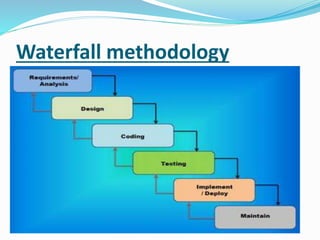
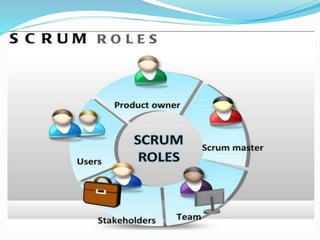
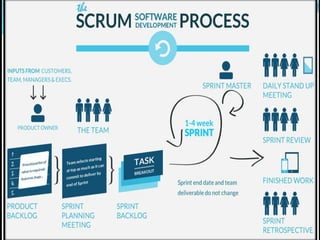
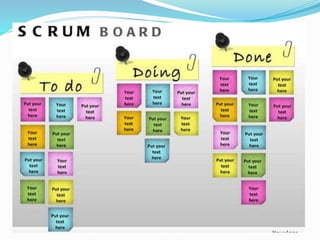
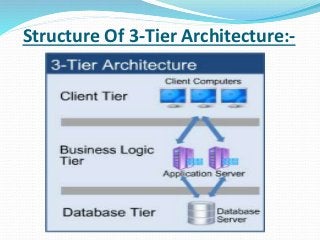
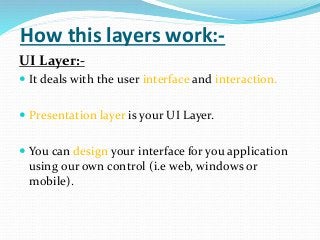
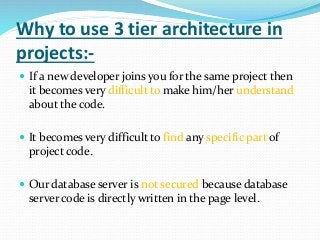
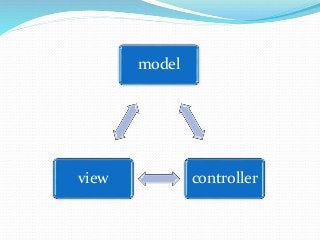
The document discusses various topics related to software development life cycles including waterfall, agile, scrum frameworks. It describes roles in scrum like product owner, scrum master, development team. It also covers 3-tier architecture, MVC pattern, coding best practices, testing strategies and source control.