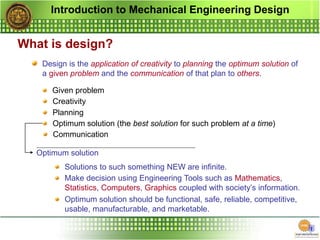
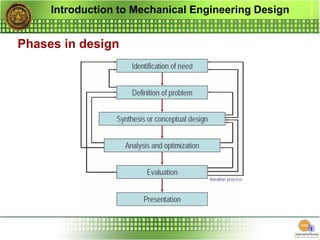
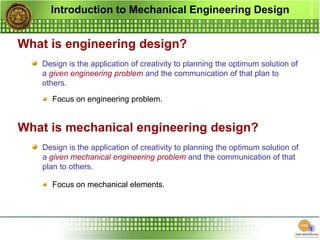
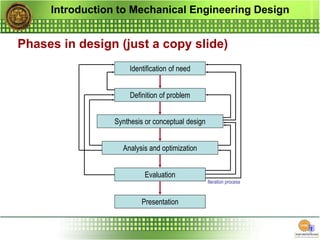
The document outlines the curriculum for a mechanical engineering design course, focusing on design principles, materials, stress and strength analysis, and the iterative nature of the design process. It emphasizes the importance of creativity, communication, and considerations such as functionality, safety, and marketability in engineering design. Additionally, it discusses the tools and methodologies involved in achieving optimal engineering solutions.