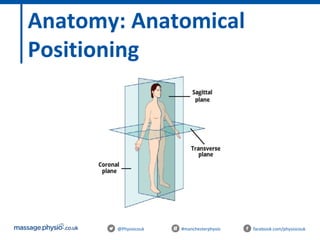
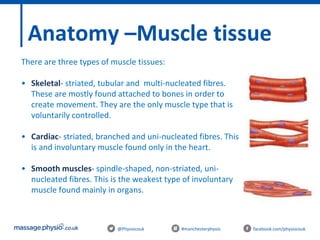
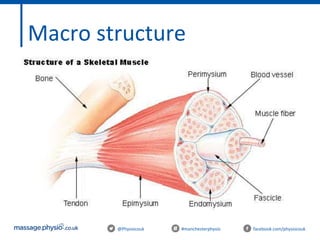
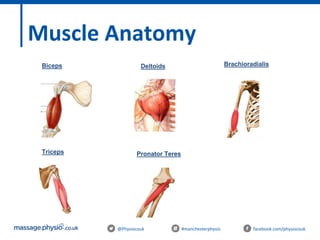
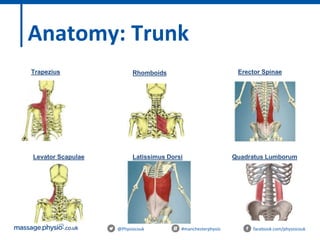
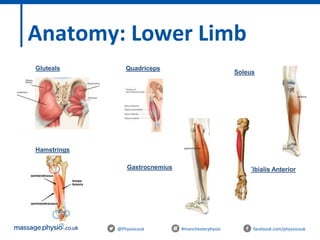
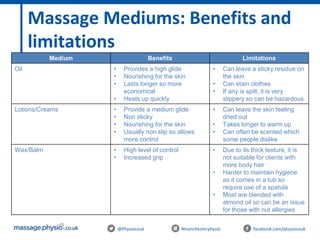
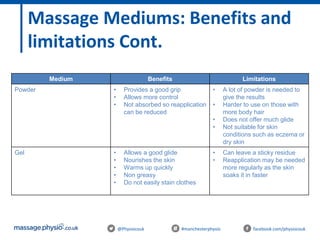
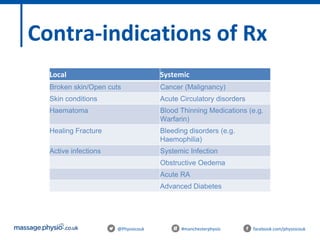
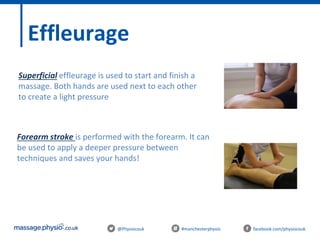
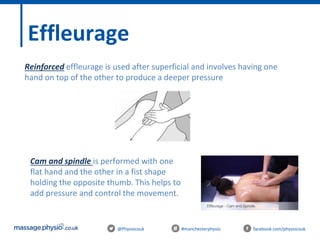
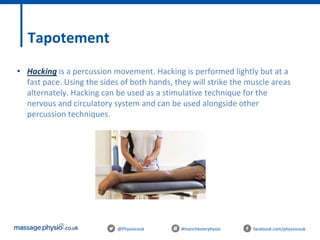
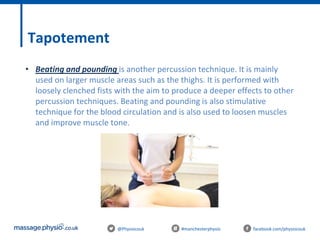
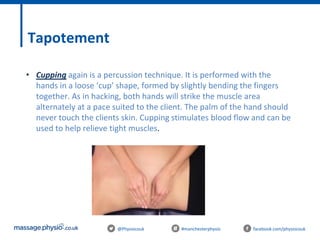
The document provides an introduction to massage therapy. It discusses the history of massage dating back to ancient cultures, outlines the aims of the course which include learning anatomy, contraindications, techniques and demonstrating techniques. It then covers massage theory including anatomical positioning, terminology, the muscular system, and benefits of massage such as physical relaxation and reduced pain as well as psychological benefits like reduced stress and anxiety. Techniques and different areas of the body that will be massaged are also mentioned.