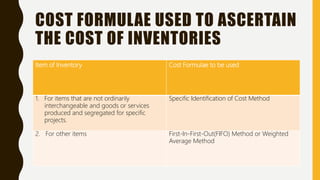
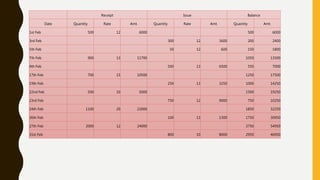
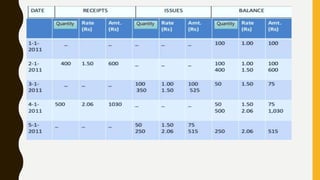
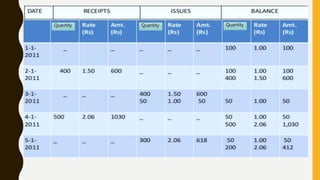
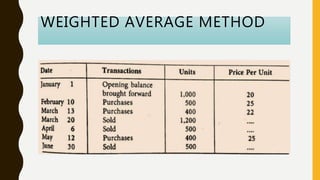
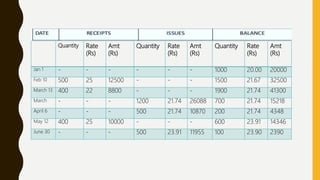
This document defines inventory and its components, which include finished goods, work in progress, and raw materials. It describes the costs included in inventory valuation, such as purchase costs, conversion costs, and other costs to bring inventory to its present condition. It also outlines costs excluded from inventory valuation, like abnormal waste and administrative overheads. Common inventory costing methods are identified as specific identification, FIFO, LIFO, and weighted average. The objectives of inventory management are given as achieving satisfactory customer service while keeping inventory costs reasonable. Examples of specific identification, FIFO, LIFO, and weighted average inventory costing methods are also provided.


![COST OF INVENTORIES INCLUDES =>
1. Cost of Purchase[ INCLUDES Purchase Price + Duties & Taxes(which are not
subsequently recoverable) + other expenditure directly attributable to
acquisition(Like Freight Inward) ] BUT [ EXCLUDES Trade Discount , Rebates ,
Duty Drawbacks Subsidies and Taxes(which are subsequently recoverable) ]
2. Cost of Conversion [ INCLUDES Direct Labour , Direct Expenses , Sub
Contracted Work and Production Overheads absorbed on the basis of Normal
Capacity]
3. Other costs incurred in bringing the inventories to their present location and
condition , e.g. , cost incurred in designing products for specific customers.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pom-1-210512125621/85/Inventory-Management-3-320.jpg)