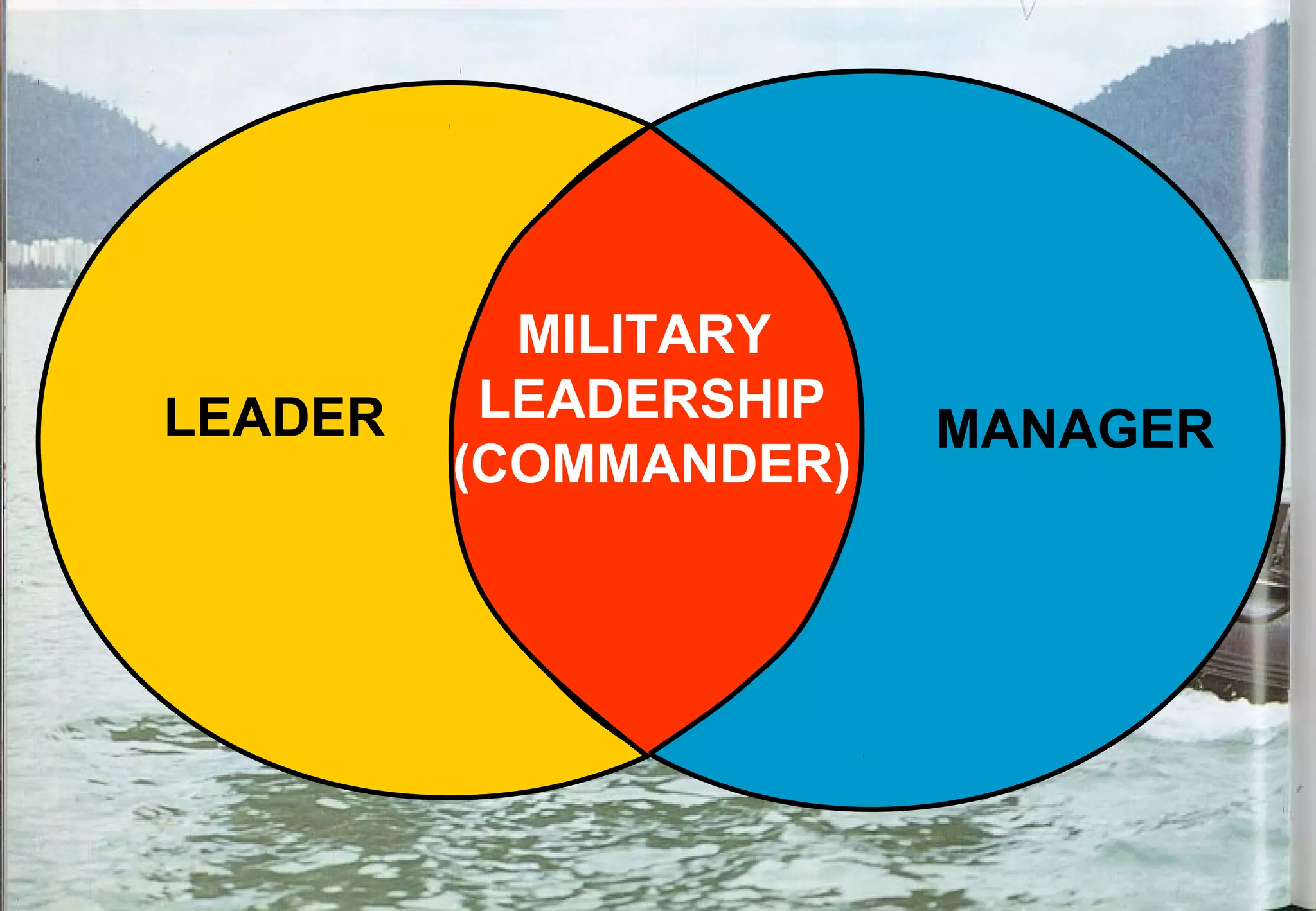
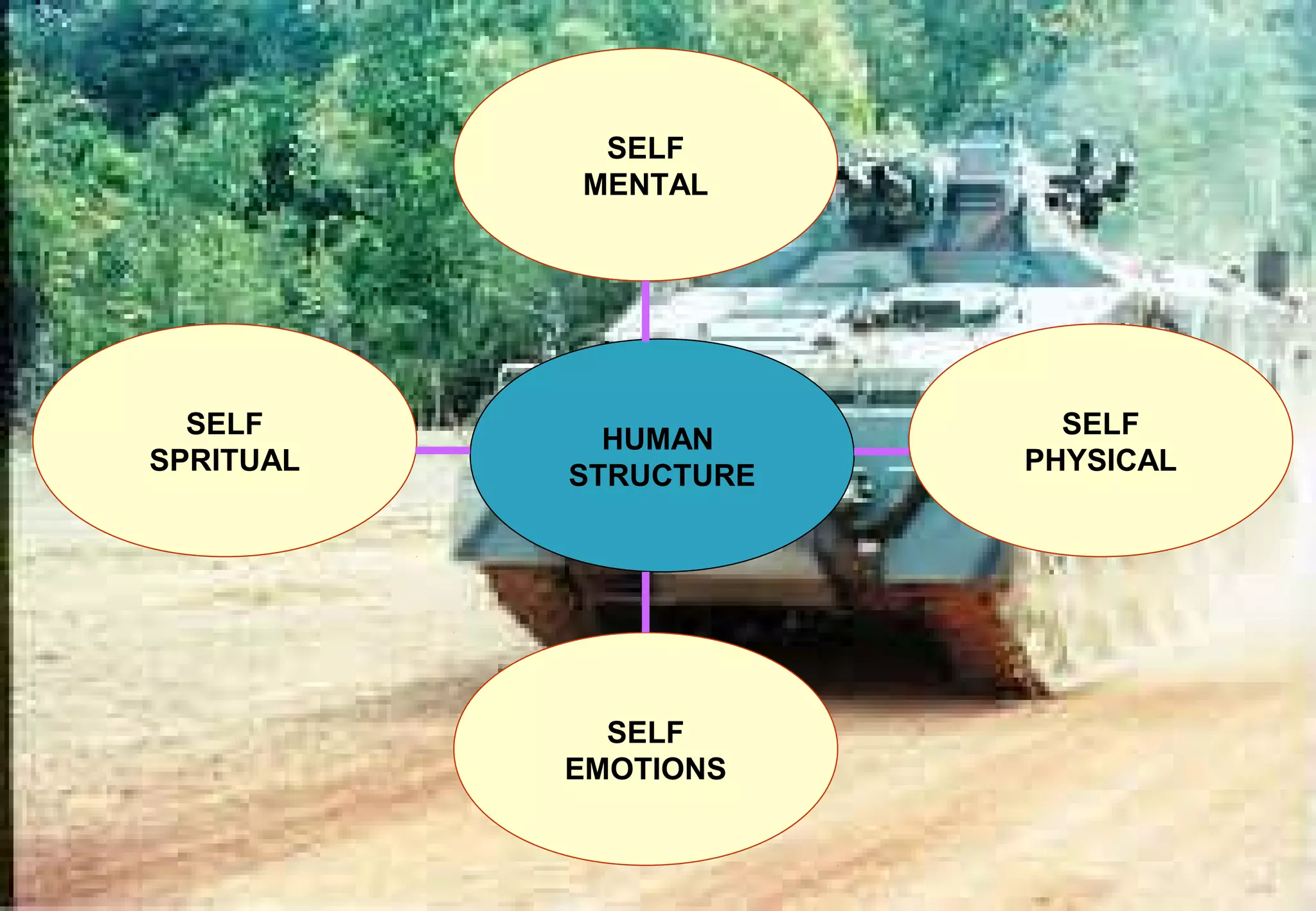
This document provides an overview of a course on military leadership given at the National Defence University of Malaysia. It introduces the lecturer, scope of the course, and key topics that will be covered such as the concepts of military leadership, qualities of an effective leader, and human motivation. The course will examine the differences between a leader and a manager in the military context and identify the traits and principles needed for effective military leadership.