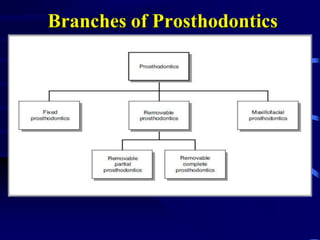
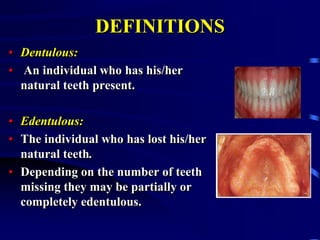
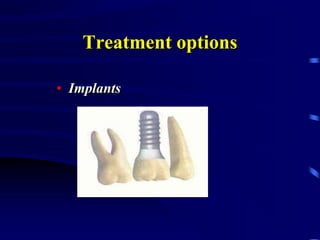
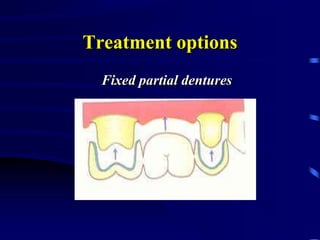
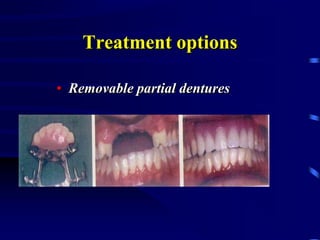
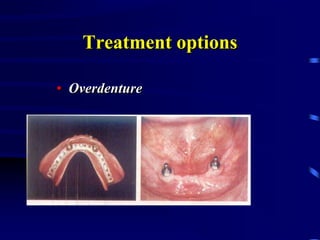
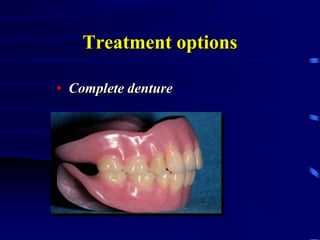
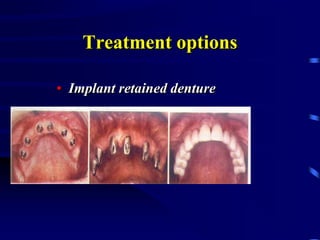
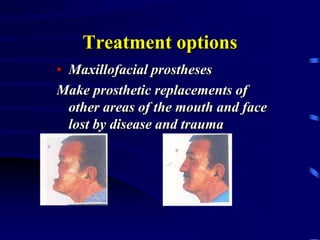
This document provides an introduction to prosthodontics, which is the branch of dentistry dealing with replacing missing teeth and oral structures. It defines key terms like prosthetics, prosthodontics, prosthesis, dentulous, and edentulous. The types of prostheses are outlined, including partial dentures, fixed partial dentures, removable partial dentures, and complete dentures. Reasons for tooth loss and sequelae of tooth loss are described. Finally, the various treatment options for tooth replacement are summarized, such as preservation techniques, crowns, implants, dentures, and maxillofacial prostheses.