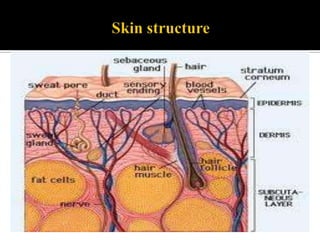
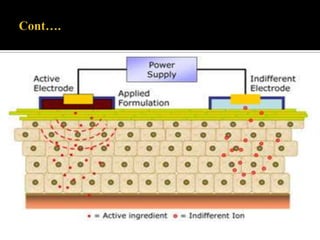
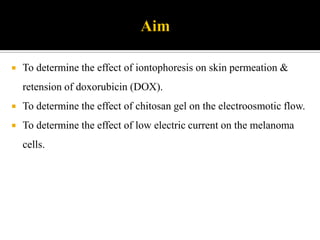
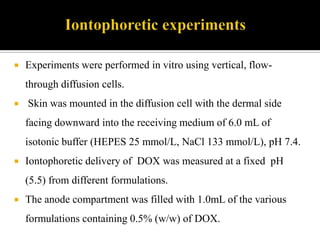
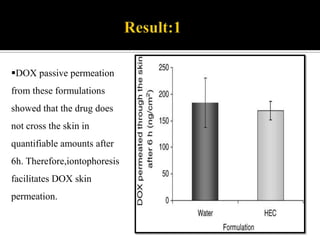
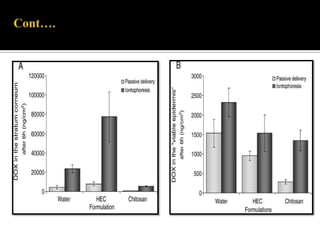
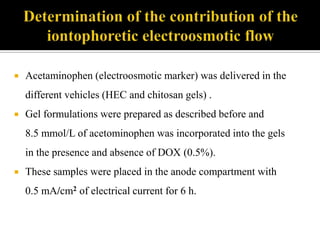
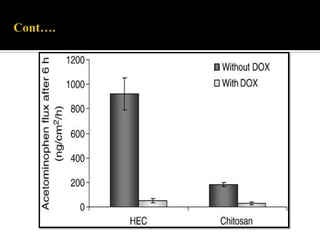
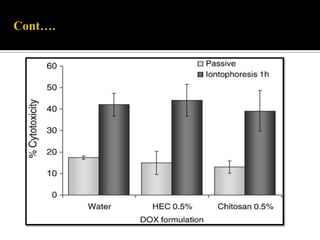
This study aimed to determine the effect of iontophoresis and chitosan gel on doxorubicin (DOX) skin penetration and cytotoxicity. Results showed that iontophoresis significantly increased DOX skin permeation and retention compared to passive delivery. While iontophoresis of hydroxyethylcellulose gel delivered more DOX to the stratum corneum, chitosan gel delivered similar amounts to deeper skin layers by competing for binding sites. Iontophoresis also increased DOX cytotoxicity against melanoma cells independently of the formulation used.