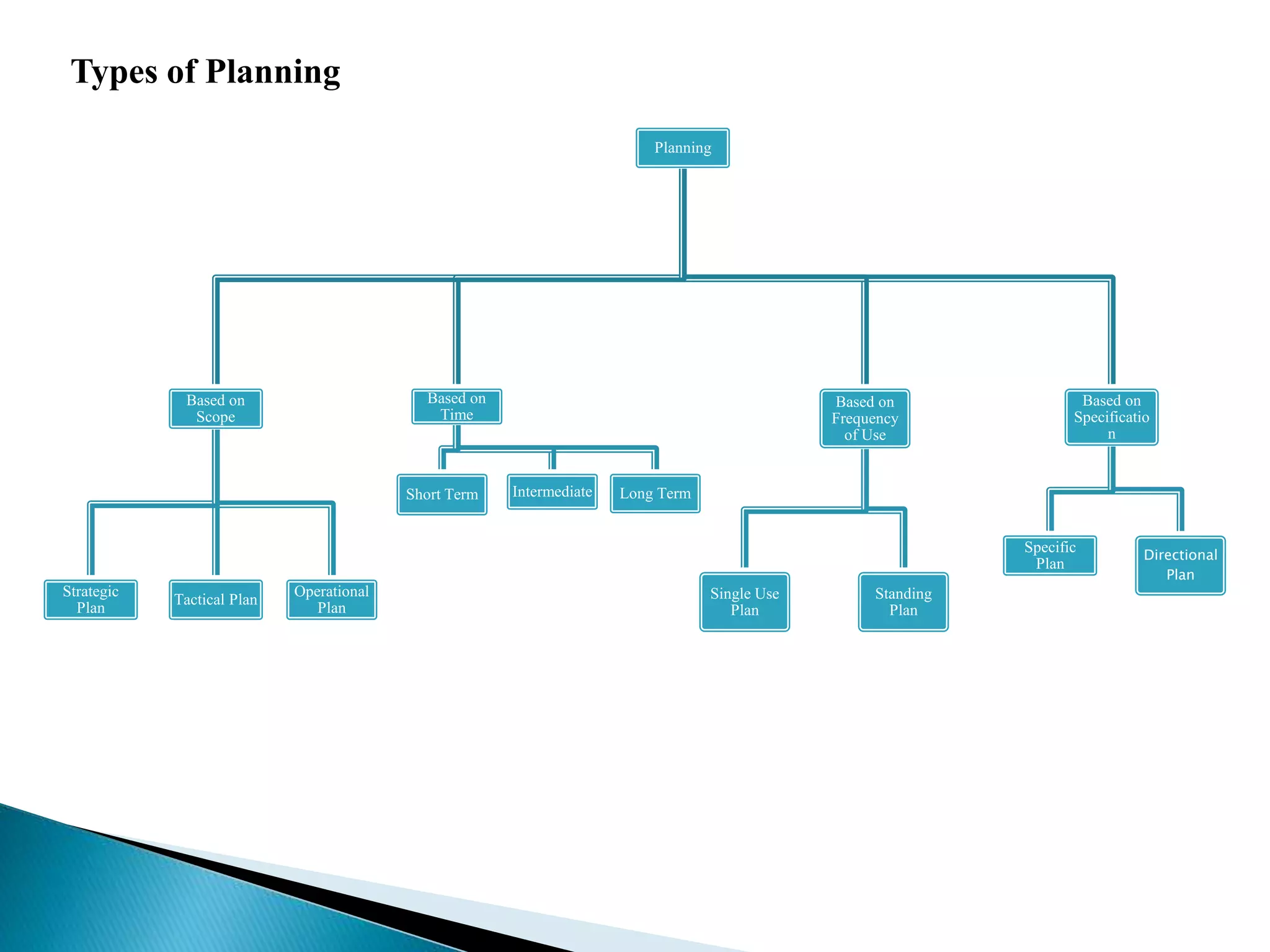
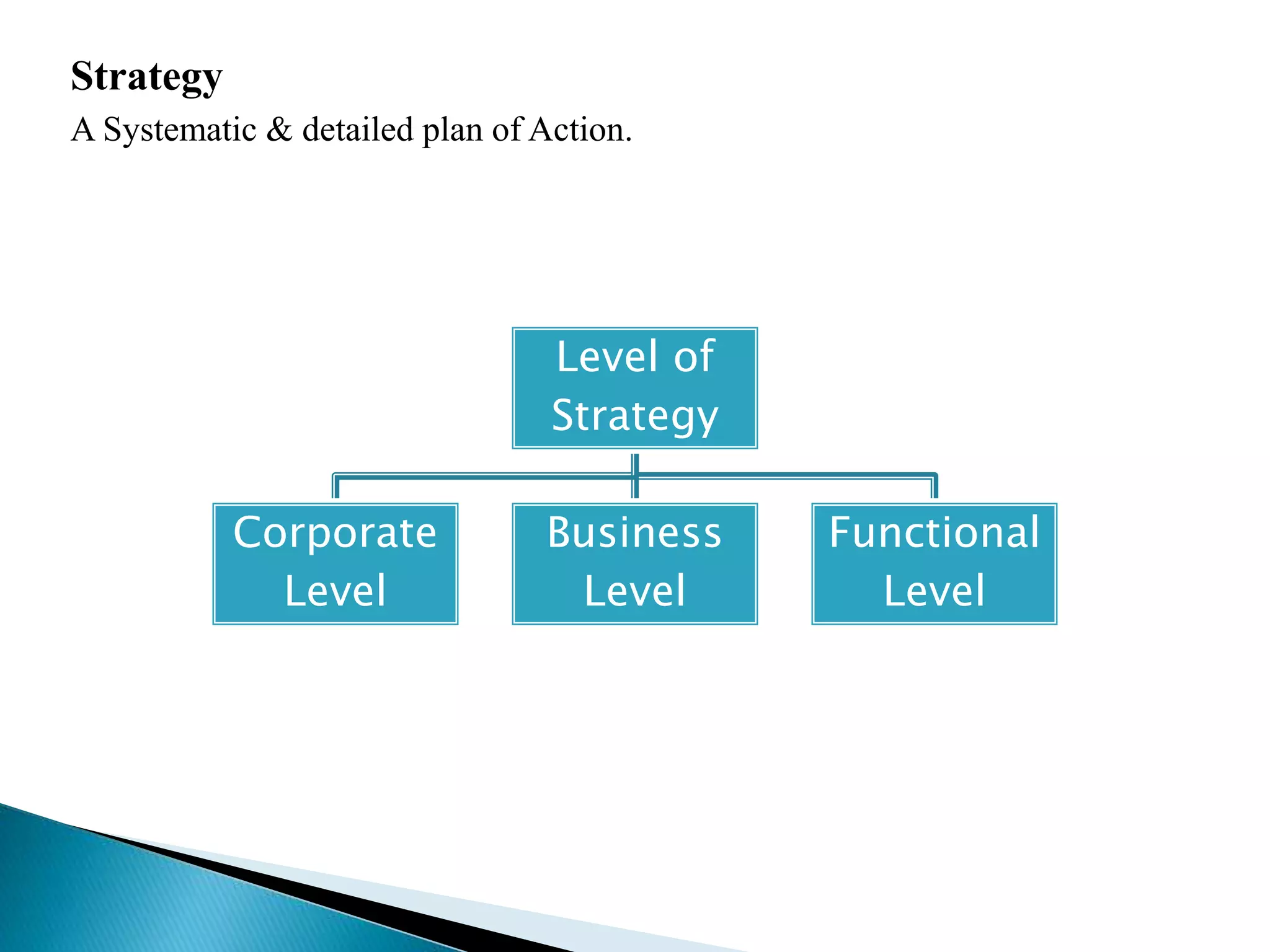
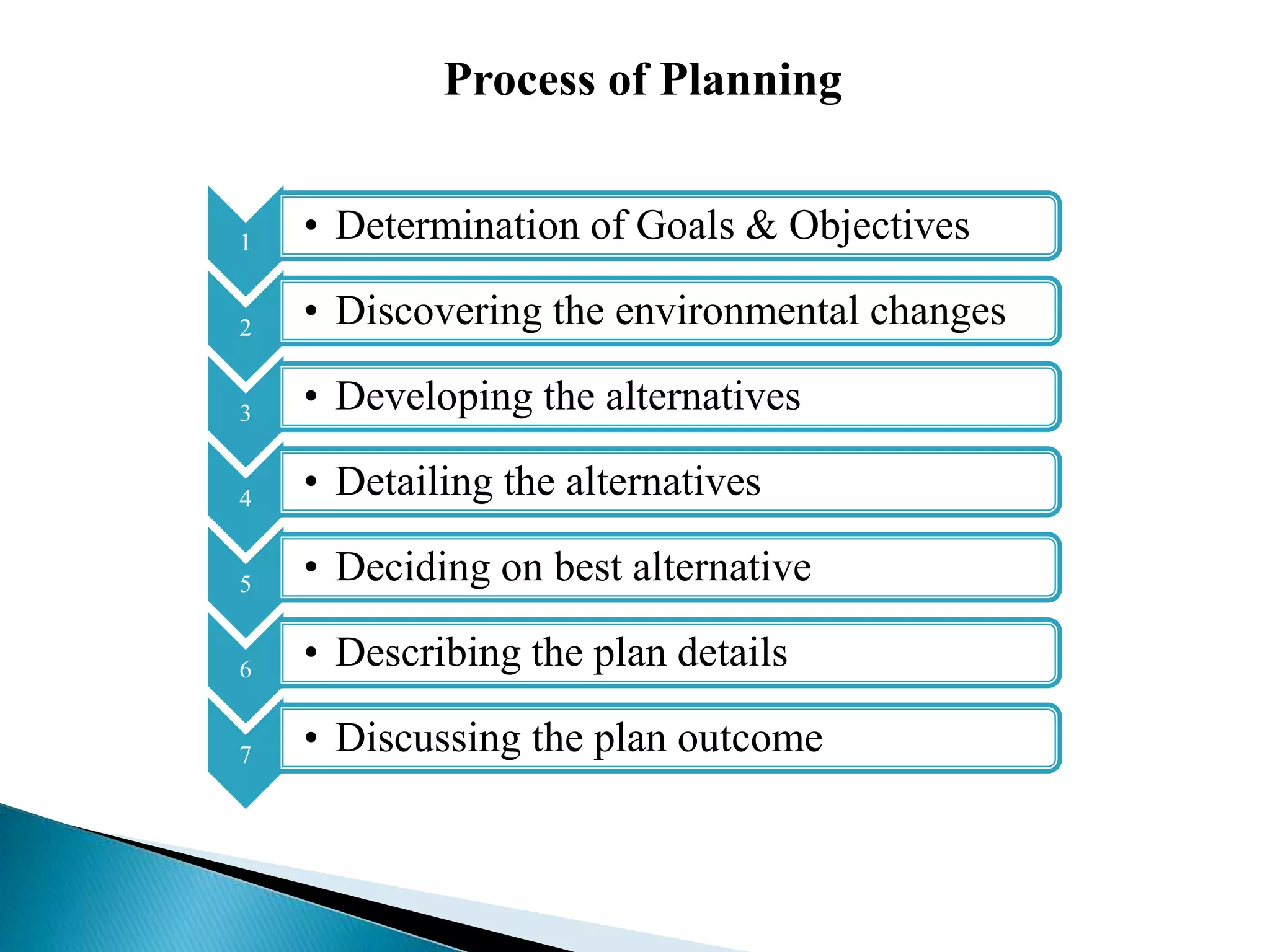
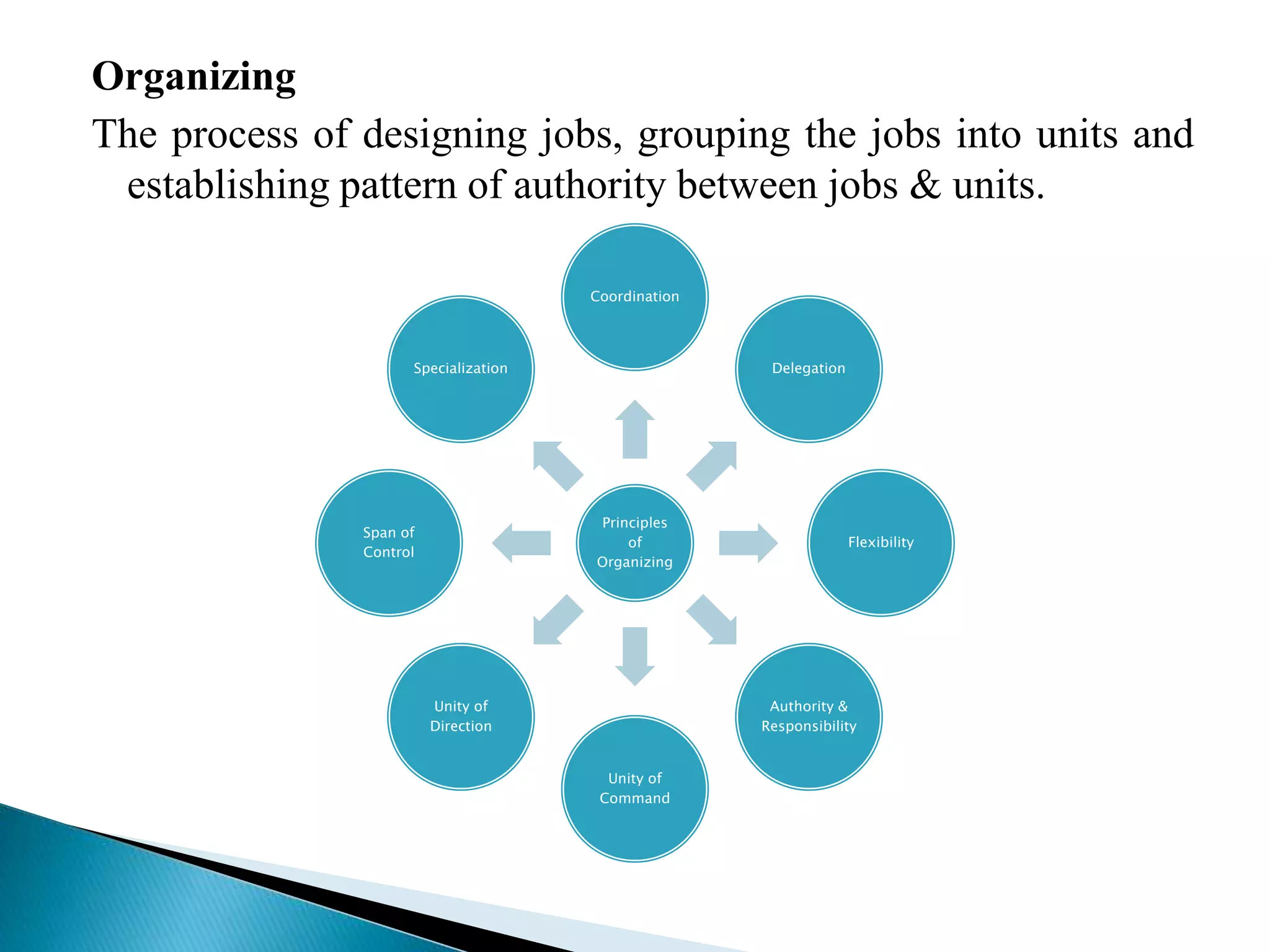
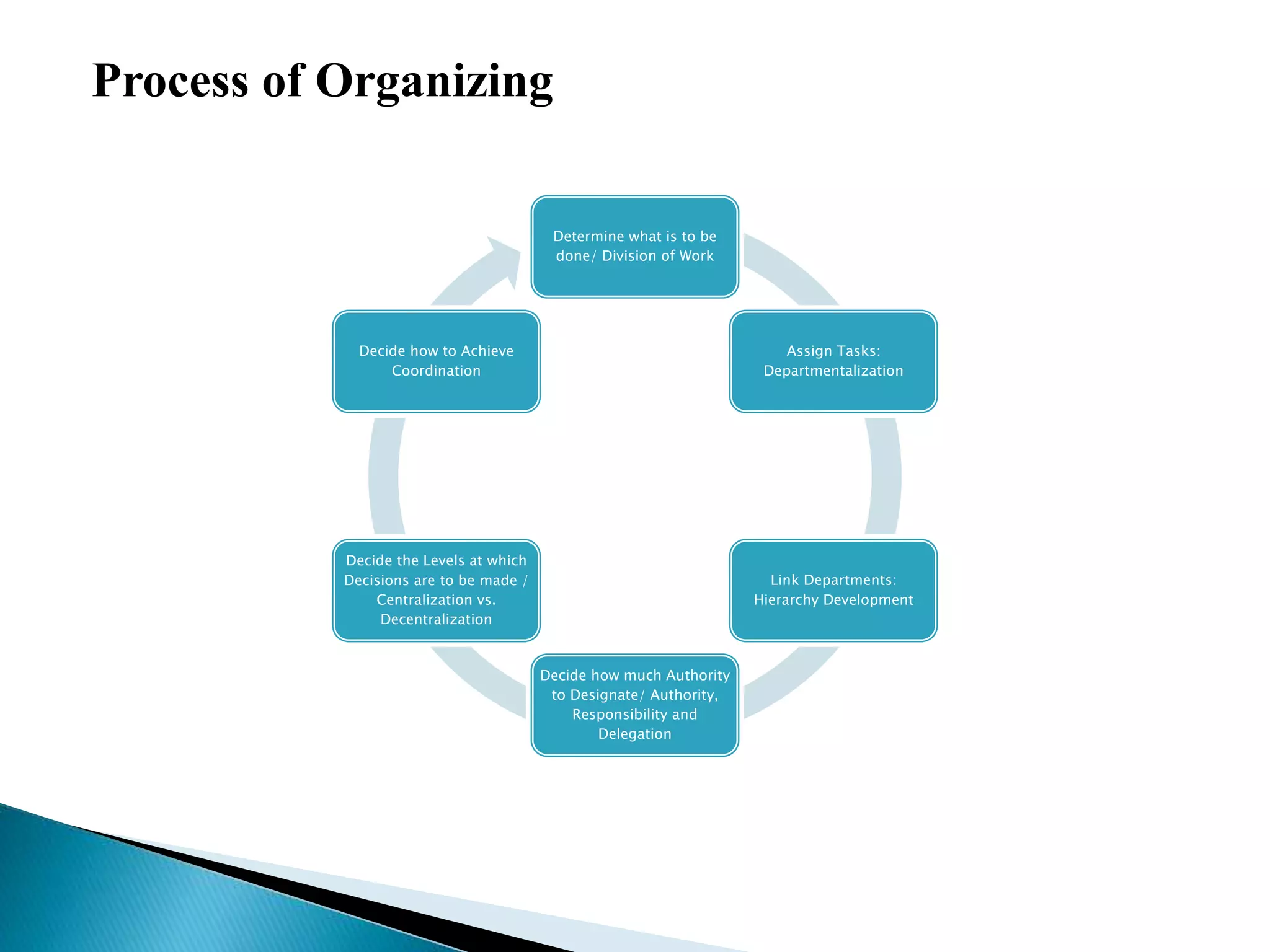
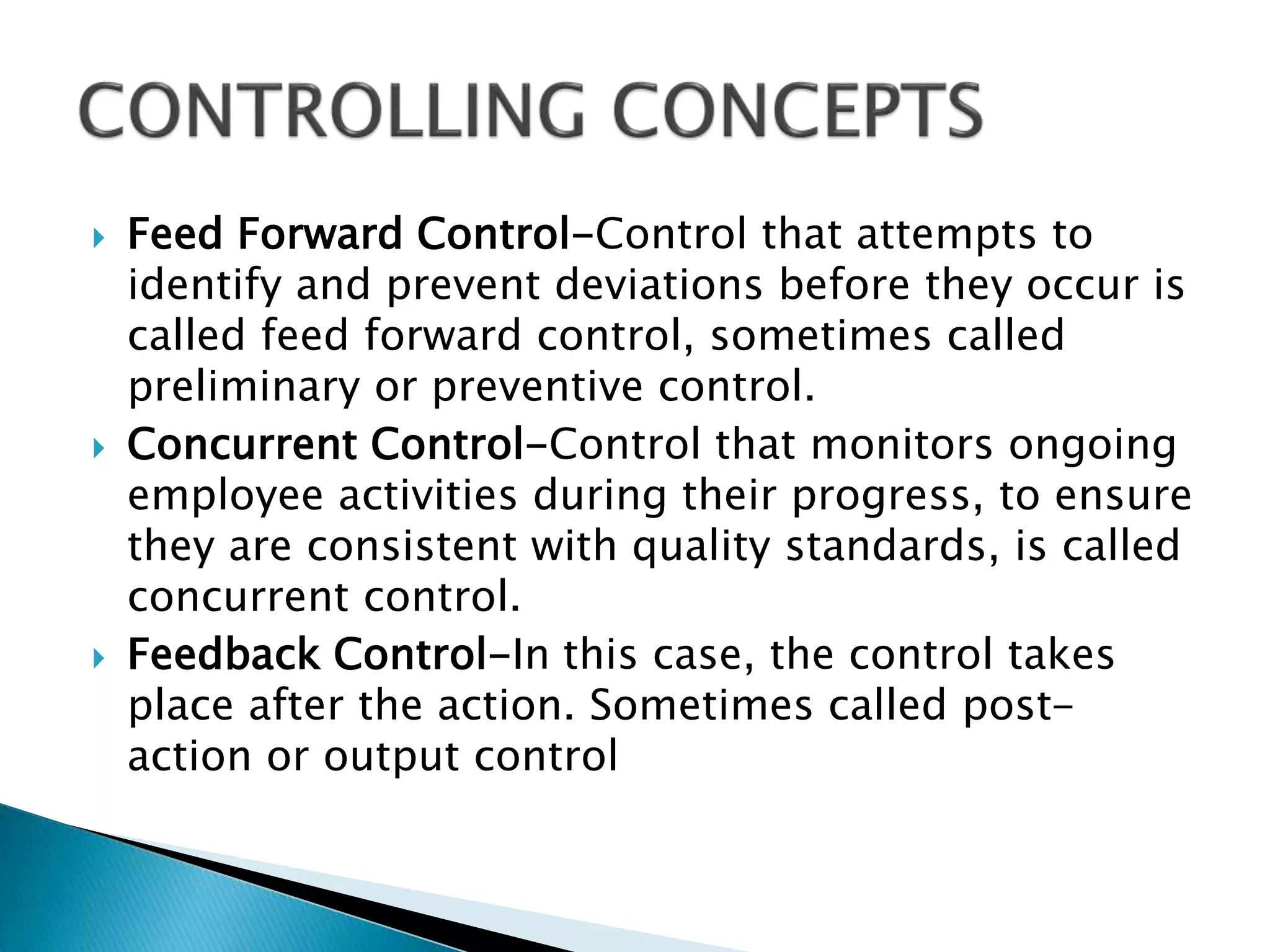
The document discusses the key concepts of management by objective (MBO). It explains MBO as a formal process that establishes common goals for managers and subordinates and reviews progress toward those goals. The steps in MBO are outlined as establishing long and short-term organizational and individual objectives, periodic performance reviews, and encouraging manager responsibility. Benefits of MBO include planning, accountability, participative management, job enrichment, and feedback.