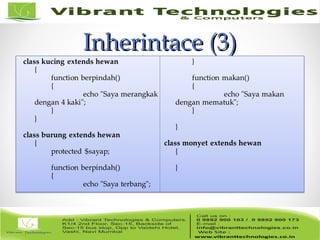
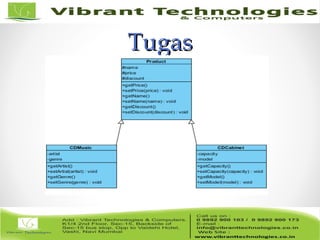
The document provides an introduction to object-oriented programming (OOP) in PHP, covering key concepts such as classes, objects, encapsulation, inheritance, and visibility levels for member variables. It includes code examples for creating classes, methods, properties, and discusses best practices for data access through getters and setters, as well as the use of constructors and destructors. Additionally, it outlines tasks for applying these concepts to create related classes for products and music CDs.