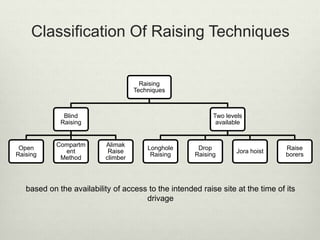
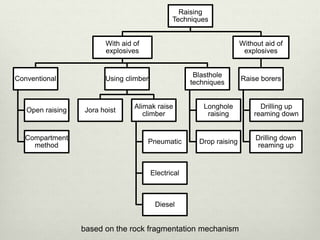
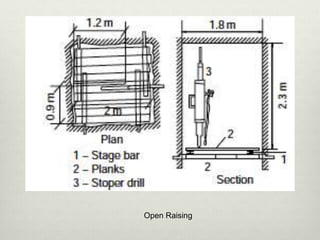
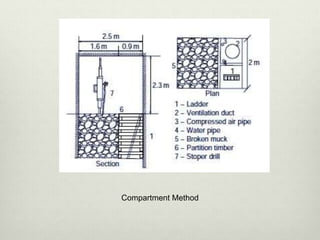
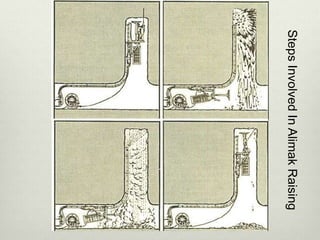
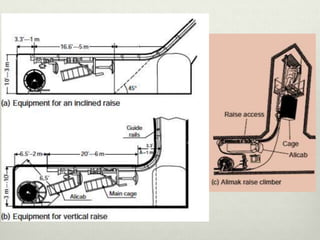
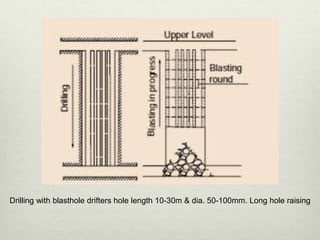
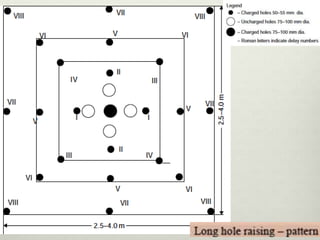
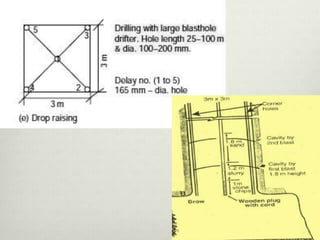
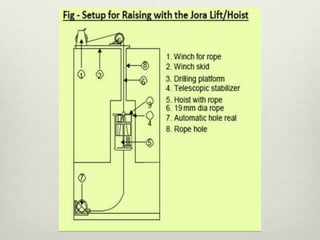
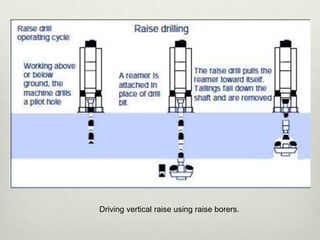
This document discusses various techniques for raising, which is the vertical or steeply inclined excavation that connects different levels in underground mines. The key raising techniques discussed include open raising using drilling and blasting in short lengths, compartment method which divides the raise into sections, Alimak raise climber which uses a rack and pinion mechanism, longhole raising using long parallel drill holes, drop raising which uses large diameter blast holes, Jora hoist with a caged platform, and raise borers which drill and ream a circular raise without explosives. The Alimak raise climber is noted as generally the best adopted technique, first used in India in 1972.