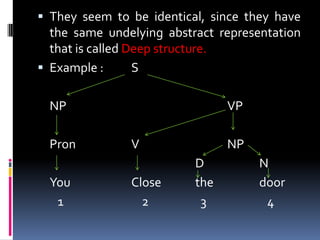
The document introduces the topic of syntax, which is the study of the principles and rules for how words are combined to form phrases, clauses, and sentences in a language. It discusses word categories, phrase and clause structure, sentence structure types including simple, compound, complex, and compound-complex sentences. The document also covers the difference between surface structure, the syntactic form of sentences, and deep structure, the underlying abstract representation.