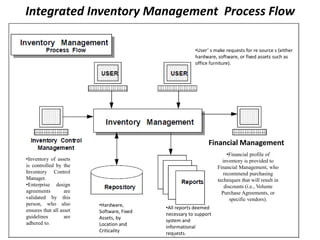
Inventory management systems help track inventory levels and ensure adequate supply. They are used by companies that sell or manufacture products. There are three main reasons for these systems: managing lead times and timing of orders, forecasting future demand, and taking advantage of bulk purchase discounts. The systems help determine optimal order quantities and timing to minimize total costs of ordering, delivery, and storage while meeting customer demand.