This document provides an introduction to Objective-C, beginning with an overview of what Objective-C is and the prerequisites for learning it. It then demonstrates a simple "Hello World" program to get started. The rest of the document outlines key Objective-C concepts like objects, methods, inheritance, properties, protocols, categories and class extensions. It also discusses the Foundation framework and common Objective-C data types like NSString, NSNumber, NSArray and NSDictionary. The document uses examples to illustrate how to define and use Objective-C objects.


![Hello World!
//
// main.m
#include <stdio.h>
#include <Foundation/Foundation.h>
int main(int argc, const char **argv)
{
NSString *message = @"Hello World!";
printf("%sn", [message cString]);
return 0;
}
Saturday, March 9, 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objective-cabeginnersdive-130309214601-phpapp01/85/Objective-C-A-Beginner-s-Dive-5-320.jpg)
![Hello World!
• Objective-C String Literal
• @”Hello World!” //
// main.m
• C Function #include <stdio.h>
#include <Foundation/Foundation.h>
• printf() int main(int argc, const char **argv)
{
NSString *message = @"Hello World!";
• main() printf("%sn", [message cString]);
return 0;
•
}
Objective-C message
• [message cString]
Saturday, March 9, 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objective-cabeginnersdive-130309214601-phpapp01/85/Objective-C-A-Beginner-s-Dive-6-320.jpg)










![Object Method Calling
• Not like C, C++, or Java
• Based on Smalltalk message passing
• The Square Brackets [] are your friend!
[object method];
[object methodWithVar:value];
[object methodWithVar1:val1
! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! var2:val2];
Saturday, March 9, 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objective-cabeginnersdive-130309214601-phpapp01/85/Objective-C-A-Beginner-s-Dive-18-320.jpg)


![Generic Constructor
- (id)init {
if (self = [super init]) {
// initialize variables
}
return self;
}
Saturday, March 9, 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objective-cabeginnersdive-130309214601-phpapp01/85/Objective-C-A-Beginner-s-Dive-21-320.jpg)
![Constructor Example
// default constructor
- (id)init {
// calls my custom constructor
return [self initWithInt:0];
}
// custom constructor
- (id)initWithInt:(int)myInt {
if (self = [super init]) {
_myInt = myInt;
}
return self;
}
Saturday, March 9, 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objective-cabeginnersdive-130309214601-phpapp01/85/Objective-C-A-Beginner-s-Dive-22-320.jpg)

![Inheritance Example
// //
// MyObject.m // MyObject.h
// Implementation // Interface
#import “MyObject.h” #import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@implementation MyObject @interface MyObject : NSObject {
int _myInt;
- (id)init { }
if (self = [super init]) {
_myInt = 5; - (id)init;
}
return self; @end
}
@end
Saturday, March 9, 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objective-cabeginnersdive-130309214601-phpapp01/85/Objective-C-A-Beginner-s-Dive-24-320.jpg)






![Example Category
// //
// NSString+Reverse.m // NSString+Reverse.h
// Category // Category
#import "NSString+Reverse.h" #import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import <stdlib.h>
@interface NSString (Reverse)
@implementation NSString (Reverse)
- (NSString *)reverse;
- (NSString *)reverse {
int length = [self length]; @end
char *newString =
! ! calloc(length+1, sizeof(char));
int current = 0;
const char *cstr = [self cString];
for (int i=length-1; i >= 0; i--) {
newString[current] = cstr[i];
current++;
}
NSString *new =
! ! [NSString stringWithCString:newString];
free(newString);
return new;
}
@end
Saturday, March 9, 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objective-cabeginnersdive-130309214601-phpapp01/85/Objective-C-A-Beginner-s-Dive-31-320.jpg)



![MyObject
// //
// MyObject.m // MyObject.h
#import "MyObject.h" #import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import "MyProtocol.h"
@interface MyObject ()
@property (assign, nonatomic) int myPrivateInt; @interface MyObject : NSObject <MyProtocol>
@end
@property (assign, nonatomic) int myInt;
@implementation MyObject
// default constructor
@synthesize myInt = _myInt; - (id)init;
@synthesize myPrivateInt = _myPrivateInt;
// custom constructor
- (id)init { - (id)initWithInt:(int)myInt;
return [self initWithInt:0];
} @end
- (id)initWithInt:(int)myInt {
if (self = [super init]) {
_myInt = myInt;
! ! _myPrivateInt = 5;
}
return self;
}
- (NSString *)stringMyInt {
return [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%d", _myInt];
}
@end
Saturday, March 9, 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objective-cabeginnersdive-130309214601-phpapp01/85/Objective-C-A-Beginner-s-Dive-35-320.jpg)

![Using MyObject
MyObject *obj = [[MyObject alloc] init];
obj.myInt = 5;
NSLog(@"%in", obj.myInt);
MyObject *other = [MyObject alloc];
other = [other initWithInt:5];
[other setMyInt:10];
NSLog(@"%in", [obj myInt]);
Saturday, March 9, 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objective-cabeginnersdive-130309214601-phpapp01/85/Objective-C-A-Beginner-s-Dive-37-320.jpg)
![Using MyObject
• alloc class method
• use of init and
initWithInt: methods MyObject *obj = [[MyObject alloc] init];
obj.myInt = 5;
•
NSLog(@"%in", obj.myInt);
splitting up the alloc and
init method calls
MyObject *other = [MyObject alloc];
other = [other initWithInt:5];
• use of dot syntax and [other setMyInt:10];
NSLog(@"%in", [obj myInt]);
generated methods
• NSLog() for printing
messages to the console
Saturday, March 9, 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objective-cabeginnersdive-130309214601-phpapp01/85/Objective-C-A-Beginner-s-Dive-38-320.jpg)








![NSArray
• Immutable object array
• NSMutableArray for mutable arrays
• Object Literal Syntax
@[object1, object2, ..., objectN];
• Object Subscripting Syntax
array[0] = object;
id object = array[0];
Saturday, March 9, 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objective-cabeginnersdive-130309214601-phpapp01/85/Objective-C-A-Beginner-s-Dive-47-320.jpg)
![NSDictionary
• Immutable object dictionary
• NSMutableDictionary for mutable
• Object Literal Syntax
@{key1:value1, key2:value2, ...};
• Object Subscripting Syntax
dictionary[key] = object;
id object = dictionary[key];
Saturday, March 9, 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objective-cabeginnersdive-130309214601-phpapp01/85/Objective-C-A-Beginner-s-Dive-48-320.jpg)



![Forin Loops Example
NSArray *array = @[@1, @2, @3, @4, @5];
for (NSNumber *num in array) {
NSLog(@"%@", num);
}
for (id num in [array reverseObjectEnumerator]) {
NSLog(@"%@", num);
}
Saturday, March 9, 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objective-cabeginnersdive-130309214601-phpapp01/85/Objective-C-A-Beginner-s-Dive-52-320.jpg)
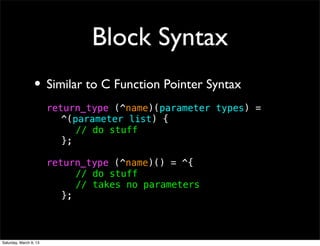
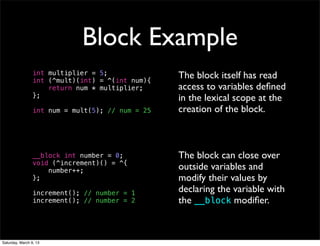


![Referencing Counting
• Nearly-Manual Memory Management
• Objects have a counter showing how many
references are using them
• Retain Objects when you receive them
[object retain];
• Release Objects when you’re done using them
[object release];
• Objects deallocate themselves when their retain
count reaches 0
Saturday, March 9, 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objective-cabeginnersdive-130309214601-phpapp01/85/Objective-C-A-Beginner-s-Dive-58-320.jpg)



