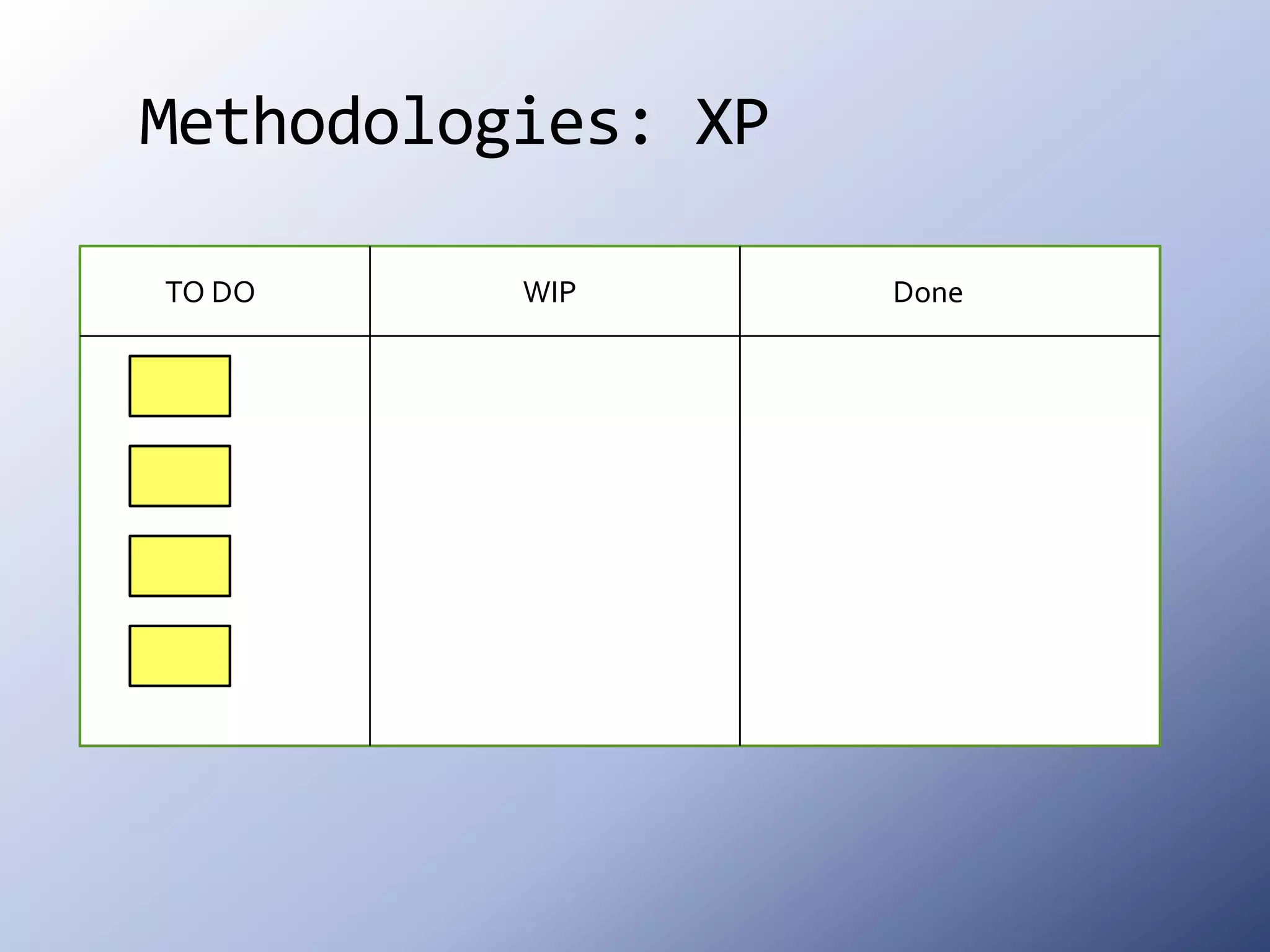
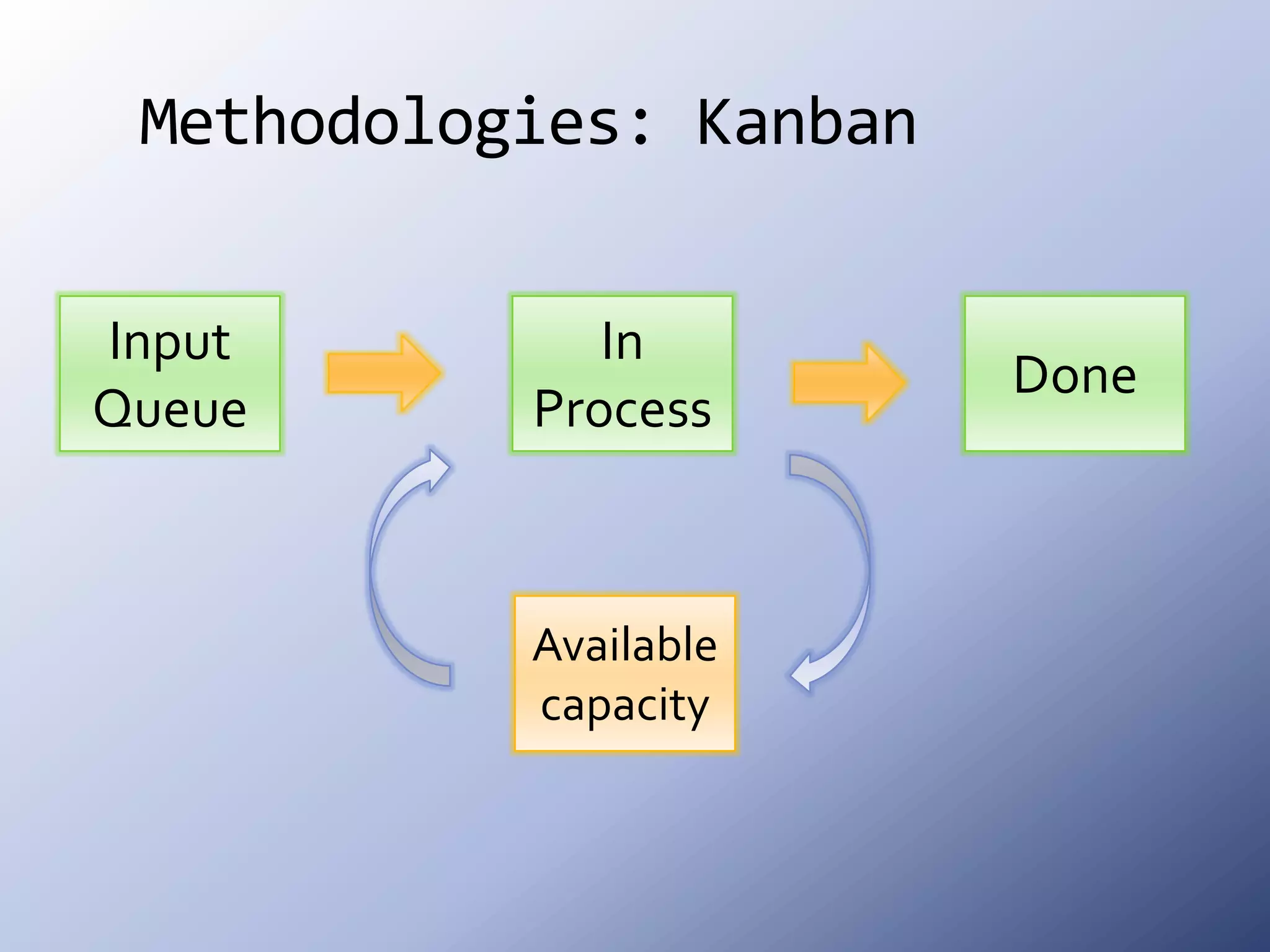
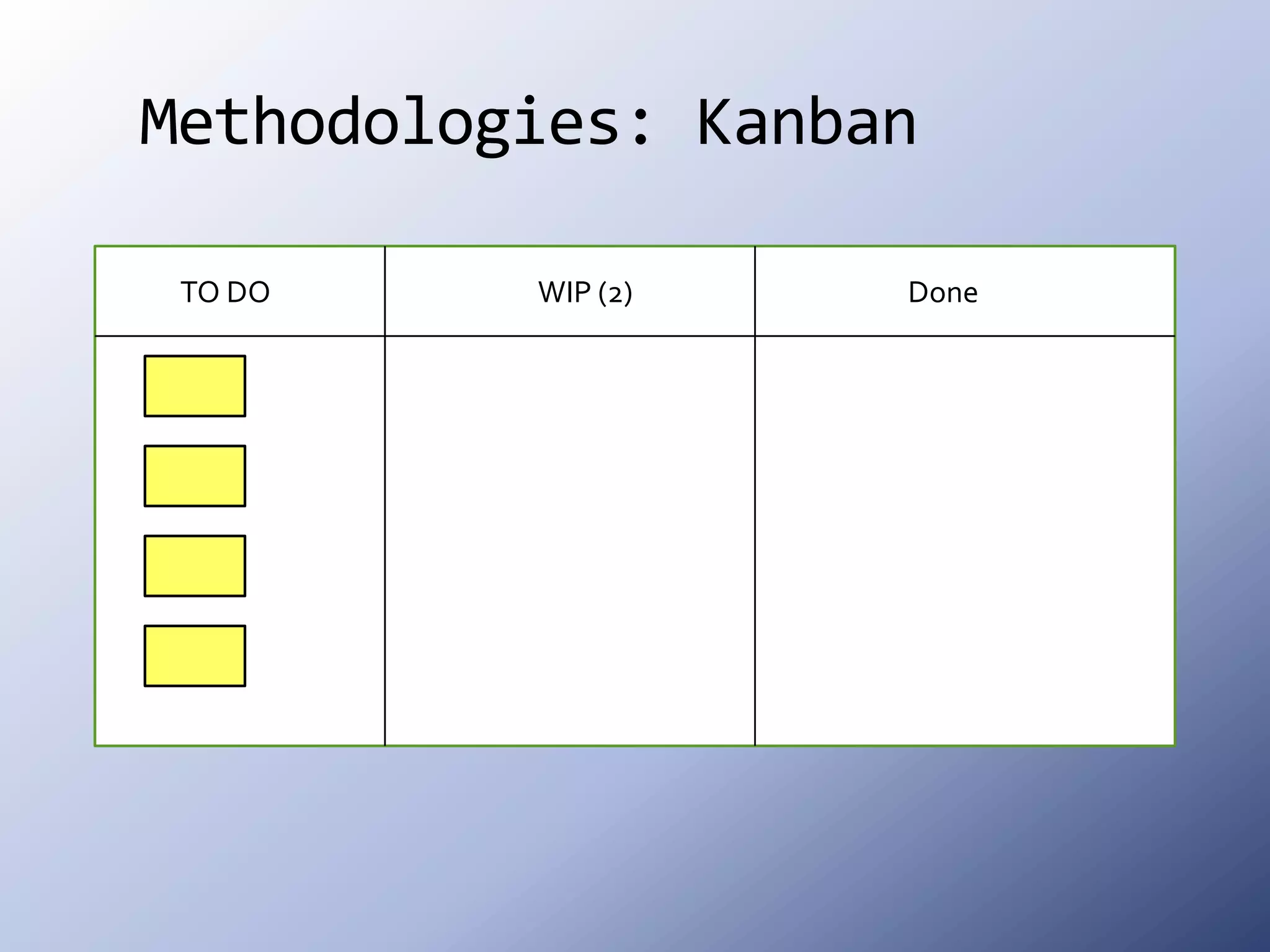
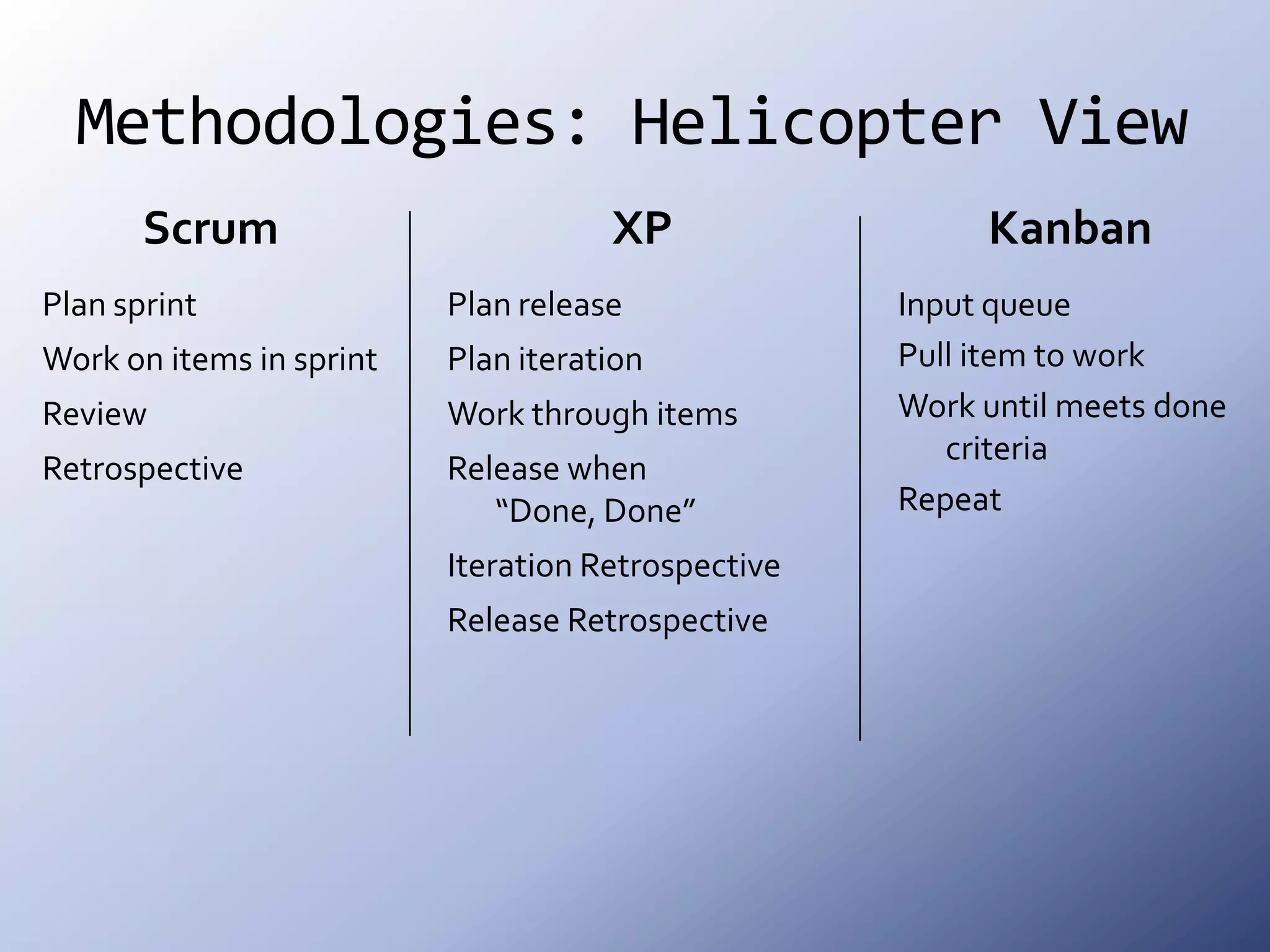
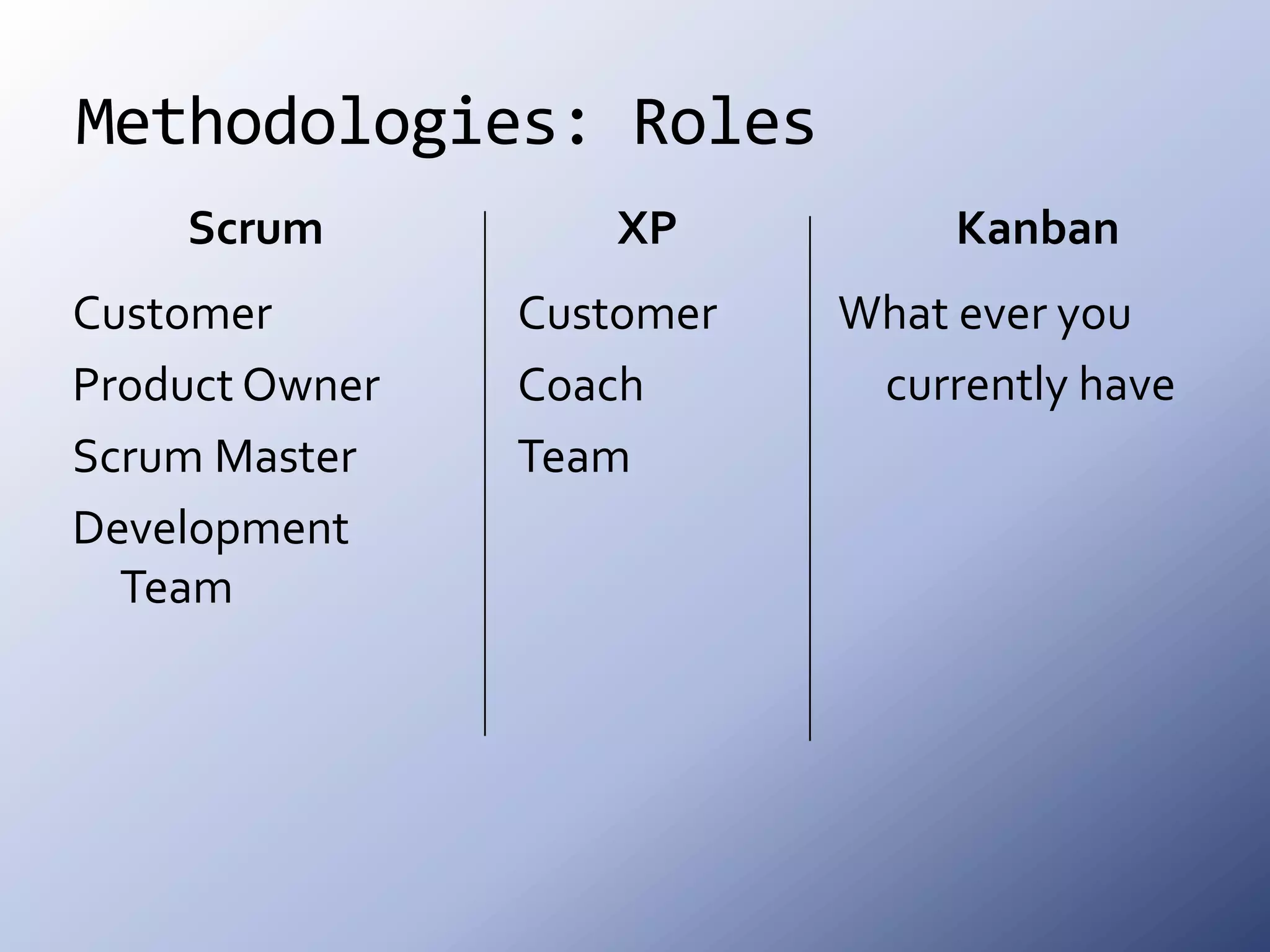
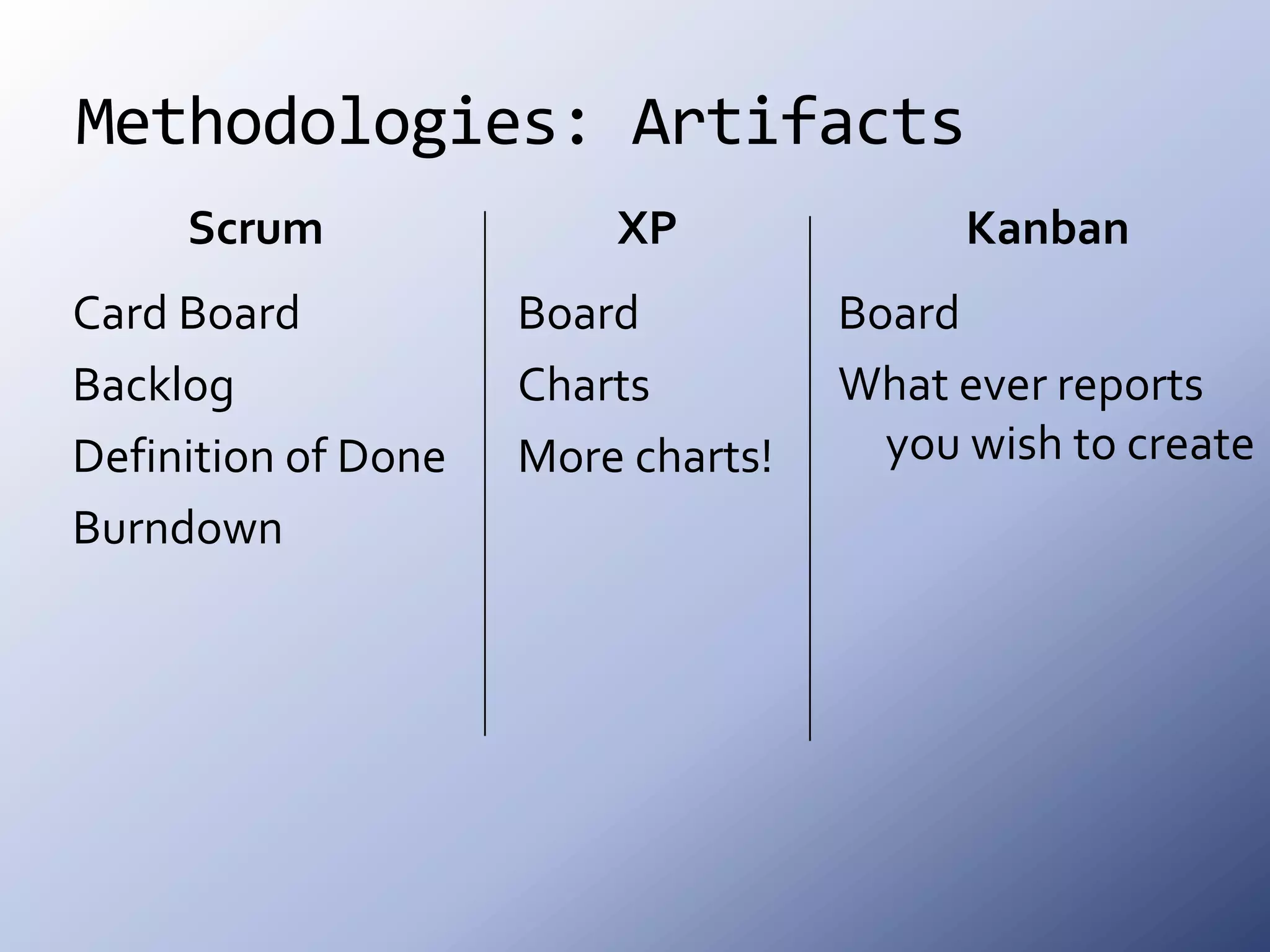
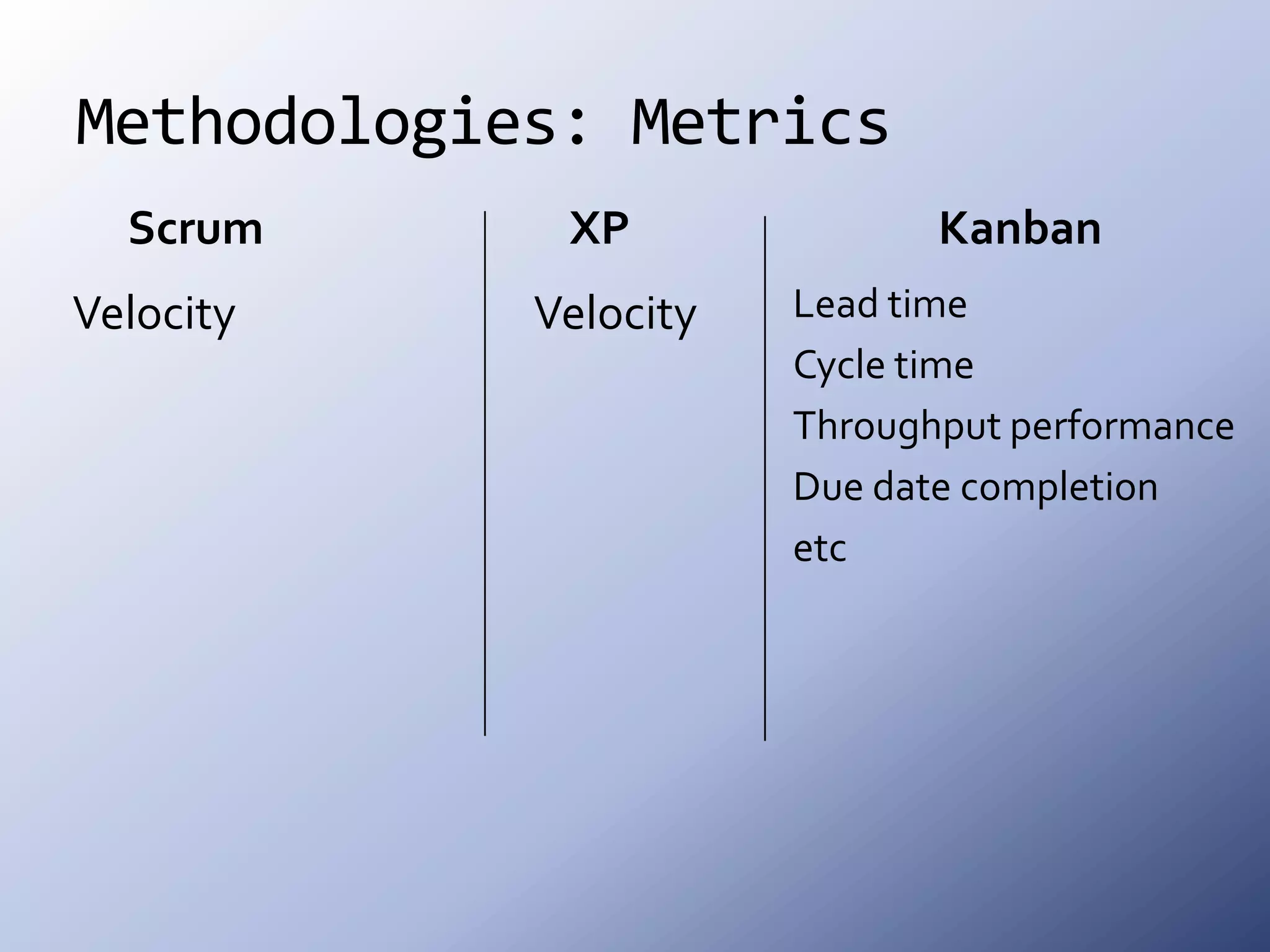
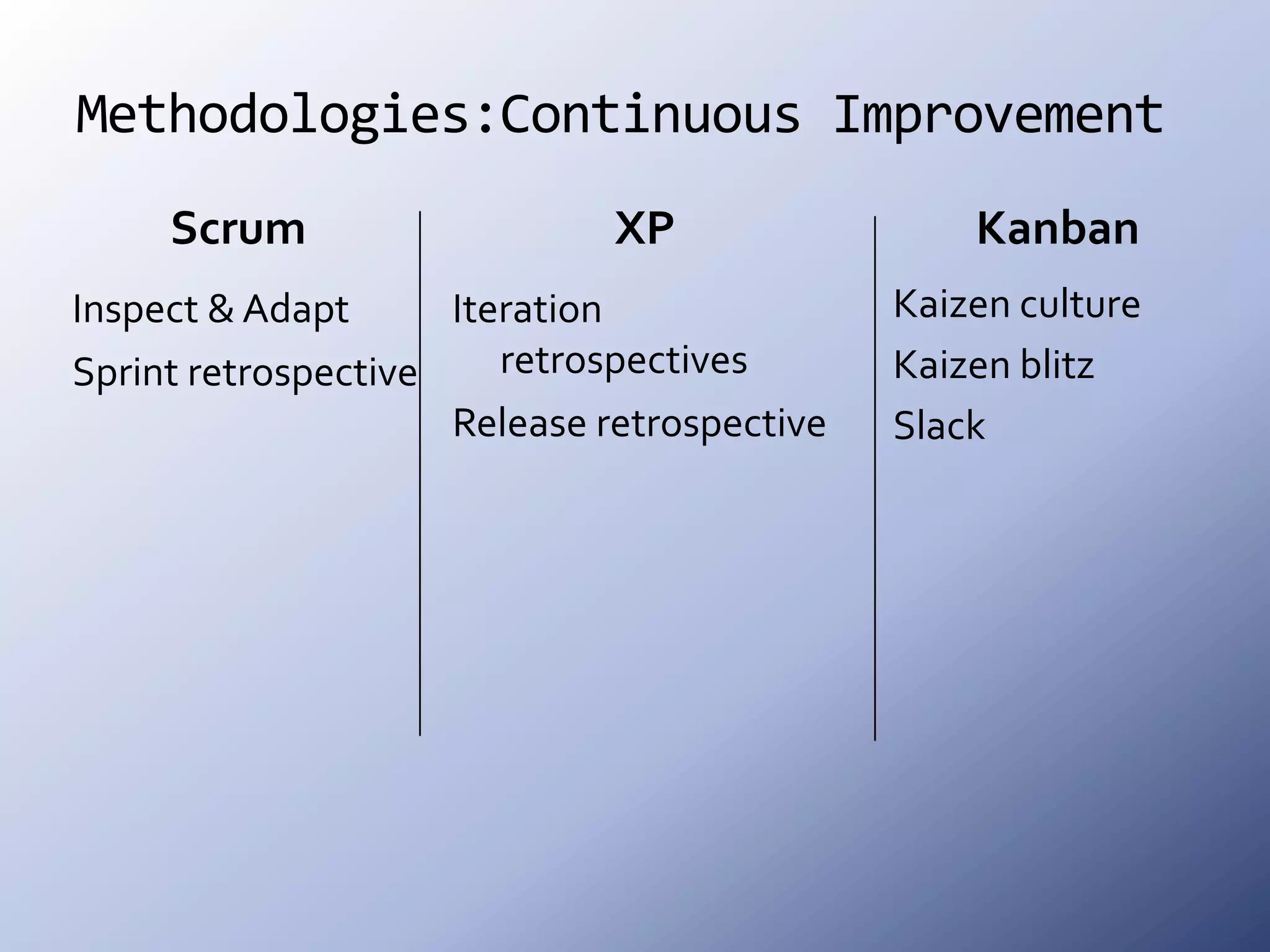
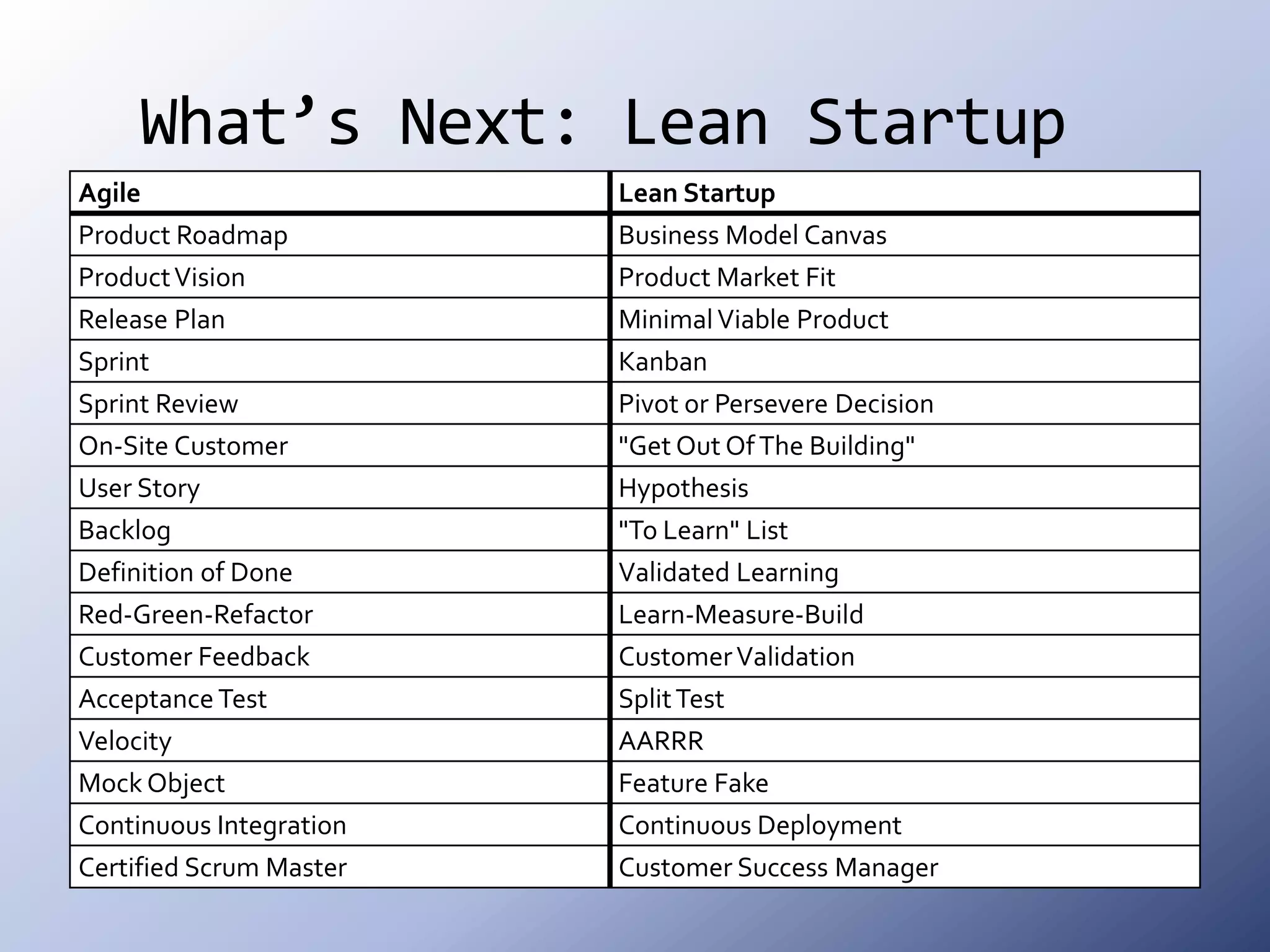
This document discusses the roots and evolution of agile methodologies. It traces agile back to problems with traditional heavyweight processes in the 1980s and the development of early agile frameworks like Scrum, XP, and DSDM. It then covers key agile concepts like collaboration, communication, and self-organizing teams. Finally, it summarizes popular methodologies like Scrum, XP, and Kanban, and looks at future trends like Scrumban, lean startup, and the potential decline of rigid project constraints. The overarching message is that teams should adopt agile principles and tailor processes and practices to their specific needs.