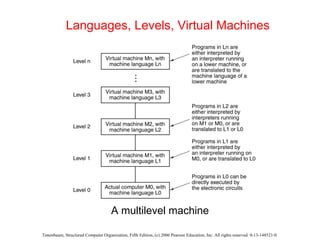
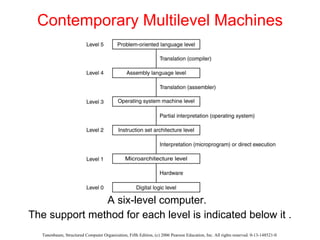
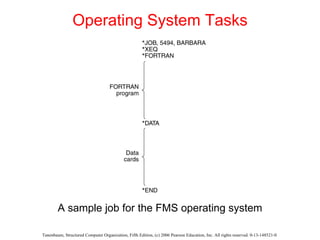
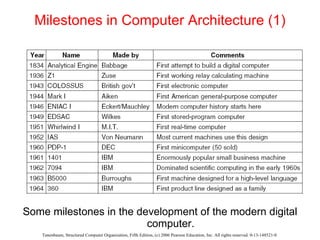
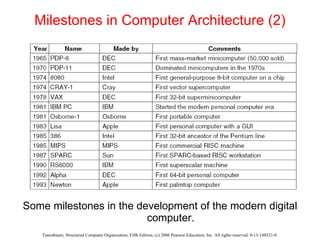
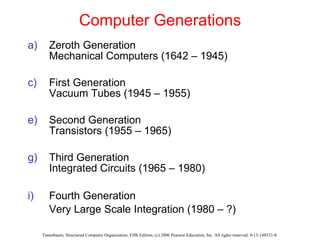
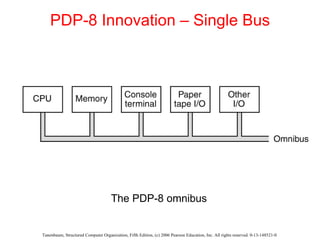
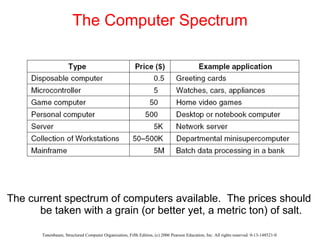
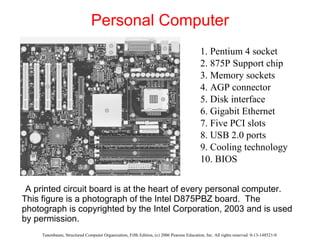
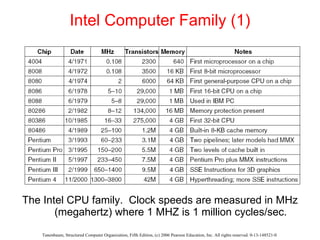
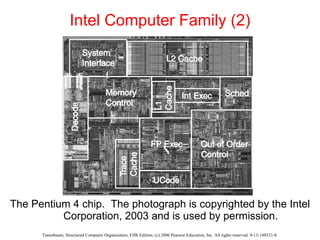
The document discusses the evolution of multilevel computer architectures from early machines with multiple hardware levels to modern systems with operating systems and microcode. It provides an overview of important milestones in computer architecture such as different generations of computers and von Neumann's original machine design. Examples are given of different computer families including Intel, Sun Microsystems, and embedded systems.