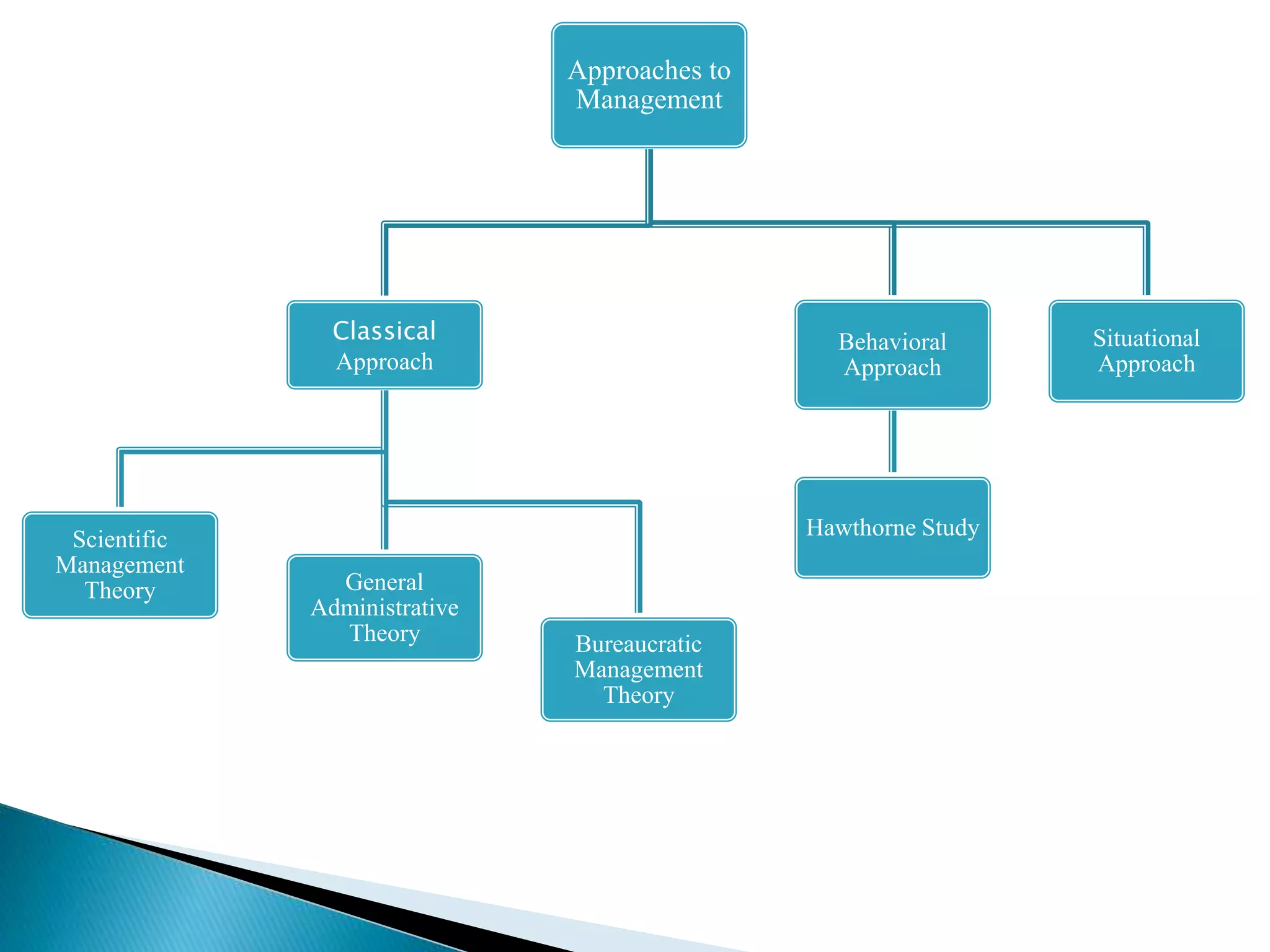
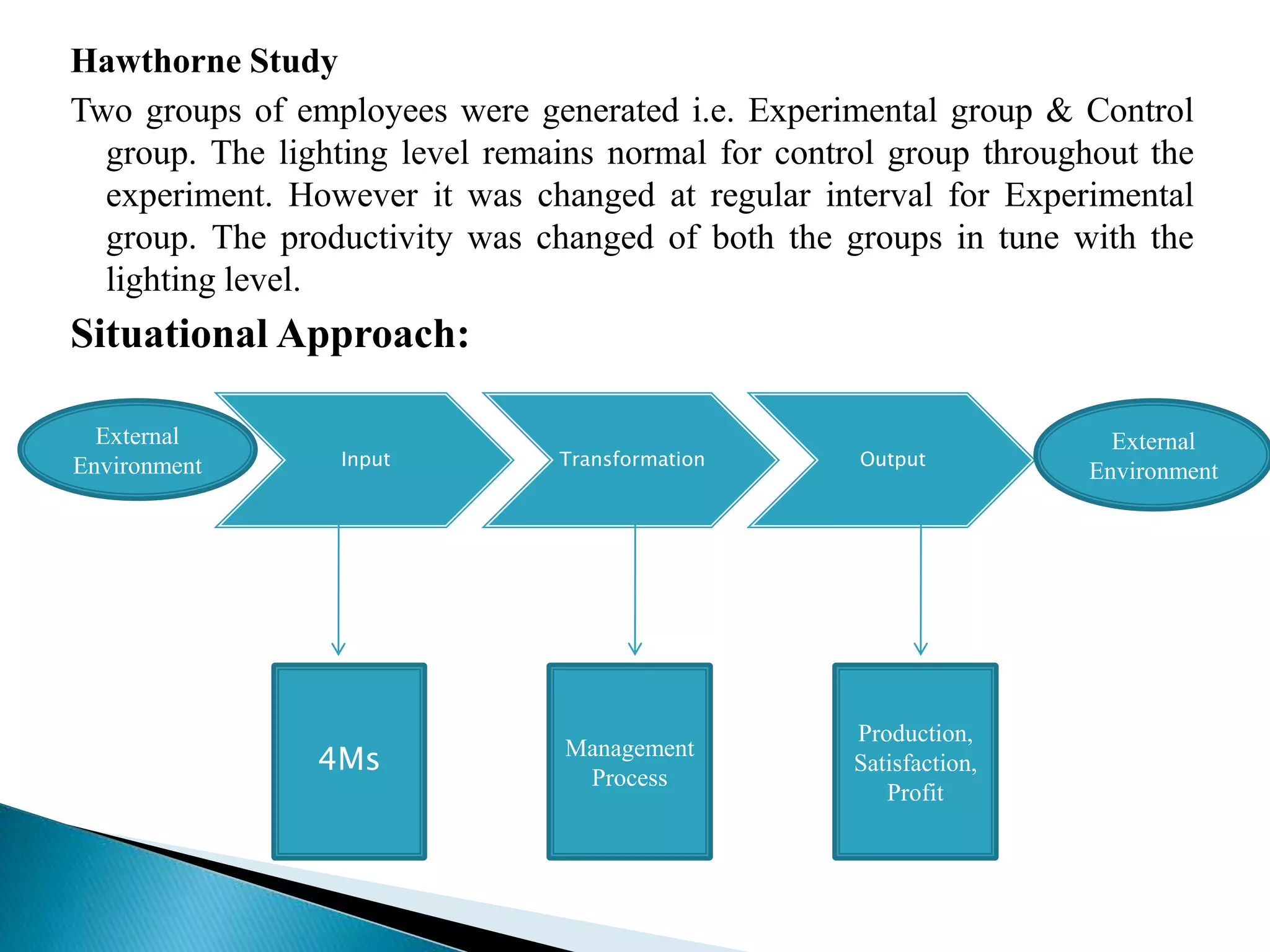
The document discusses the definition, principles, approaches, and responsibilities of management. It defines management as the process of coordinating work activities through other people to efficiently achieve organizational goals. Several classical and behavioral approaches to management are described, including scientific management and Hawthorne studies. The roles and social responsibilities of managers are outlined as well, such as responsibilities to owners, employees, customers, government, and the public.