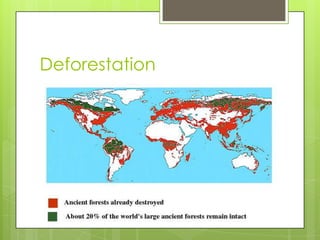
The document discusses invasive species and their threats and impacts. It defines invasive species as alien species whose introduction causes economic, environmental, or health harm. Invasive species bring diseases that native species lack immunity against, prey upon native species without natural defenses, compete more efficiently than native species, can hybridize with and eliminate native gene pools through interbreeding, and alter habitats in ways that harm native species. Examples highlighted include the chestnut blight fungus, brown tree snake on Guam, gray squirrels in Europe and Italy, and zebra mussels in North America. The document also asserts that humans are the most invasive species, through activities like industrial pollution, disease spread, habitat destruction including deforestation, overexploitation of resources