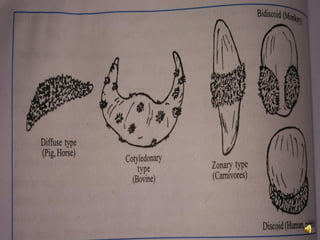
The document introduces placenta, its types, and functions in different animals. It defines placenta as the intimate connection between the fetal and maternal tissues that allows physiological exchange. Placentas are classified based on whether they cause decidua loss during birth and their gross shape. Functions of the placenta include transporting nutrients and gases, storing waste, biosynthesizing hormones, excreting wastes, acting as a protective barrier, and providing passive immunity transfer from dam to fetus.