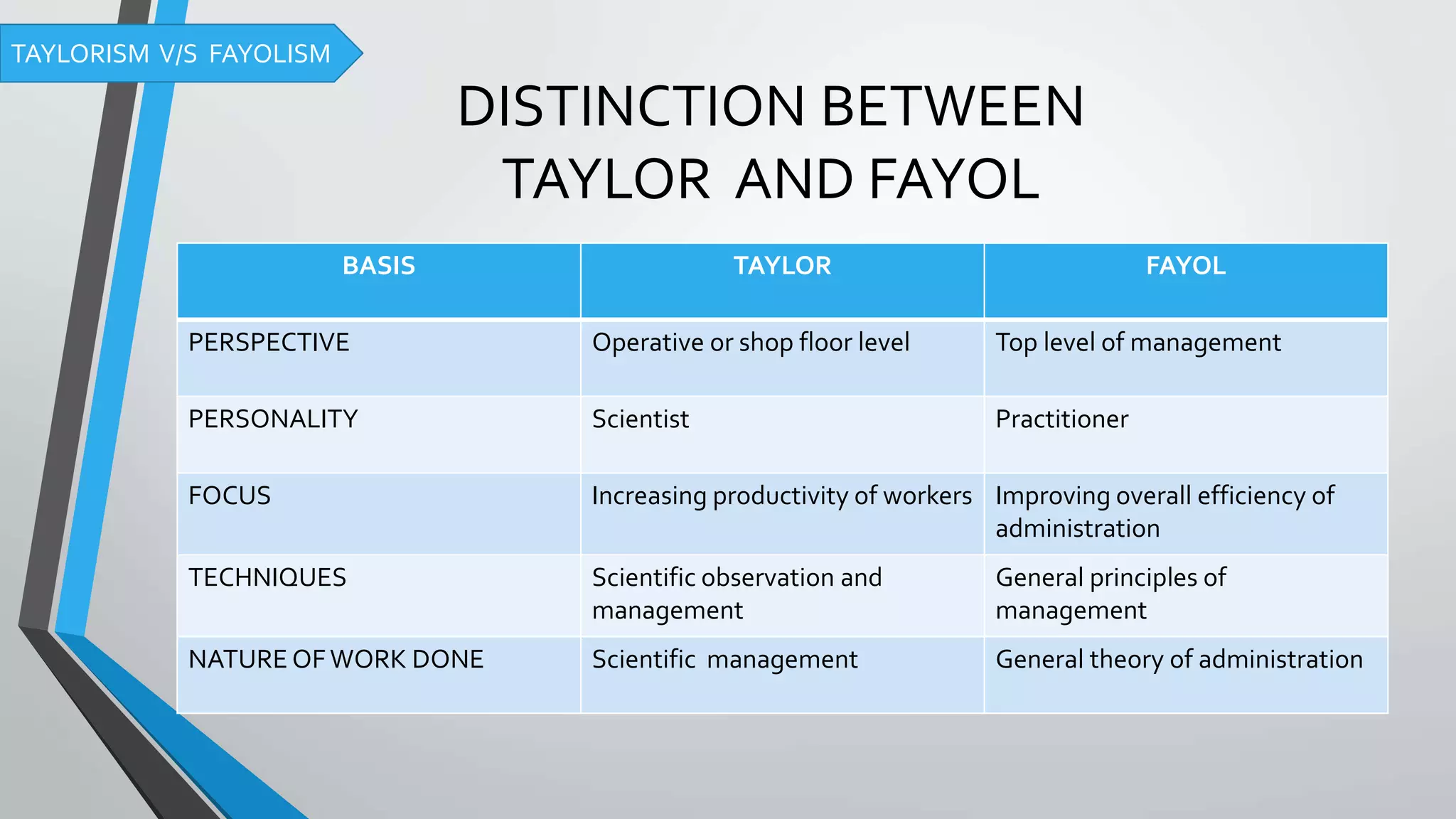
Taylorism and Fayolism are two classical management theories. Taylorism, developed by Frederick Winslow Taylor, focuses on scientific management and increasing worker productivity through methods like time and motion studies. Fayolism, developed by Henri Fayol, provides a more general framework for management including five primary functions and fourteen principles of administration to improve overall efficiency. The theories differ in their focus, with Taylorism aimed at the production/shop floor level and Fayolism at the top management level.