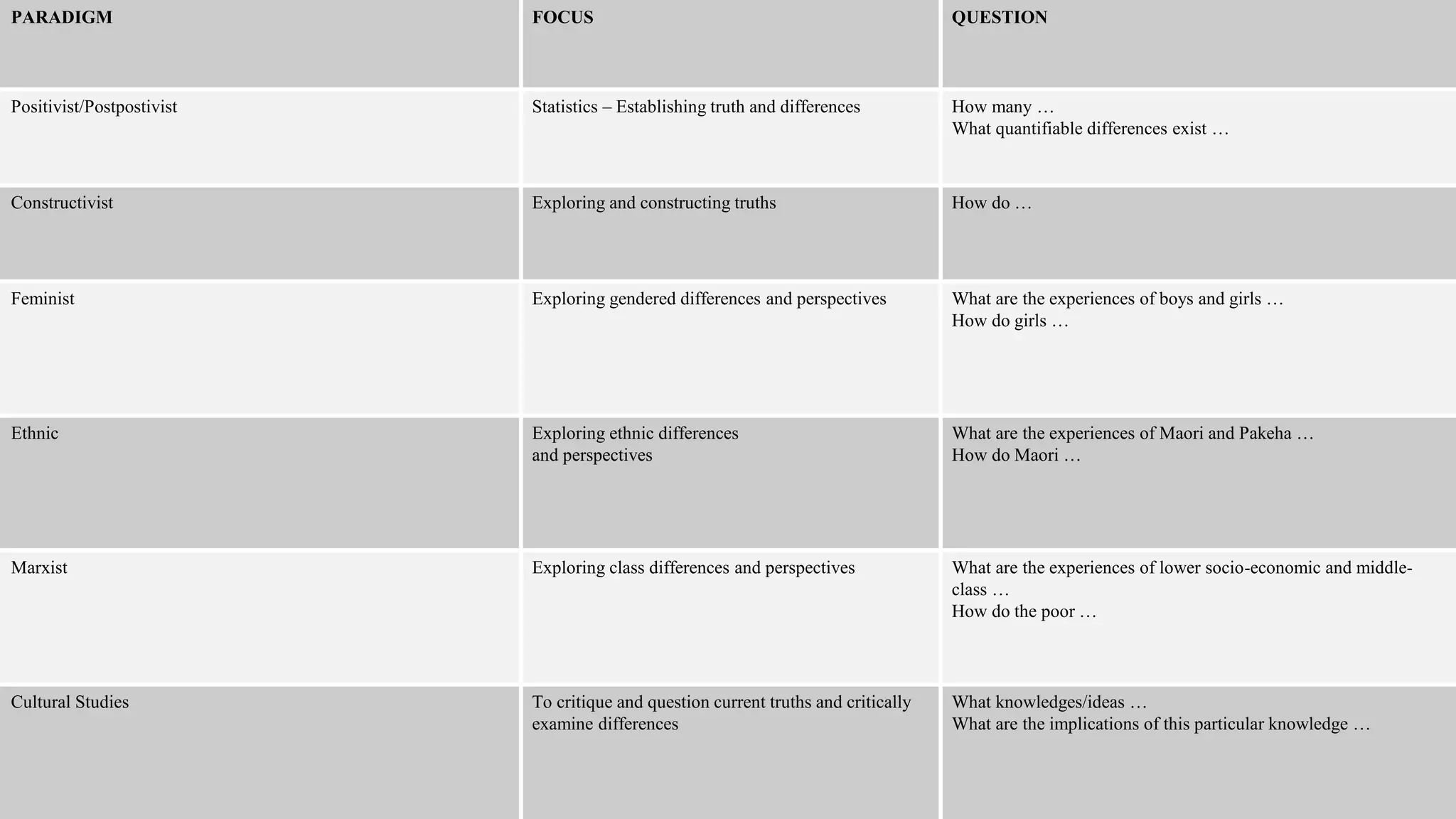
The document introduces various research paradigms, methodologies, and ethics applicable to studying youth experiences with boot camps, highlighting the need for alignment between research questions, methodologies, and constraints. It covers seven paradigms: positivist, constructivist, feminist, ethnic, marxist, cultural studies, and mixed methods, detailing specific aims, questions, constraints, and methodologies for each. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of ethical considerations and processes in research, including obtaining informed consent and ensuring confidentiality.