This document provides an introduction to Objective-C, including:
- Objective-C is a programming language used by Apple for iOS and Mac apps that is a superset of C and adds object-oriented capabilities.
- The language consists of objects, classes, methods, and messages that allow objects to communicate with each other.
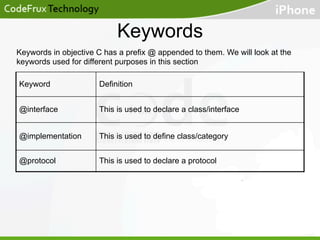
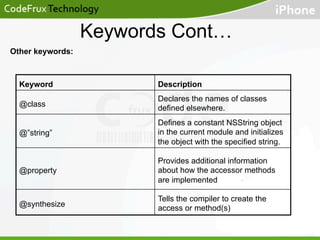
- Keywords like @interface, @implementation, and @protocol are used to define classes, categories, and protocols.
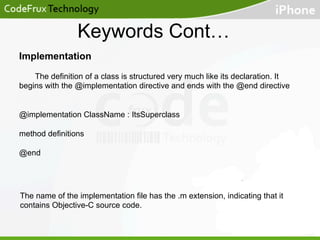
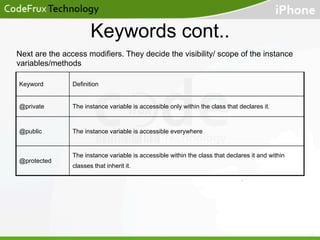
- The document discusses features like properties, memory management, and differences between instance and class methods.







![Keywords Cont…
Self
l
Self is a keyword which refers to current class.
{
[self setOrigin:someX :someY];
}
In the example above, it would begin with the class of the object receiving
the reposition message.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoobjectivec-131026070231-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-objective-c-12-320.jpg)
![Keywords Cont…
super
l
l
It begins in the superclass of the class that defines the method where
super appears.
Super is a keyword which refers to the parent class.
{
[super init];
}
{
[super dealloc];
}
In the example above, it would begin with the superclass of the class
where reposition is defined.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoobjectivec-131026070231-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-objective-c-13-320.jpg)
![Message
• It’s the most important extension to C
• Message is sent when one object asks another to perform a specific action.
• Equivalent to procedural call in C
• Simple message call looks like [receiver action], here we are asking the
.
receiver to perform the action
• Receiver can be a object or any expression that evaluates to an object.
• Action is the name of the method + any arguments passed to it.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoobjectivec-131026070231-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-objective-c-14-320.jpg)
![Message with Arguments
• Sometimes we pass one or more arguments along with the action to the
receiver.
• We add a argument by adding a colon and the argument after the action like
[receiver action: argument]
• Real world example of this is [label setText:@”This is my button”];
• String in Objective C is defined as @””;
• Multiple arguments can be passed to a action like this
[receiver withAction1:argument1 withacction2:argument2];
For example:
[button setTitle:@”OK” forState:NO];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoobjectivec-131026070231-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-objective-c-15-320.jpg)
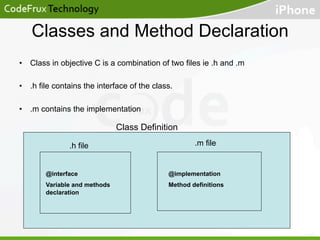


![Classes and Method Declaration
• Using the Person class
#import<stdio.h>
#import “Person.m"
int main()
{
Person *c = [[Person alloc] init]; // Allocating and initializing Person
[c setName : @”Rahul”]; // Setting Name of the allocated person
[Person printCompanyName] // calls class method
[c release]; // releasing the person object created
return 1; // return
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoobjectivec-131026070231-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-objective-c-19-320.jpg)
![Instance and Class Methods
• In objective C we can define methods at two levels ie Class Level and
Instance level
• In previous Example we declared a method with a – sign prefixed. That was
a instance level method.
• If we put + instead of – then we get a class level method.
• A instance method can be called by the instances of the class. But a class
level can be called without creating any instance.
• Example to call a instance method;
Person *p=[[Person alloc] init];
[p setName:@”Sunil”];
• Example to call class method
[Person printCompanyName];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoobjectivec-131026070231-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-objective-c-20-320.jpg)

![Creating multi parameter method
Objective-C enables programmer to use method with multiple
parameter. These parameter can be of same type or of different
type.
main.m
#import"MyClass.m"
int main()
{
MyClass *class = [[MyClass alloc]init];
NSLog(@"Sum is : %d",[class sum : 5 andb : 6 andc:10]);
[class release];
return ;
}
Output:
Sum is: 21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoobjectivec-131026070231-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-objective-c-22-320.jpg)
![Constructors
• When a class is instantiated a constructor is called which is used to initialize
the object properties
• When a constructor is called it returns an object of a class.
• If a user does not provide a constructor for a class the default one is used.
• The default constructor is
-(id) init;
id is a special keyword in Objective C which can be used to refer to any
object.
• Remember in our Person class example while instantiating the Person class
we called the constructor.
[[Person alloc] init];
It returns a person object.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoobjectivec-131026070231-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-objective-c-23-320.jpg)




![Memory Management
• In objective C a programmer has to manage memory ie allocate and
deallocate memory for objects.
• While instantiating a person object we allocated the memory for the object
by this call.
Person *p=[[Person alloc] init];
• We have to release whatever objects we create programatically. Memory
management for other objects is taken care of by the Objective C runtime.
• We use release action to release the unused memory.
The syntax for this is [p release];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoobjectivec-131026070231-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-objective-c-28-320.jpg)
