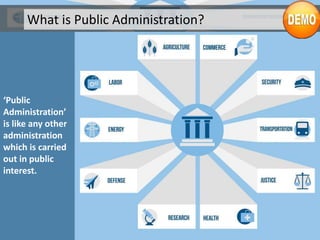
The document provides an introduction to public administration, defining it as administration conducted in public interest and highlighting its evolution from monarchies to modern democratic states. It differentiates between public and private administration, discusses Gulick’s principles of organizational structure, and introduces the new public management model which focuses on efficiency, financial control, and performance monitoring. Moreover, it underscores the significance of budgets in public administration and the changing roles of public administrators in the governance process.