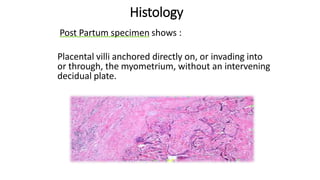
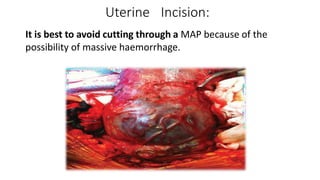
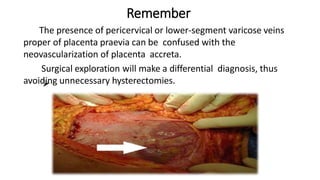
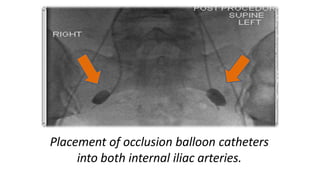
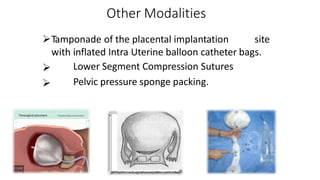
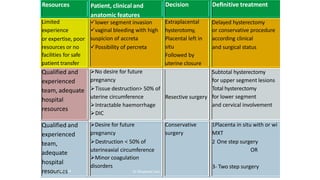
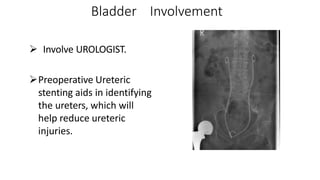
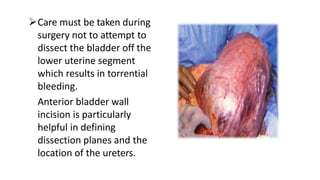
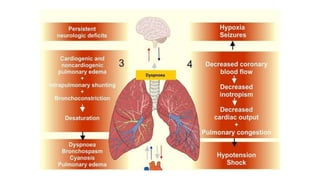
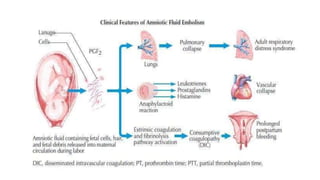
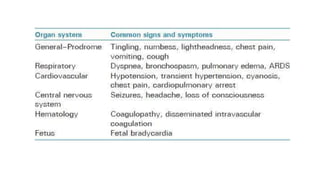
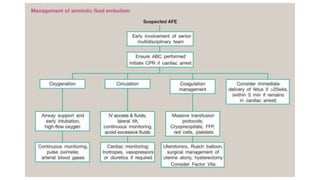
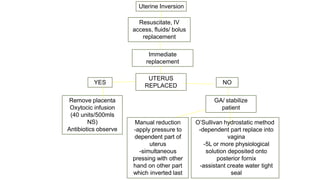
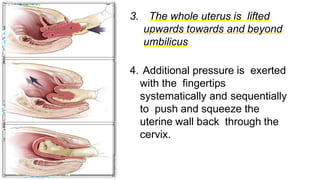
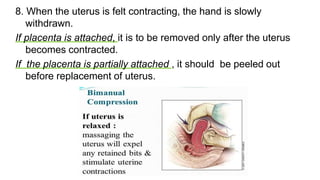
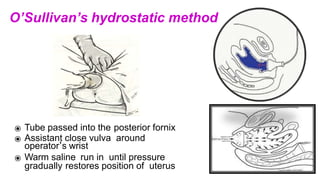
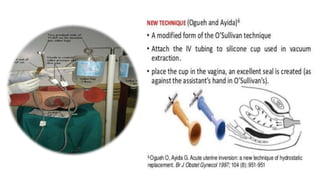
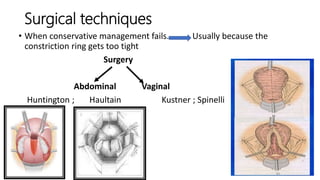
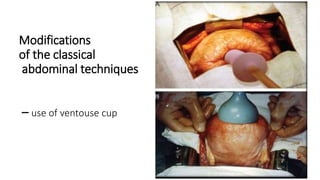
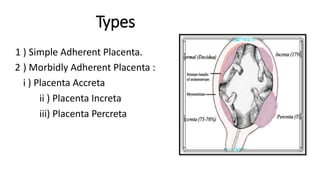
Uterine inversion and retained placenta are obstetric emergencies that require prompt recognition and management to prevent life-threatening complications like hemorrhage and shock. Uterine inversion occurs when the uterus turns inside out, and can be classified based on the extent of inversion and time since delivery. Retained placenta is defined as failure to deliver the placenta within 30 minutes of childbirth. Both conditions require urgent evaluation and treatment to replace the inverted uterus or manually remove the retained placenta while resuscitating the patient.
























![Reliability :
• Sensitivity - 93%
• Specificity - 79%
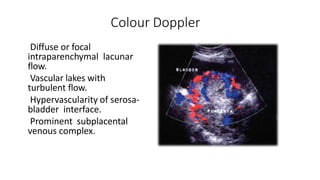
The use of power Doppler, color Doppler, or three- dimensional
imaging does not significantly improve the diagnostic
sensitivity compared with that achieved by grayscale
Ultrasonography alone.
[ Chou MM, Ho ES, Lee YH. Prenatal diagnosis of placenta previa accreta by transabdominal color
Doppler ultrasound. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;15:28–35. ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inversionretainedplacentaafe-210816160512/85/Inversion-retained-placenta-afe-41-320.jpg)


![Laboratory Findings :
•
• Several series and case reports have reported an association
between placenta accreta and otherwise unexplained elevations in
second trimester MSAFP concentration (>2 or 2.5 multiples of the
median [MOM]).
Although an elevated MSAFP level supports an ultrasound-
based diagnosis of placenta accreta, it is an inconsistent finding and
is not useful by itself for diagnosis of accreta.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inversionretainedplacentaafe-210816160512/85/Inversion-retained-placenta-afe-46-320.jpg)