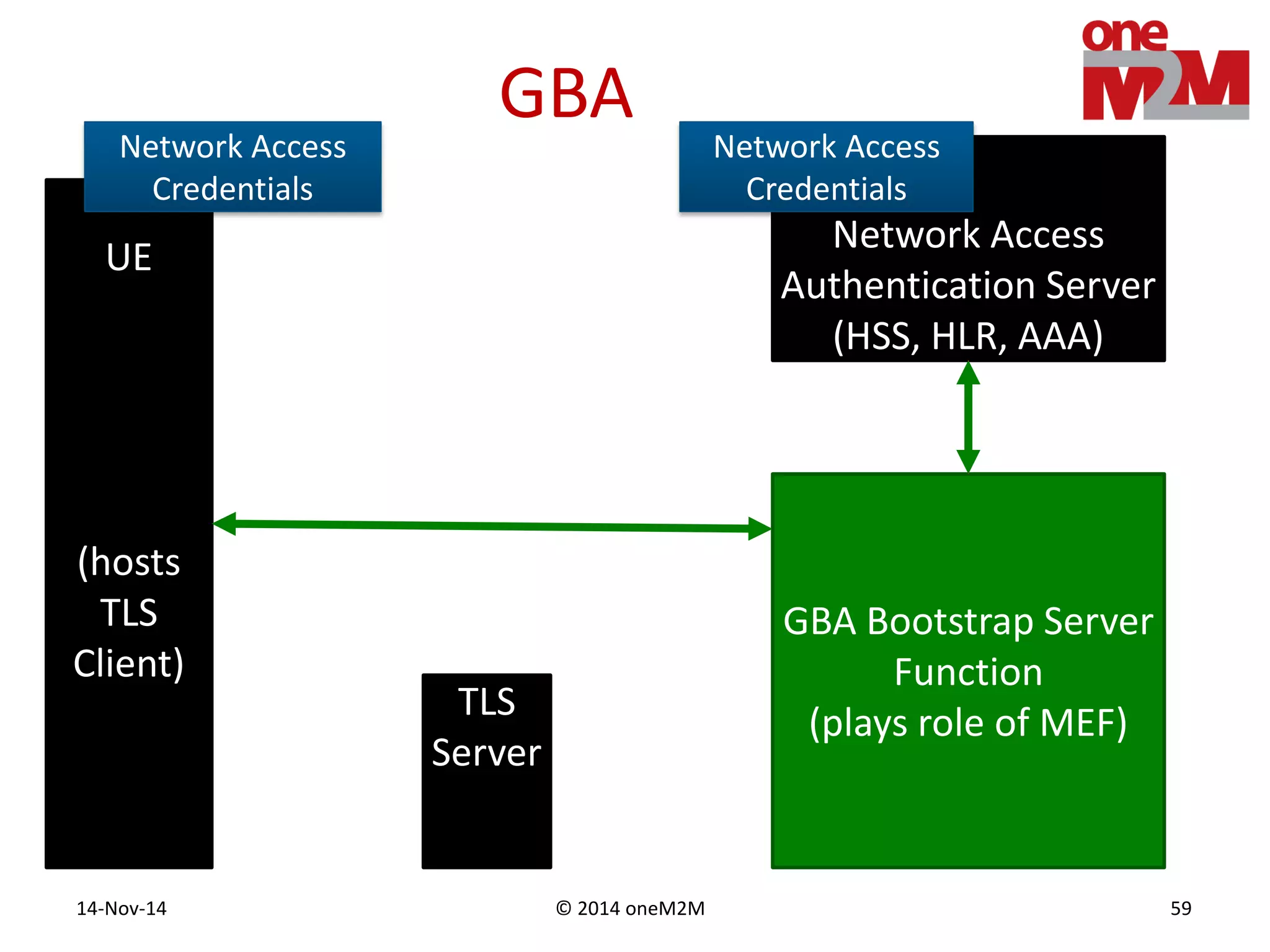
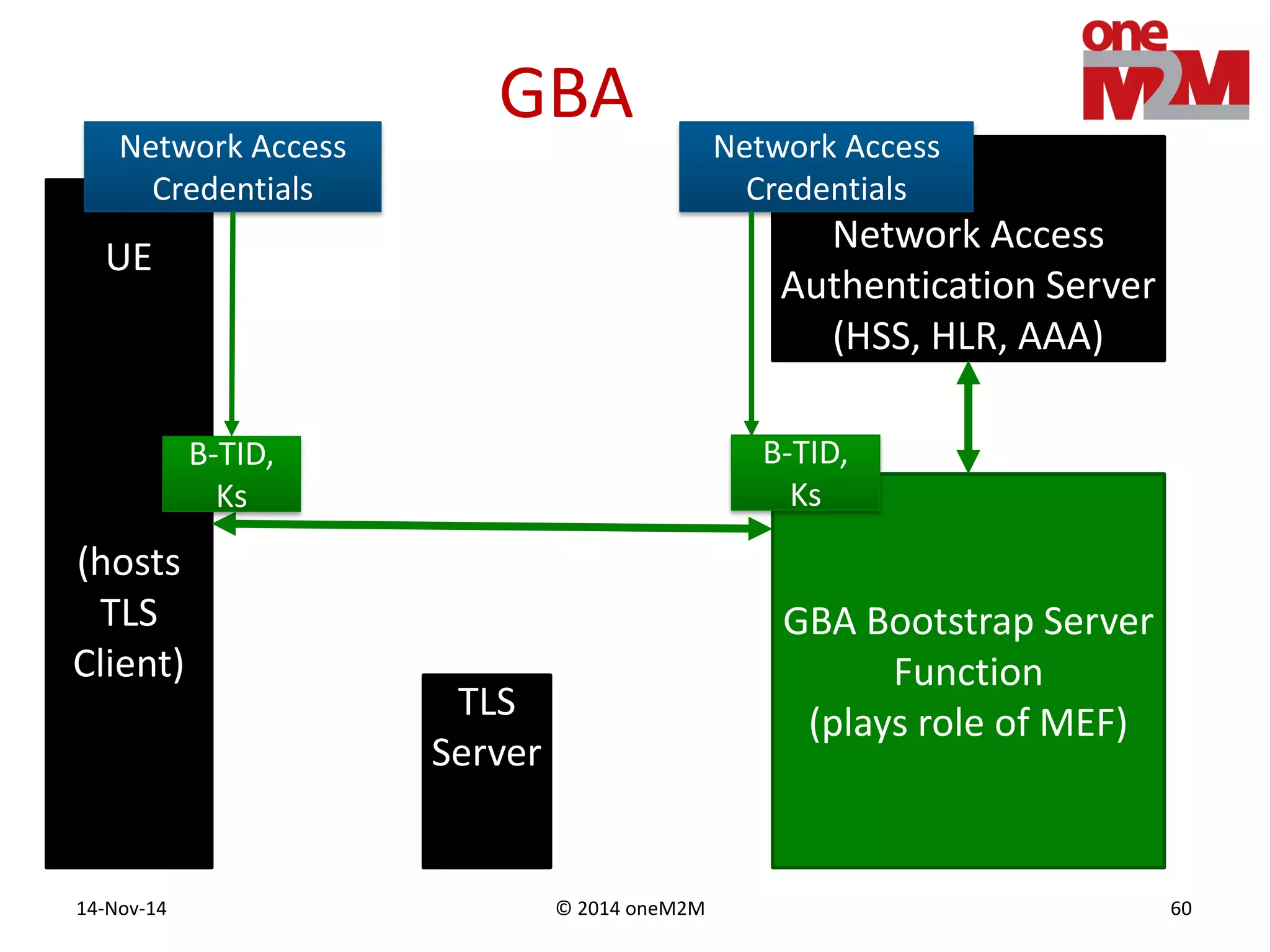
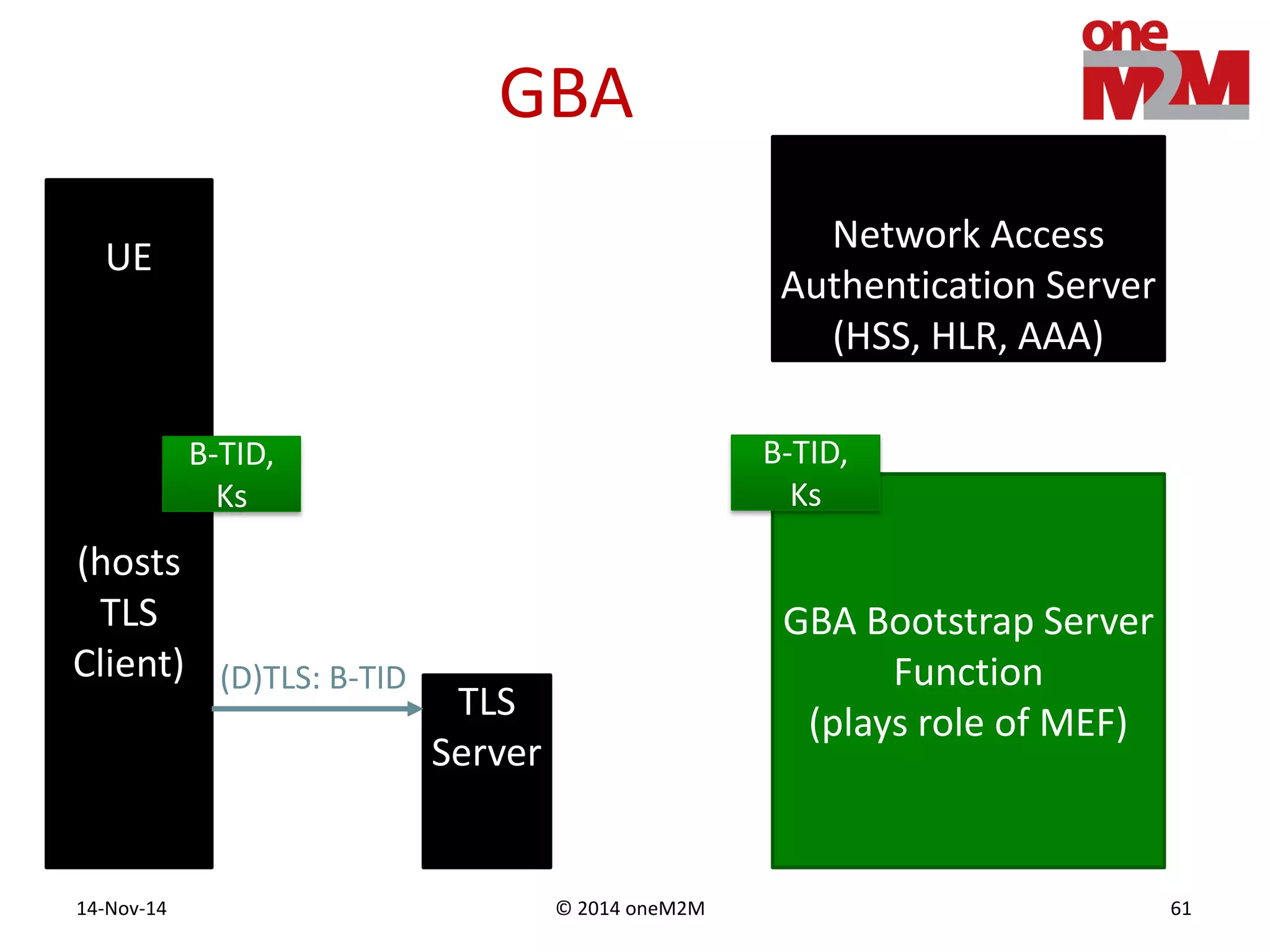
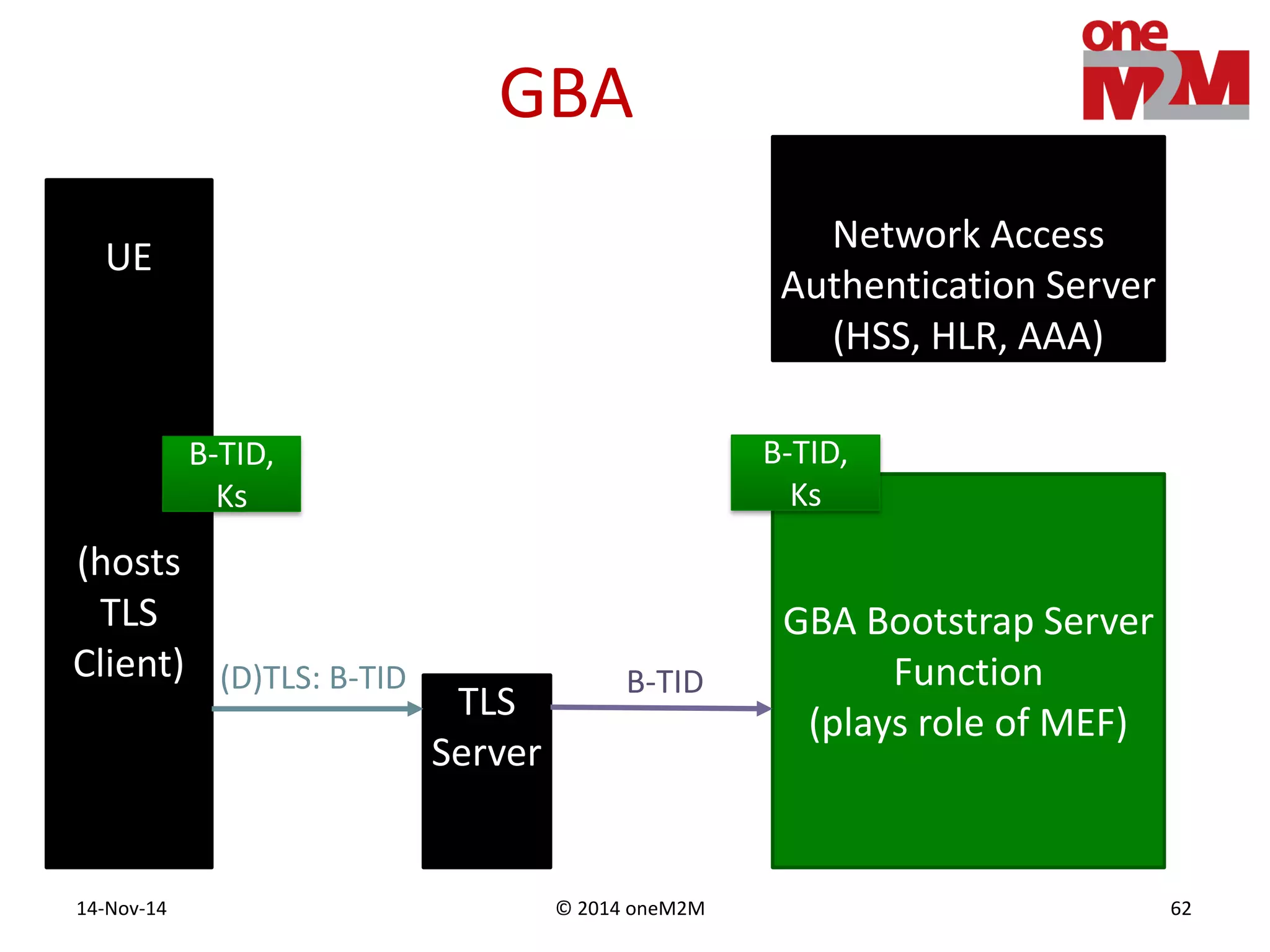
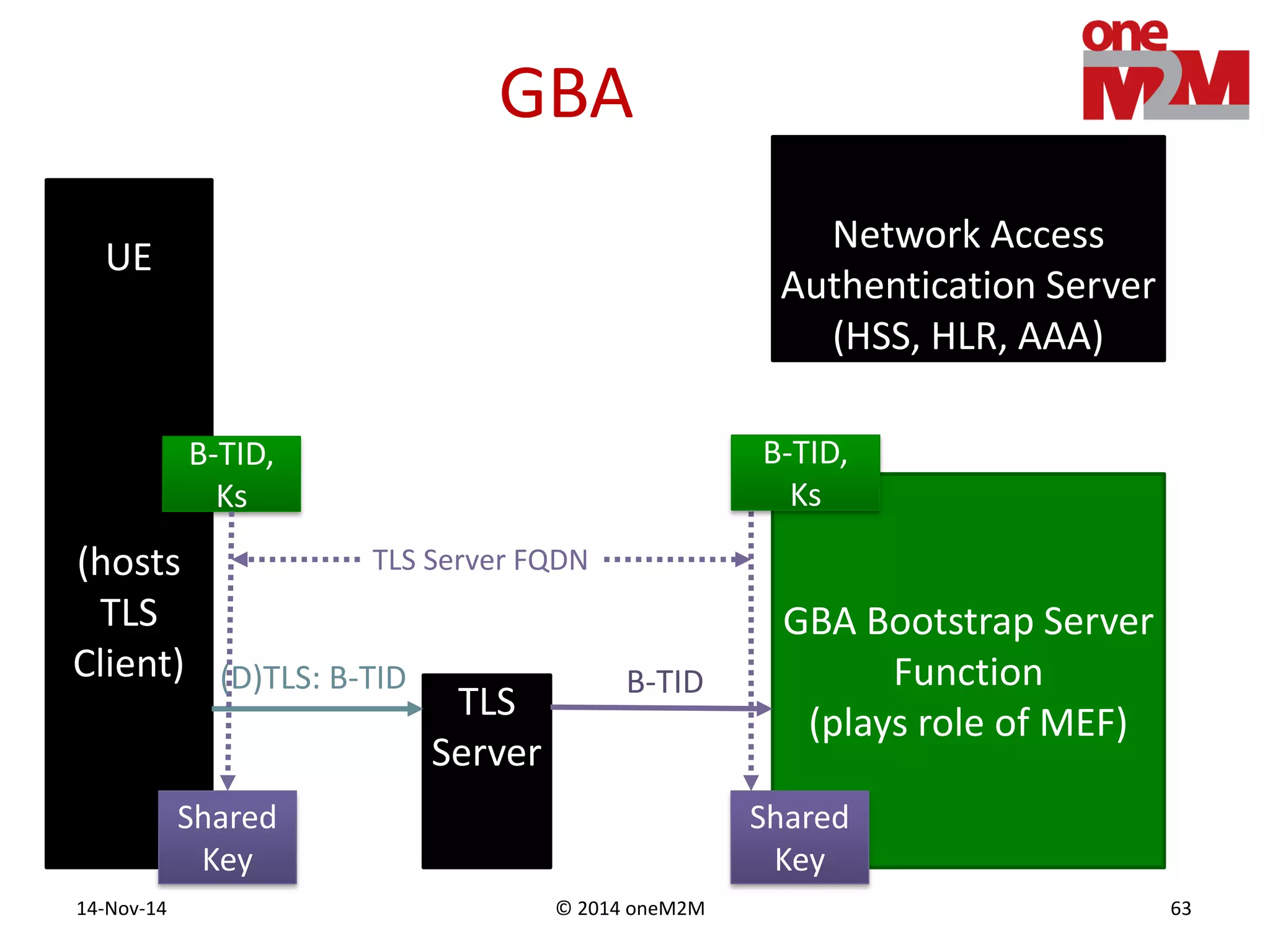
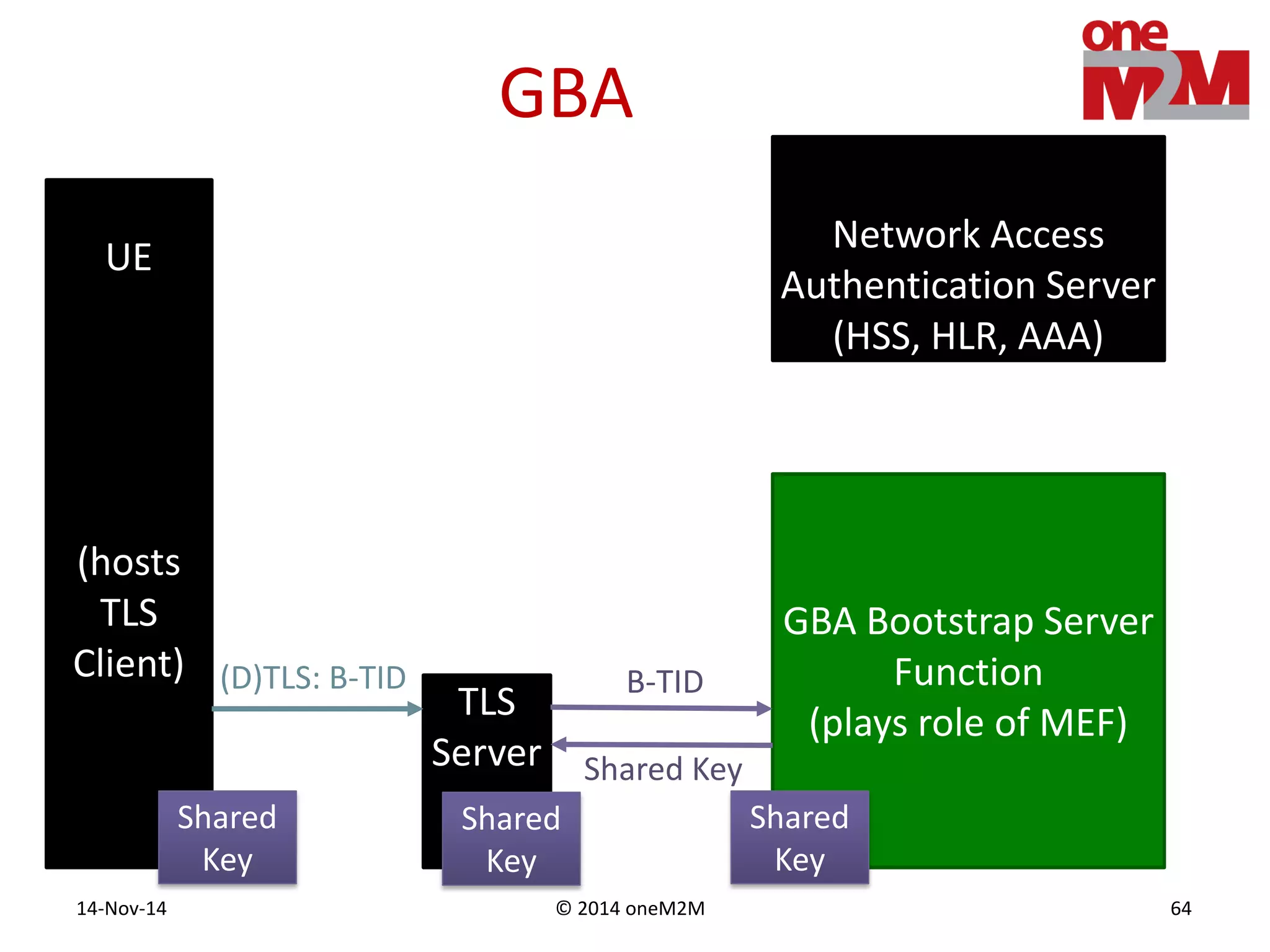
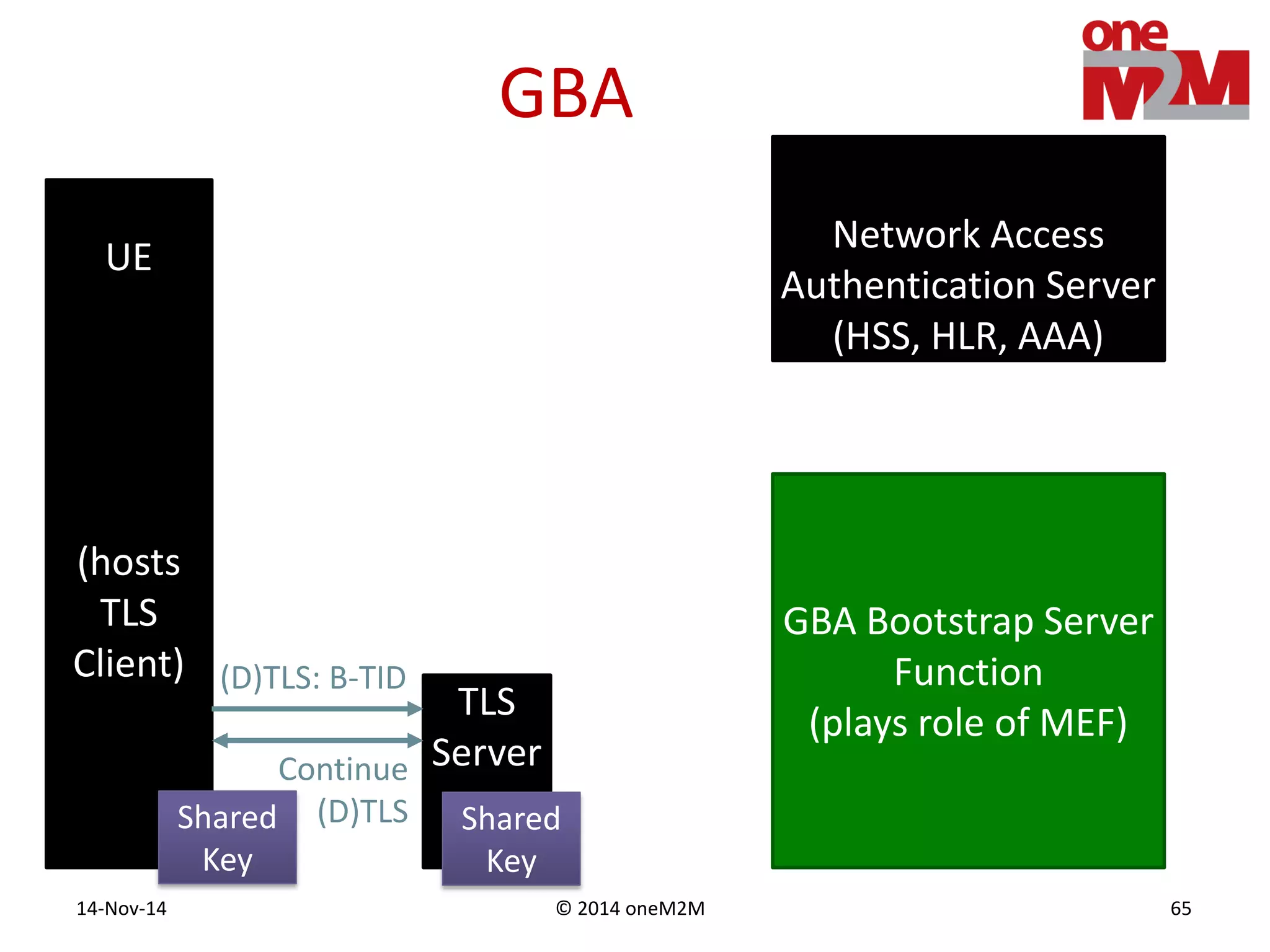
This document discusses security challenges and solutions for machine-to-machine (M2M) communications based on the oneM2M architecture. It identifies three main challenges: the large variety of deployment scenarios, the need to support any device in any deployment, and the inability of devices to make autonomous privacy decisions. The document proposes solutions such as secure communication using TLS/DTLS, remote provisioning of credentials, and access control policies to address these challenges. It also discusses future challenges around decentralization, information sharing between deployments, and more complex authentication and authorization scenarios.