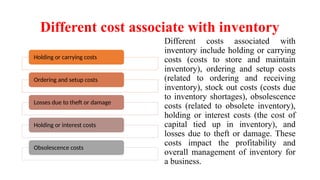
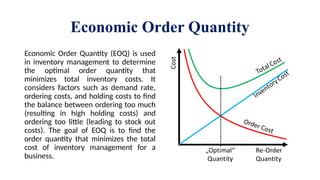
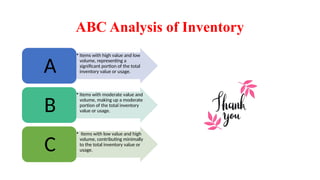
Inventory encompasses goods, raw materials, and products a business holds for resale or service delivery, crucial for supply chain management. It incurs various costs, including holding, ordering, and obsolescence costs, impacting profitability. The Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) helps determine the optimal order size to minimize total inventory costs, while ABC analysis categorizes inventory into three groups (A, B, C) based on value and volume.