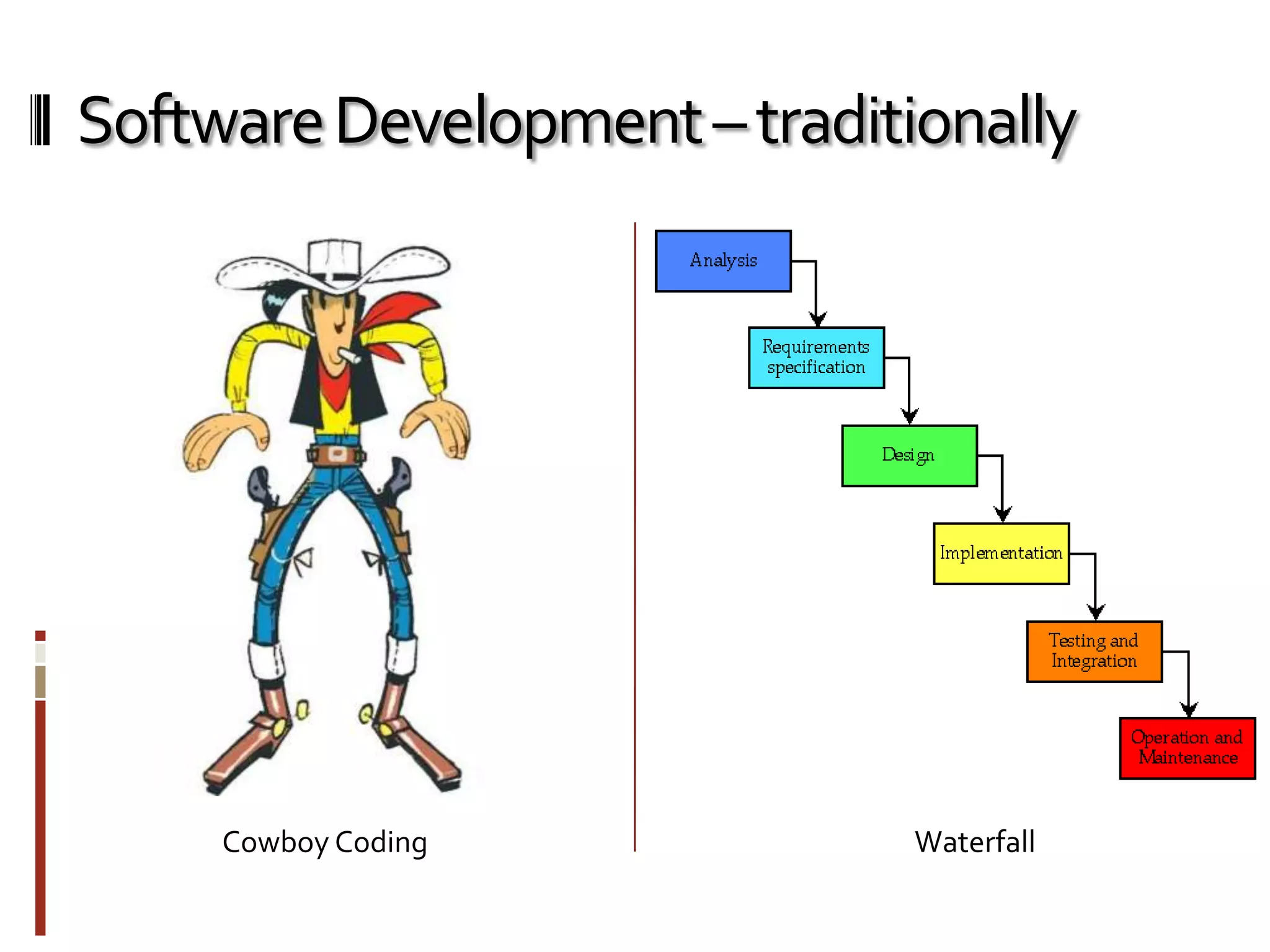
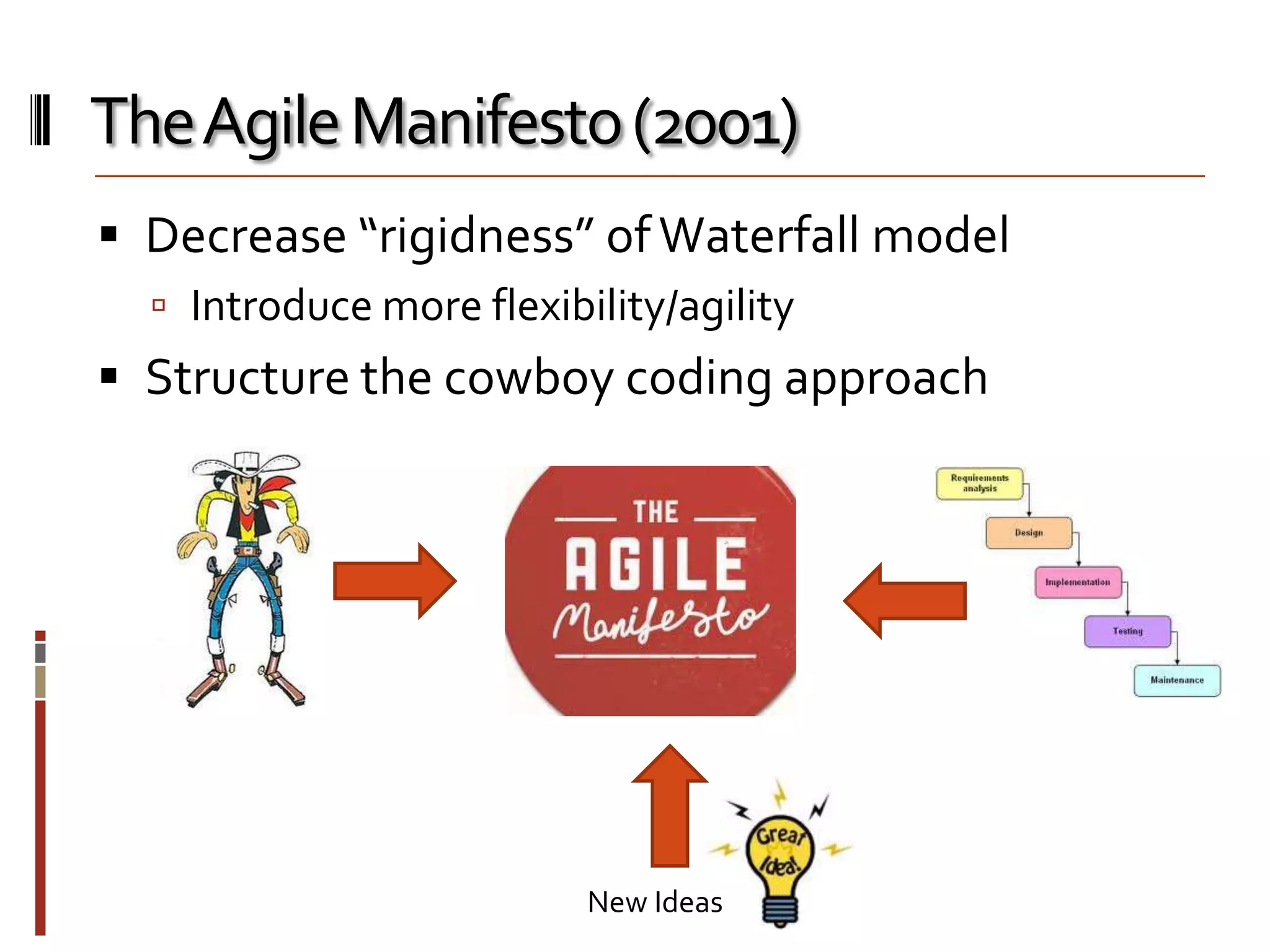
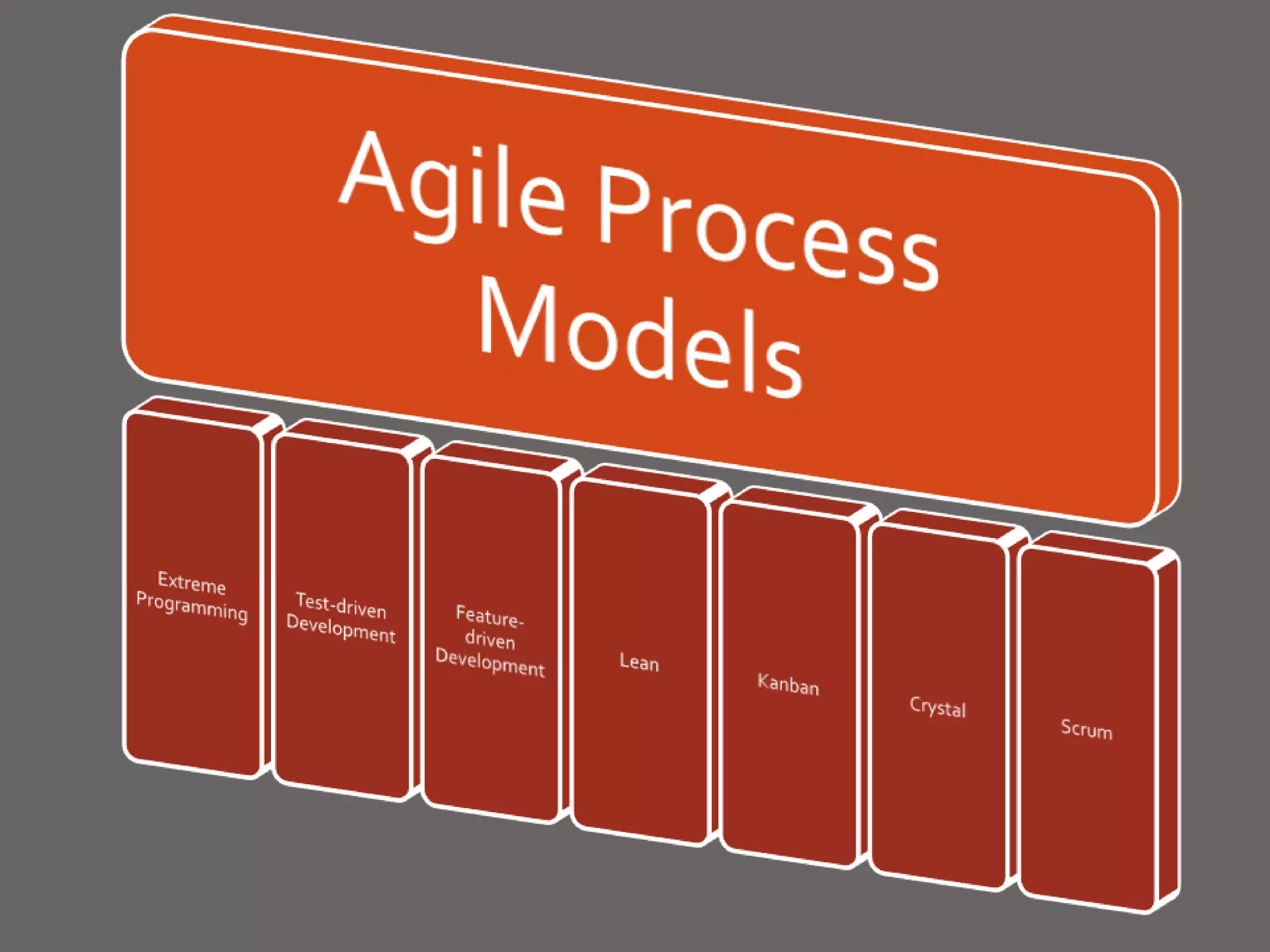
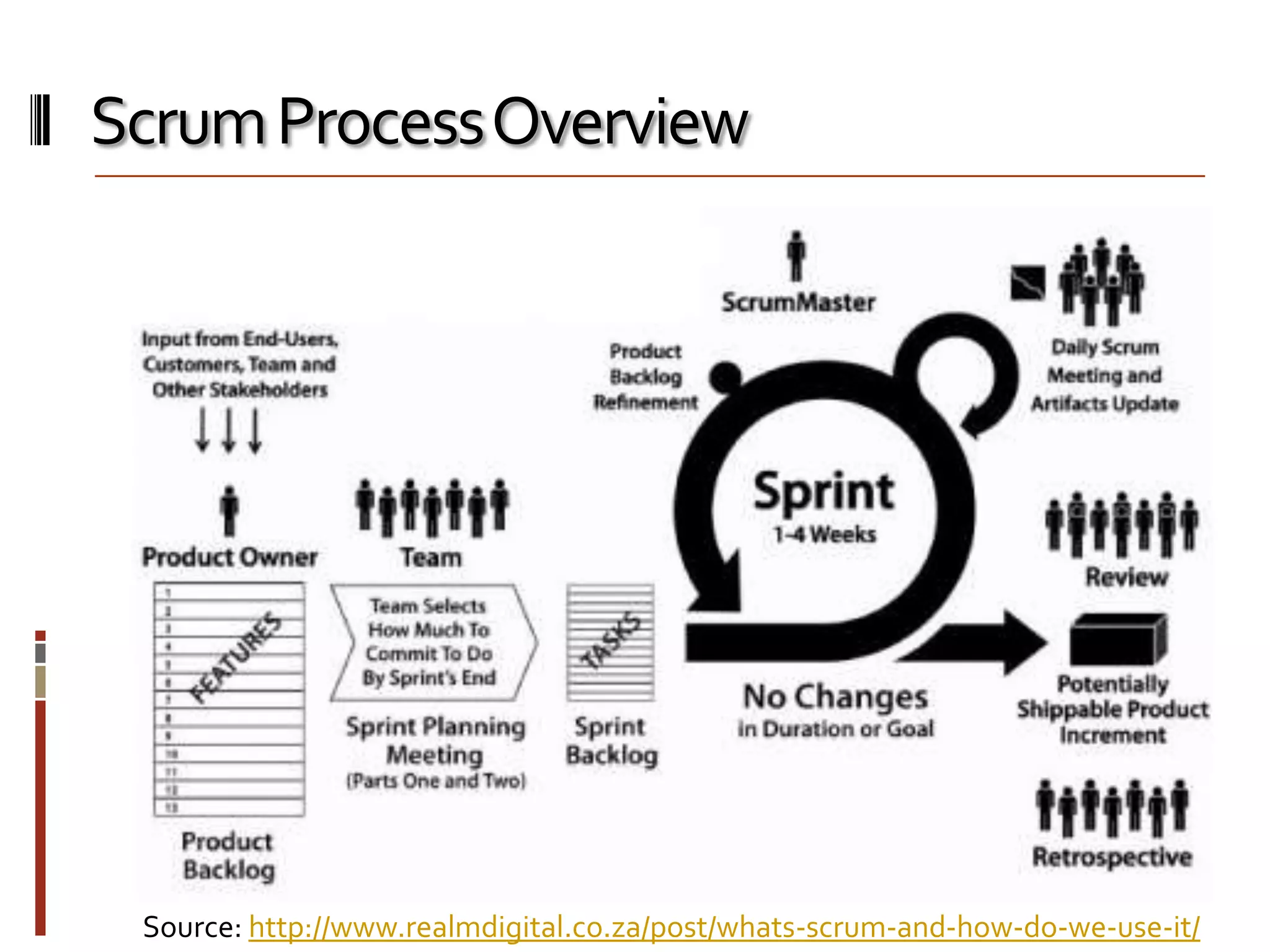
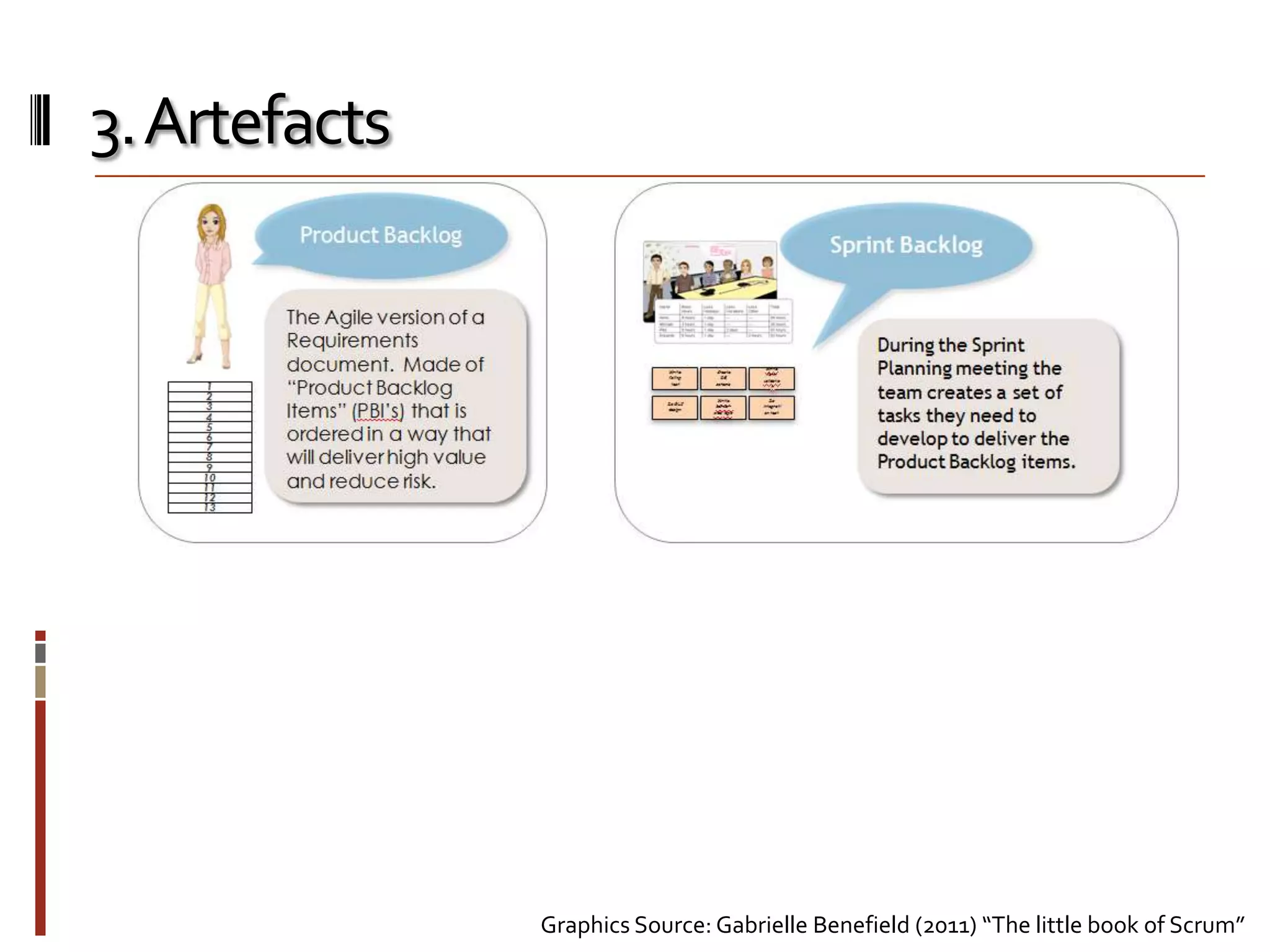
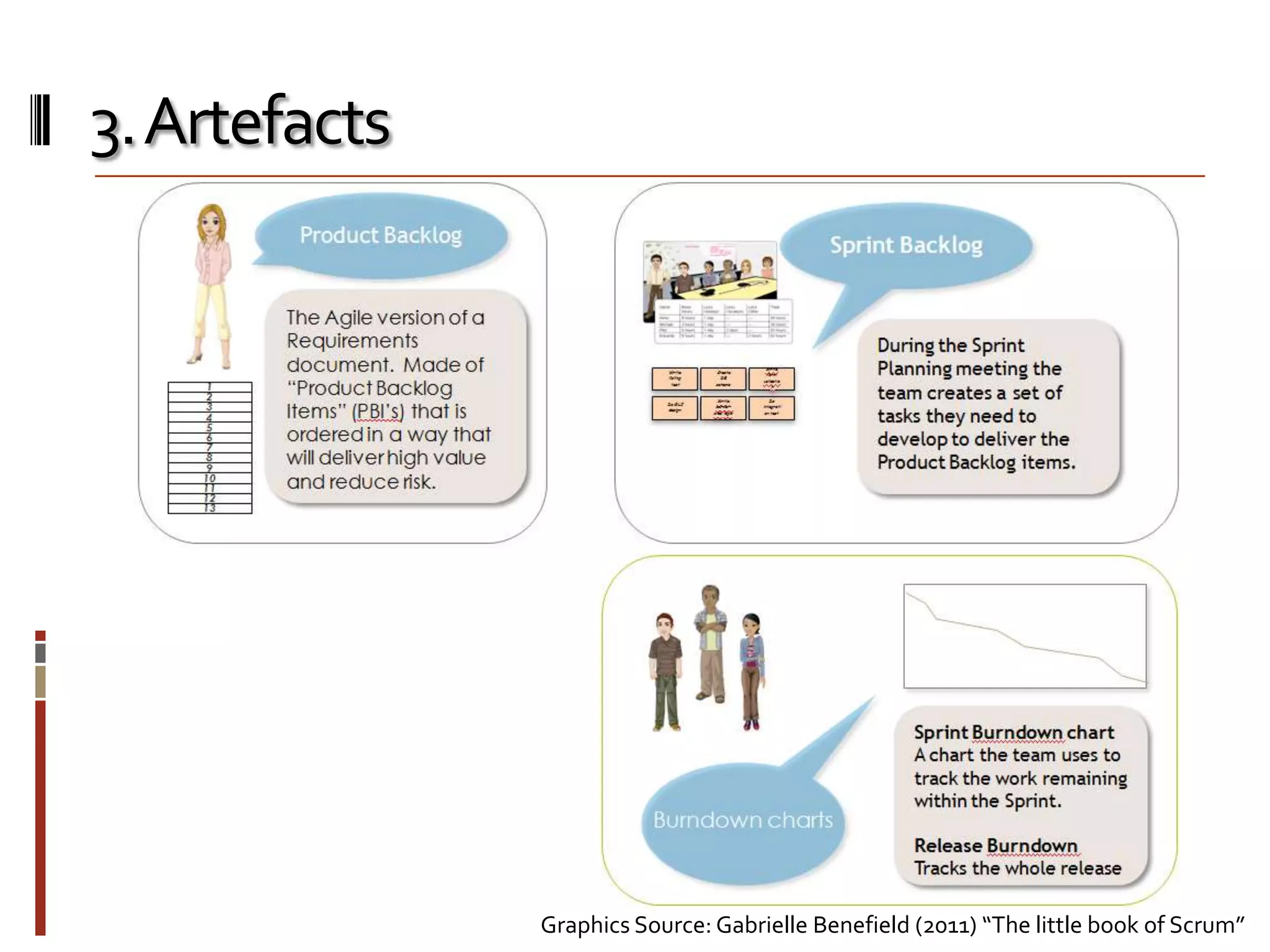
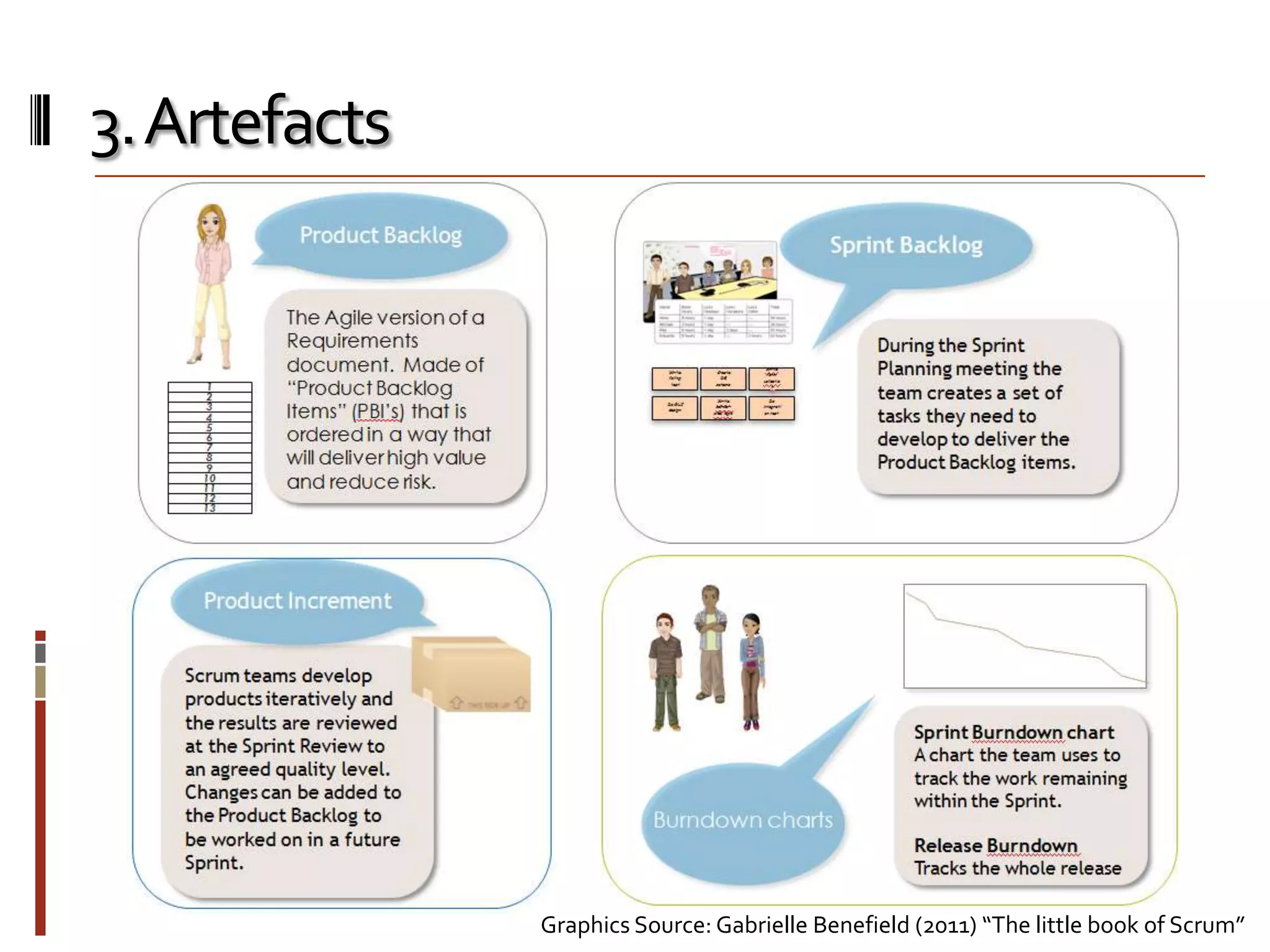
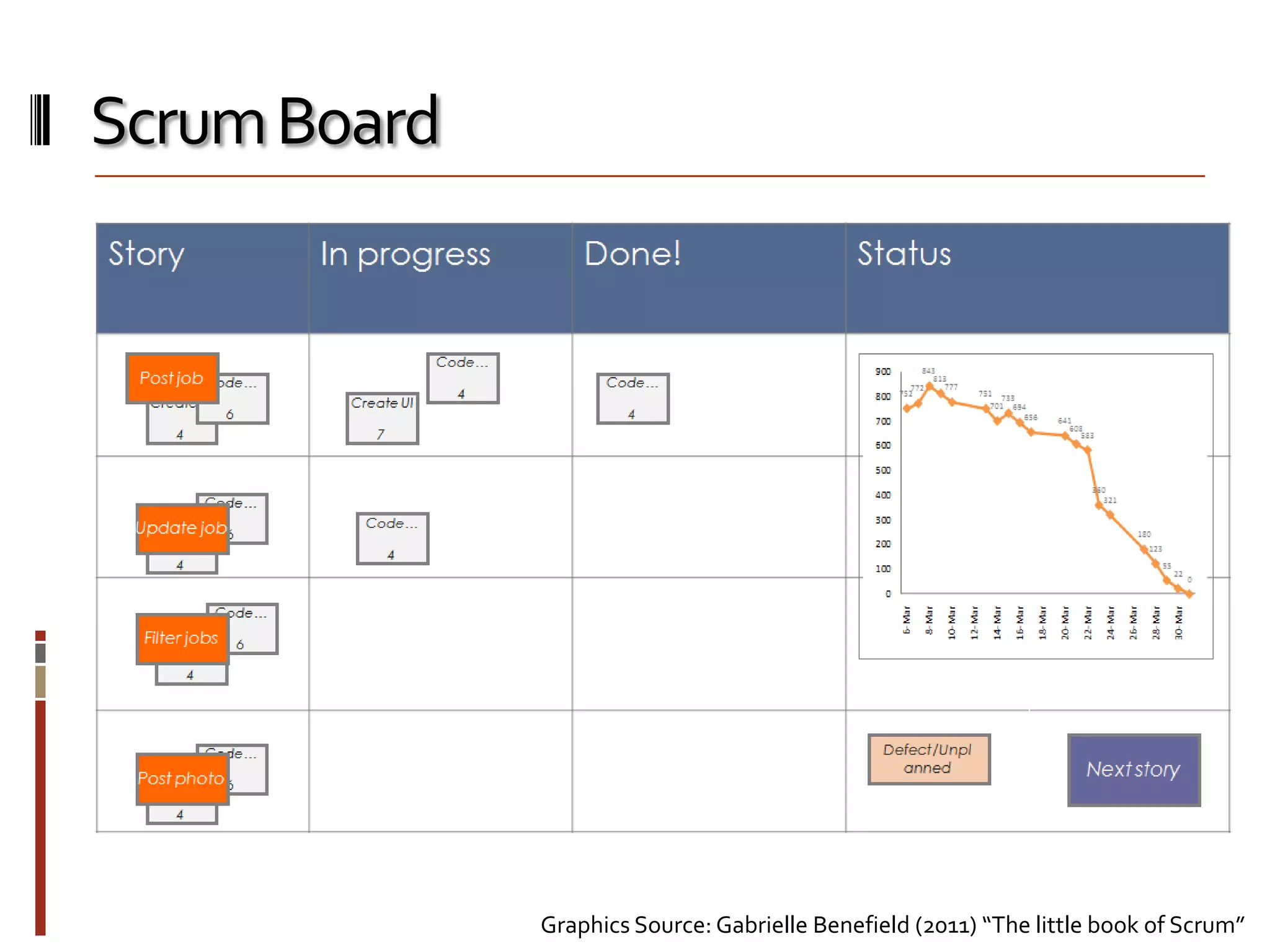
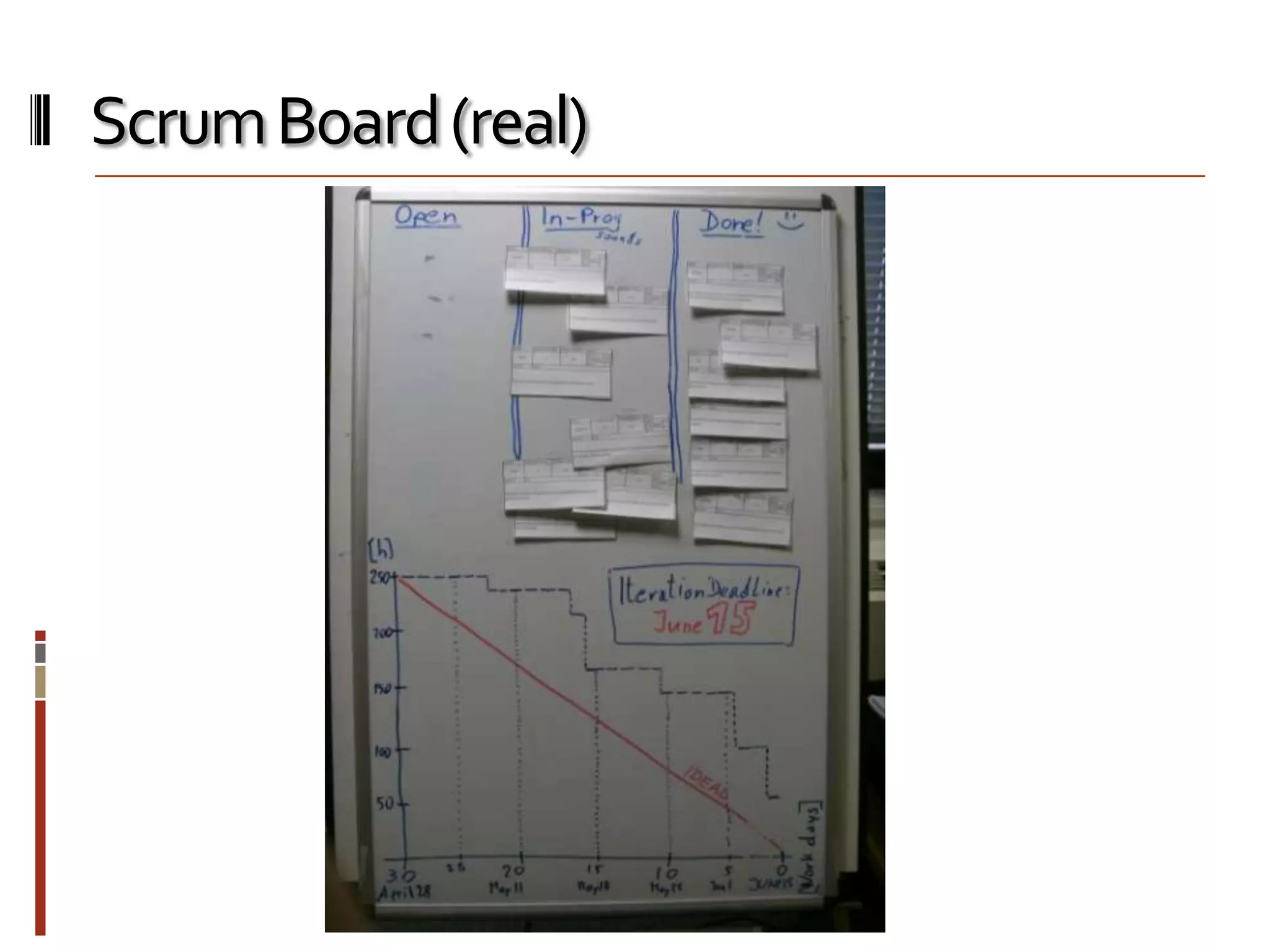
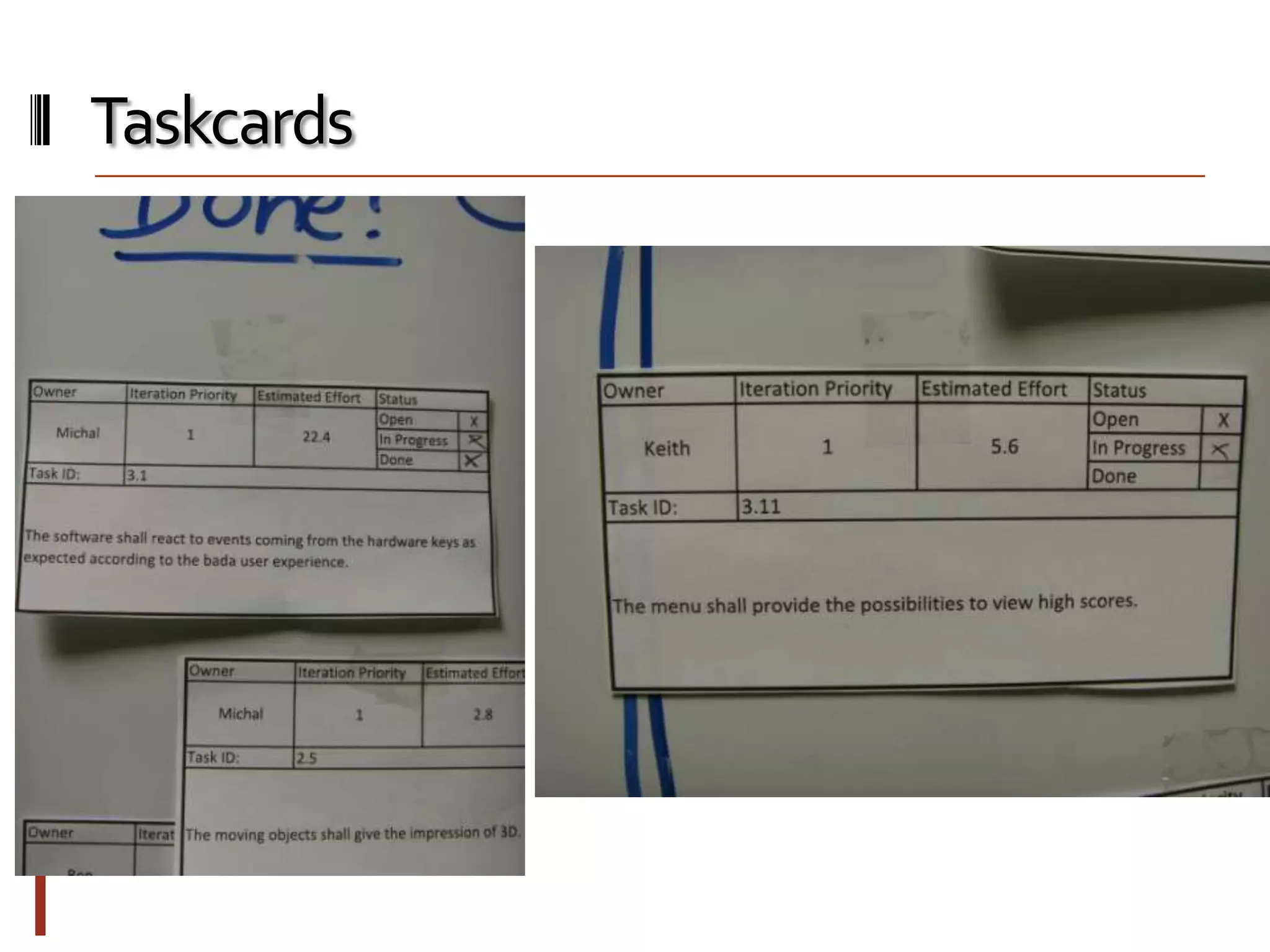
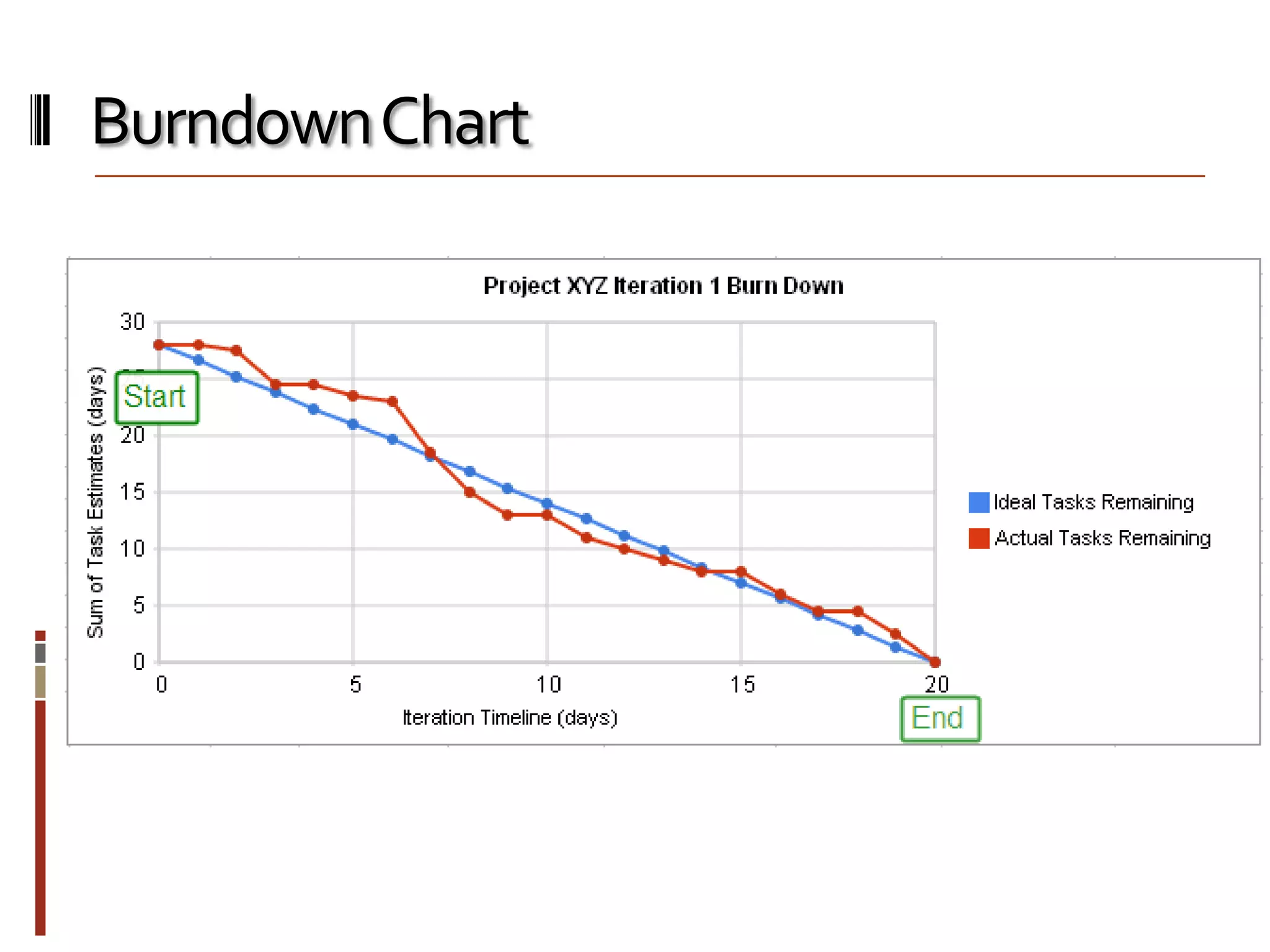
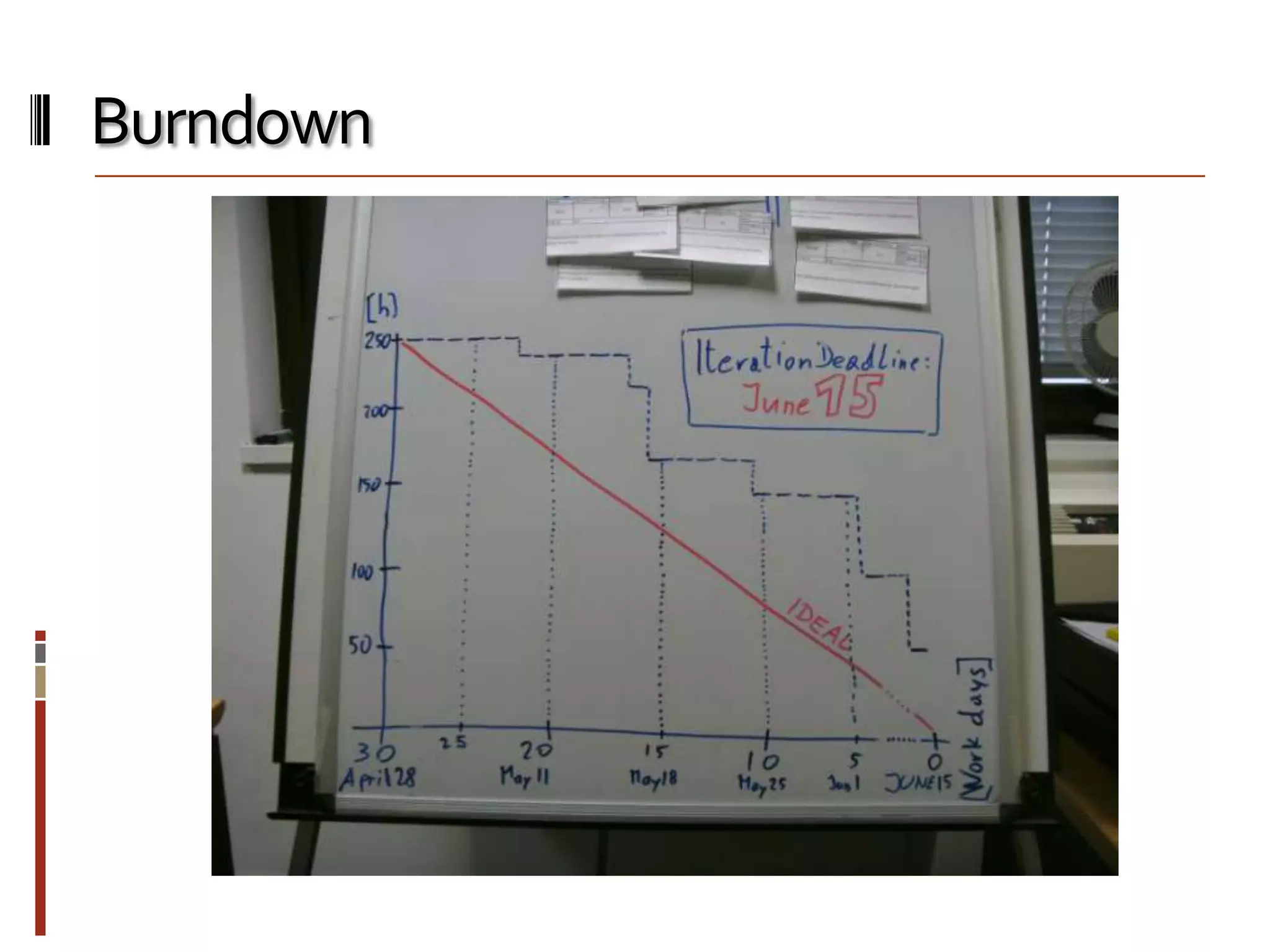
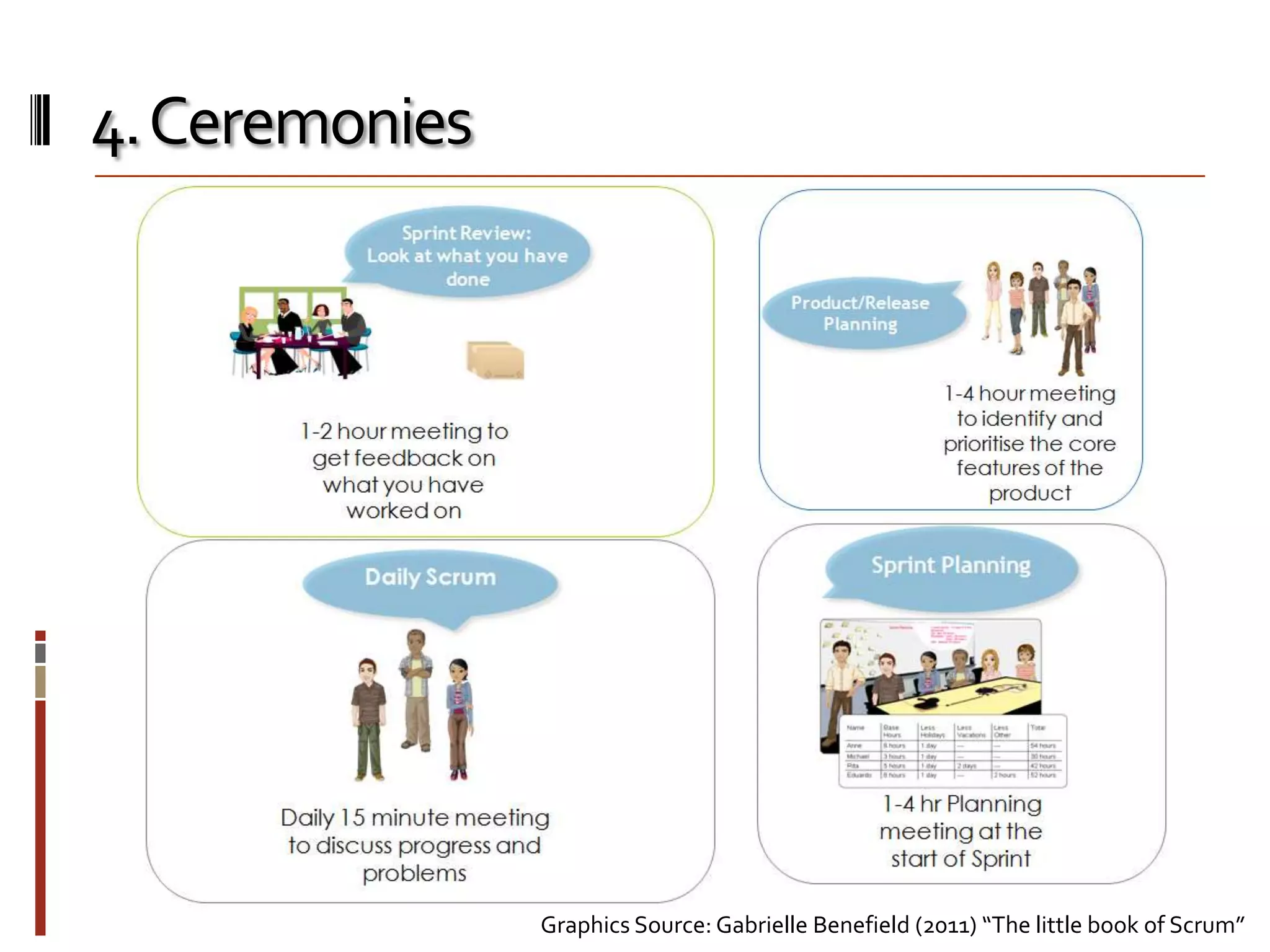
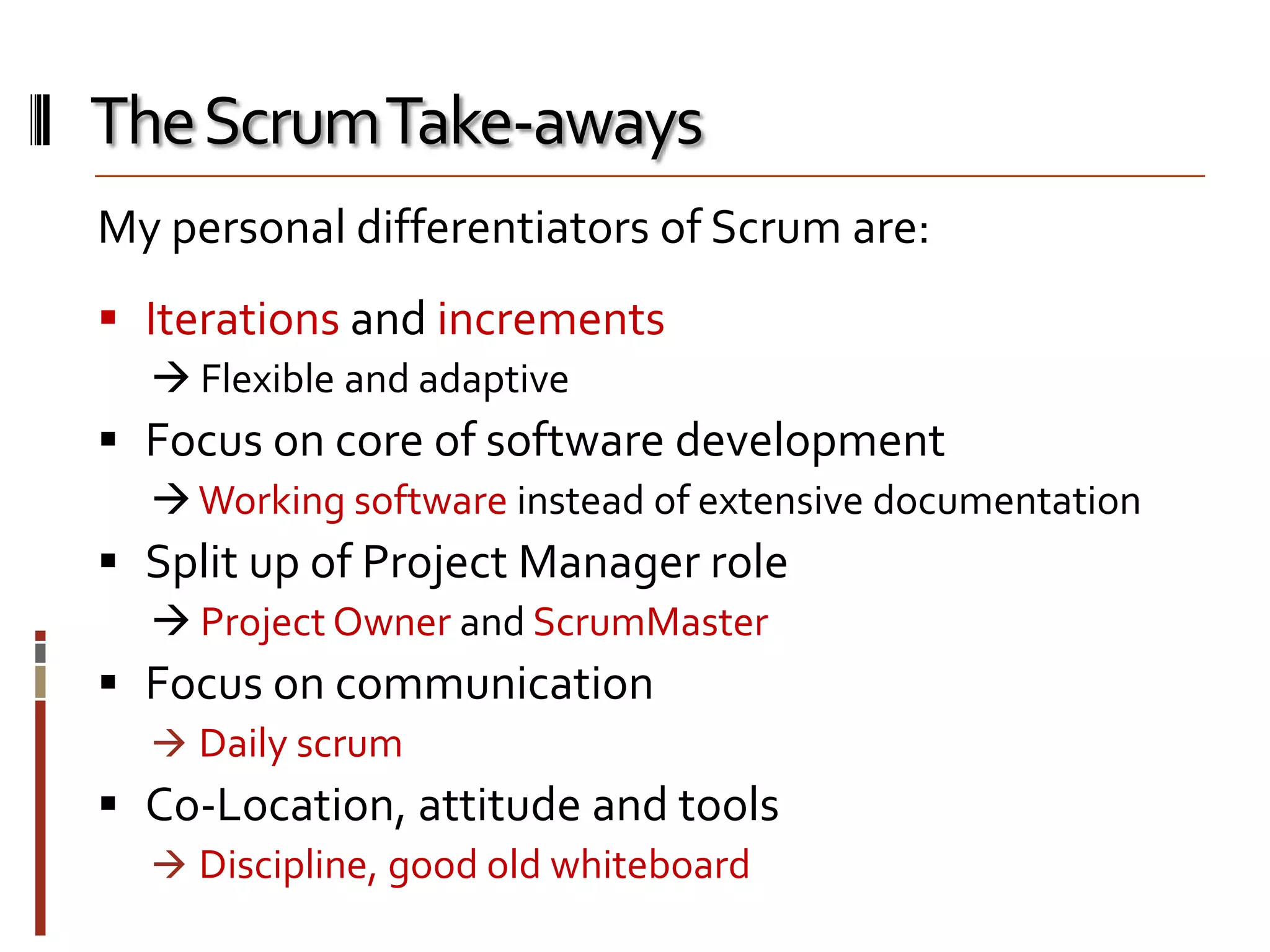
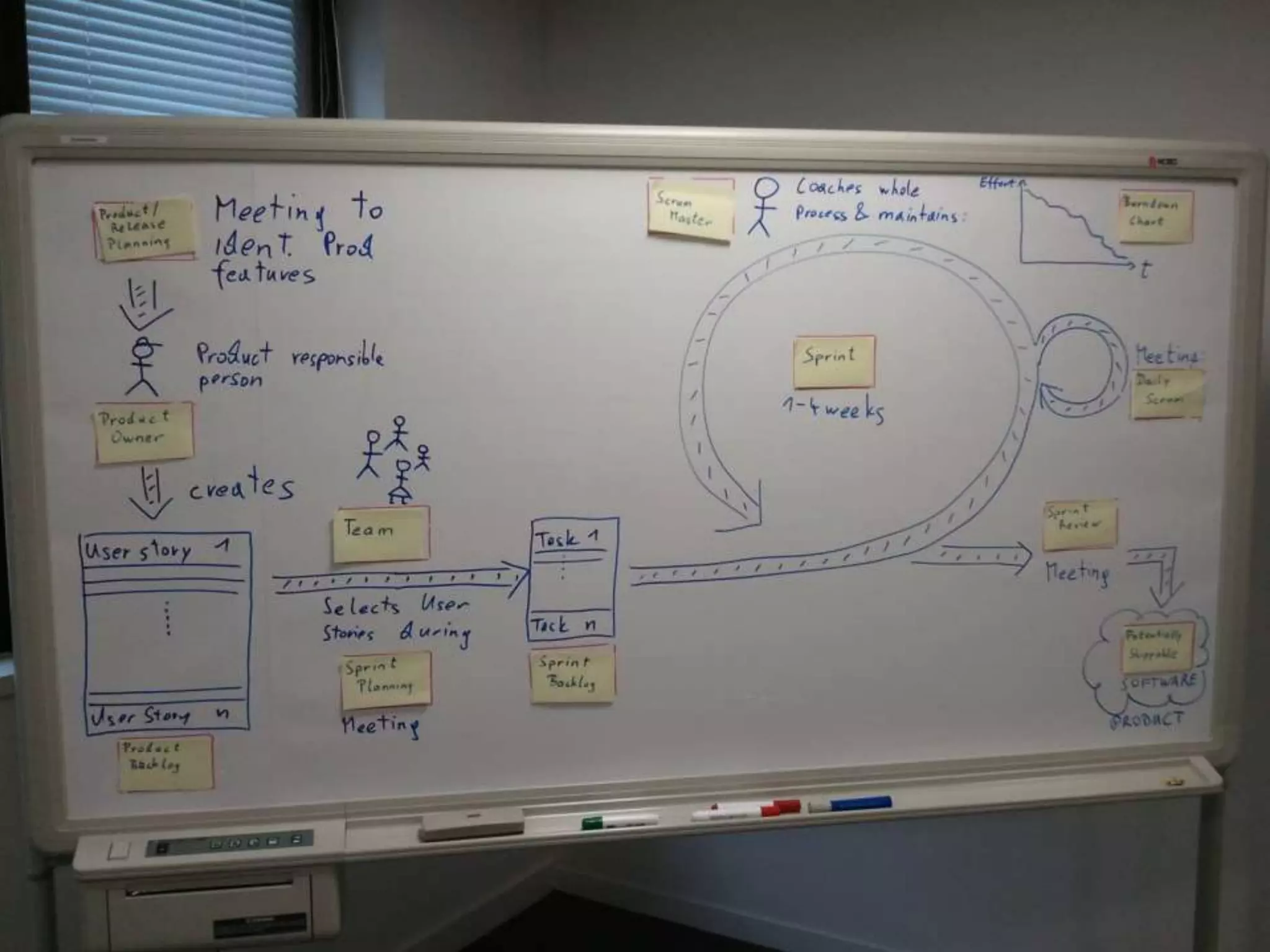
The document provides an overview of agile software development and the Scrum framework. It discusses the motivation for agile methods in response to traditional "cowboy coding" and waterfall models. The key aspects of Scrum covered include its core principles, roles of Product Owner, Scrum Master and team members, artifacts like product and sprint backlogs and task boards, ceremonies like the daily scrum, and rules. The takeaways emphasized by the document are that the Scrum foundations provide comprehensive guidance but its application should be practical and simple, with the right combination being most effective.