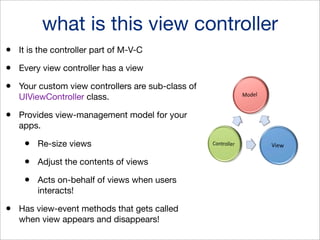
This document provides an overview of iOS programming using Xcode and Objective-C. It discusses Xcode development tools like Interface Builder and iOS Simulator. It covers the Xcode IDE, navigation, and running apps on the simulator or a device. It introduces Objective-C concepts like classes, objects, methods, and message passing. It discusses core Objective-C classes like NSString, NSNumber, NSArray, and NSDictionary. It also covers view controllers, the model-view-controller design pattern, and view controller lifecycle methods. Sample code projects are provided to demonstrate concepts like handling user interfaces and responding to user interactions.






![Object Allocation
Cat *myCat = [[Cat alloc] init];
// what exactly happens
// 1st line allocates enough memory to hold a cat object
Cat *myCat = [Cat alloc];
// 2nd line initializes the object.
[myCat init];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ios101-131125213651-phpapp01/85/iOS-101-Xcode-Objective-C-iOS-APIs-12-320.jpg)

![Message Passing in Obj-C
• In other languages you refer this as method calling.
But due to the nature of Obj-C it’s often referred as a
message (can refer it as method or function) being
passed to an object to make it do something.
• A message is passed to an object with-in square
brackets.
[objectName messageName];
• Messages can be piped together. That is a message
can be passed to an object is the result of another
message.
[[objectName messageOne] messageTwo];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ios101-131125213651-phpapp01/85/iOS-101-Xcode-Objective-C-iOS-APIs-14-320.jpg)
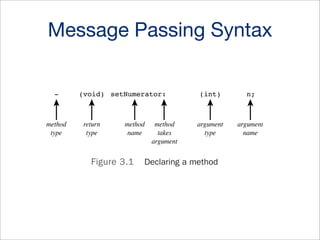

![Message Passing
• [receiver message];
• [receiver message:argument];
• [receiver message:arg1 andArg:arg2];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ios101-131125213651-phpapp01/85/iOS-101-Xcode-Objective-C-iOS-APIs-17-320.jpg)



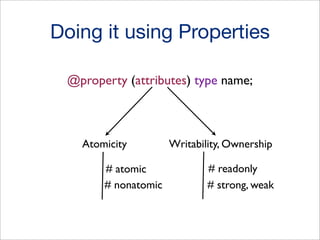
![Manual Implementation without Properties
// manual getter method
-(NSString *)getSnailName {
return snailName;
}
// manual setter method
-(void)setSnailName:(NSString *)name {
if (![name isEqualToString:snailName]) {
snailName = name;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ios101-131125213651-phpapp01/85/iOS-101-Xcode-Objective-C-iOS-APIs-21-320.jpg)




![Strings
•
Have seen glimpse of it in all our NSLog
messages
•
•
NSLog(@"Objective C is Awesome");
NSString *snailName = [[NSString alloc] init];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ios101-131125213651-phpapp01/85/iOS-101-Xcode-Objective-C-iOS-APIs-27-320.jpg)
![Strings Methods
[NSString stringWithFormat:@"%d", someInteger];
[NSString stringWithFormat:@"My integer %d", someInteger];
[snailName stringByReplacingOccurrencesOfString:@"N"
withString:@"P"];
NSString *newString = [myString appendString:@"Another String"];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ios101-131125213651-phpapp01/85/iOS-101-Xcode-Objective-C-iOS-APIs-28-320.jpg)
![NSNumbers
NSNumber *animationDuration = [[NSNumber alloc] init];
NSNumber *animationDuration = [[NSNumber alloc]
initWithBool:YES];
NSNumber *animationDuration = [[NSNumber alloc]
initWithInt:1];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ios101-131125213651-phpapp01/85/iOS-101-Xcode-Objective-C-iOS-APIs-29-320.jpg)

![NSArray & NSMutableArray
NSArray
(read-only)
•
•
Manage collections of Objects
•
•
NSMutableArray
(read write)
NSArray creates static array
Objects can be anything NSString, NSNumber, NSDictionary, even
NSArray itself.
NSMutableArray creates dynamic array
NSArray *myArray = [[NSArray alloc] init];
NSArray *myArray = [[NSArray alloc] initWithObjects:Obj1, Obj2, nil];
NSArray *myArray = @[Obj1, Obj2];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ios101-131125213651-phpapp01/85/iOS-101-Xcode-Objective-C-iOS-APIs-31-320.jpg)
![getting and setting values
•
Values are being accessed using array index
•
•
myArray[2] // will return 3rd object. Index starts from 0
Value can be set by assigning an Object for an index
•
myArray[3] = @"some value"; // will set value for 4th element](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ios101-131125213651-phpapp01/85/iOS-101-Xcode-Objective-C-iOS-APIs-32-320.jpg)



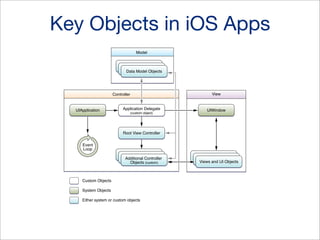
![when app finishes launching
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application
didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions{
// window is being instantiated
self.window = [[UIWindow alloc] initWithFrame:[[UIScreen
mainScreen] bounds]];
// view controller is being instantiated
self.viewController = [[ViewController alloc]
initWithNibName:@"ViewController" bundle:nil];
// every app needs a window and a window needs a root view controller
self.window.rootViewController = self.viewController;
[self.window makeKeyAndVisible];
return YES;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ios101-131125213651-phpapp01/85/iOS-101-Xcode-Objective-C-iOS-APIs-37-320.jpg)