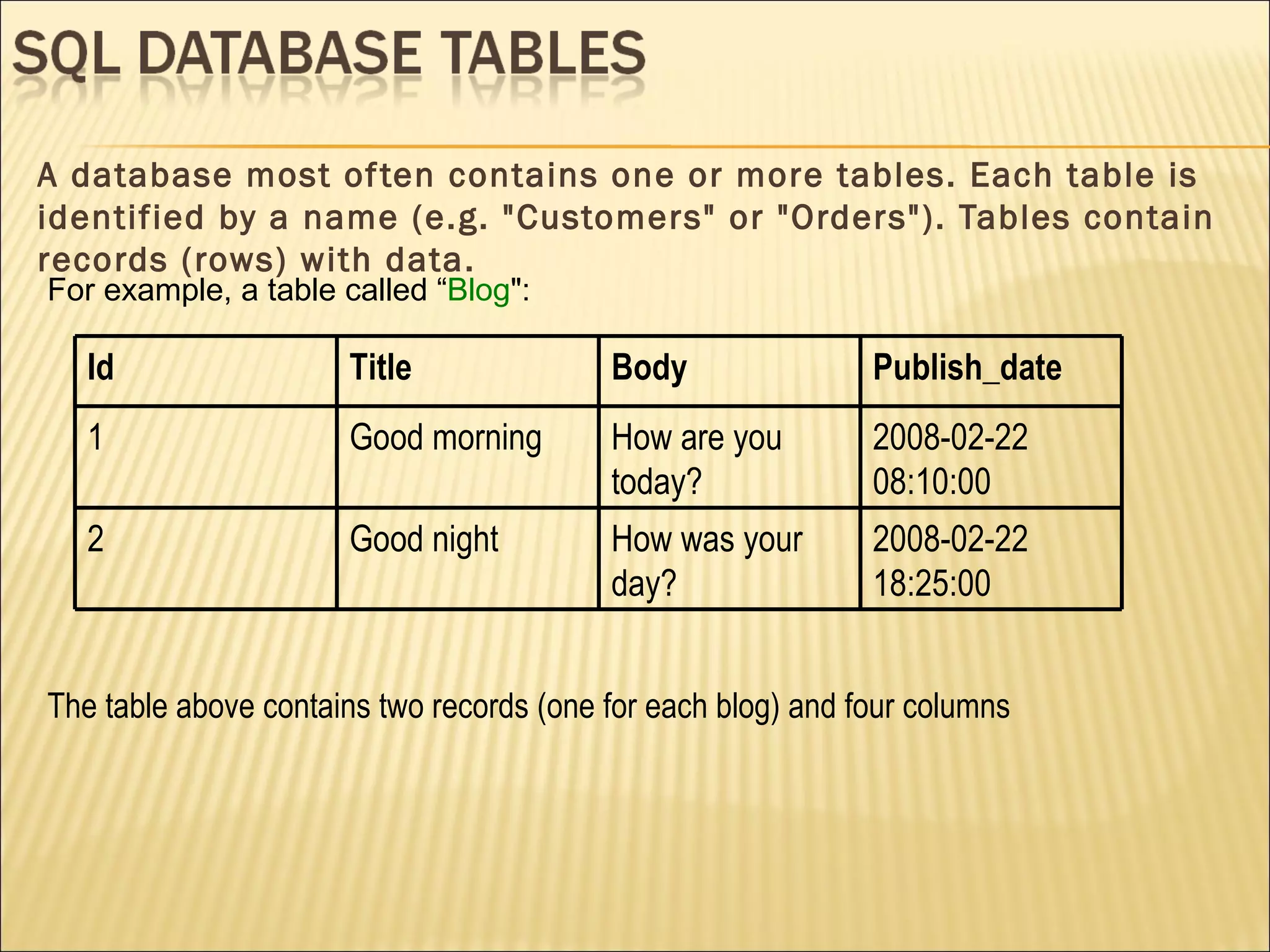
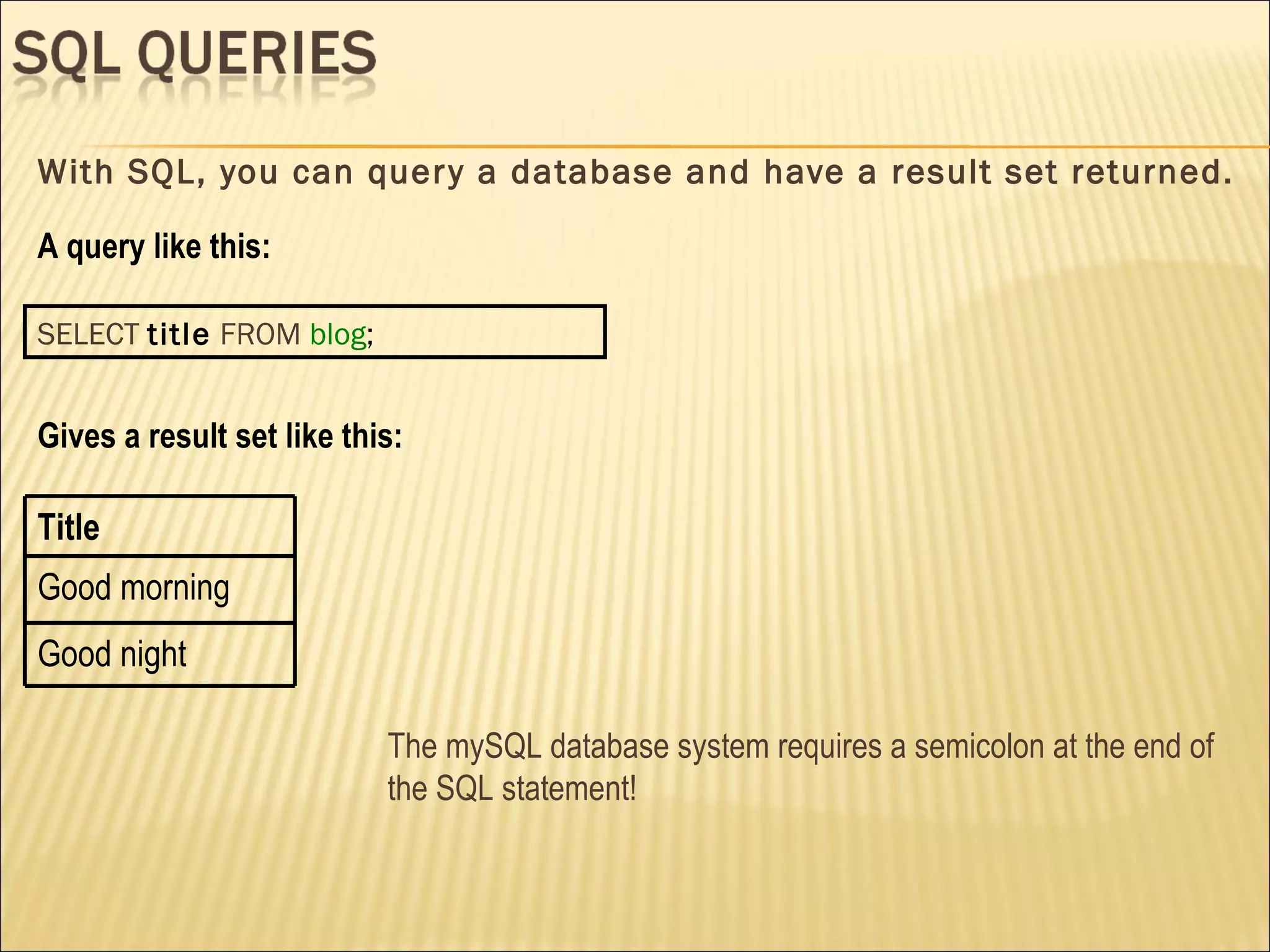
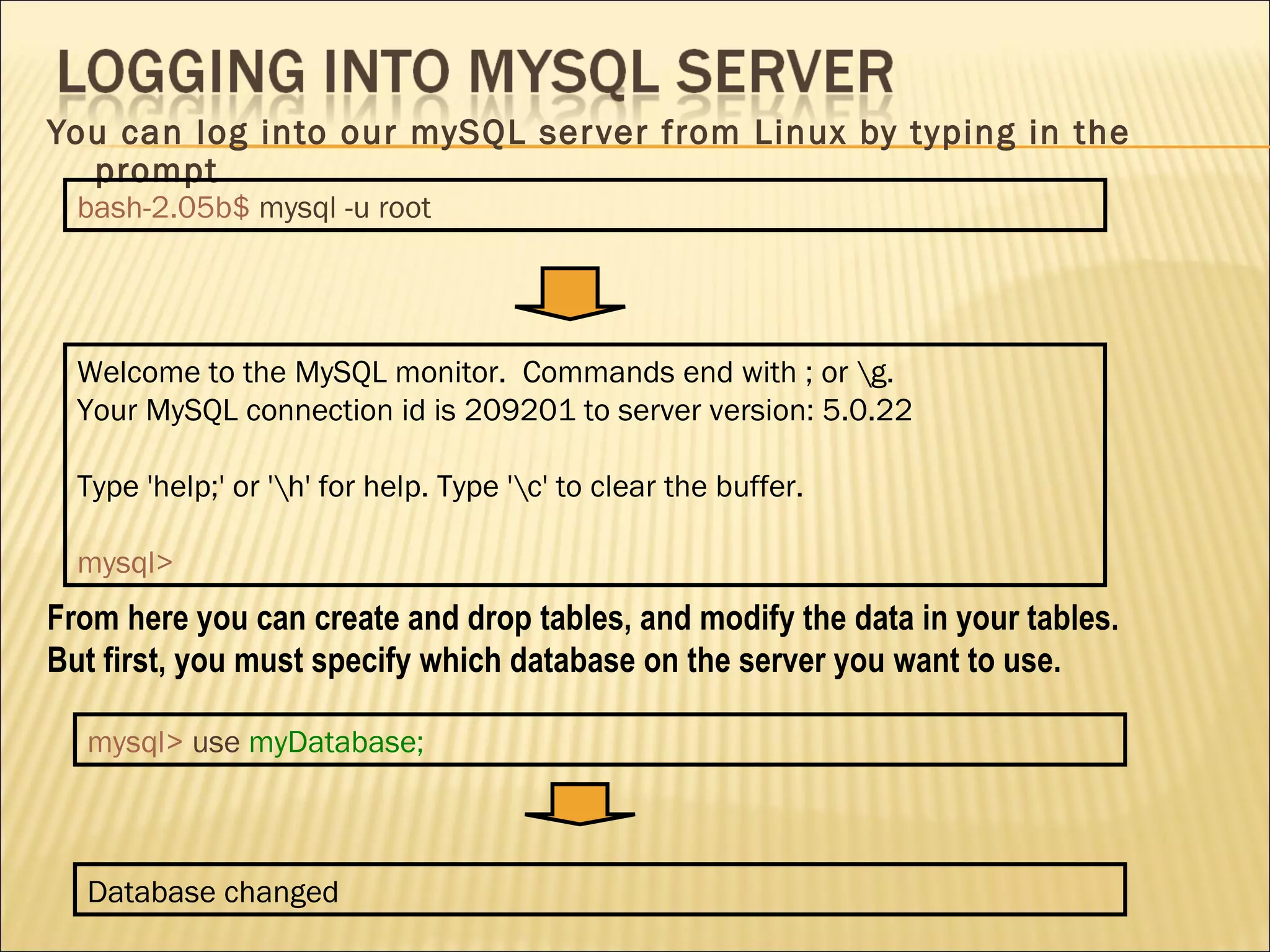
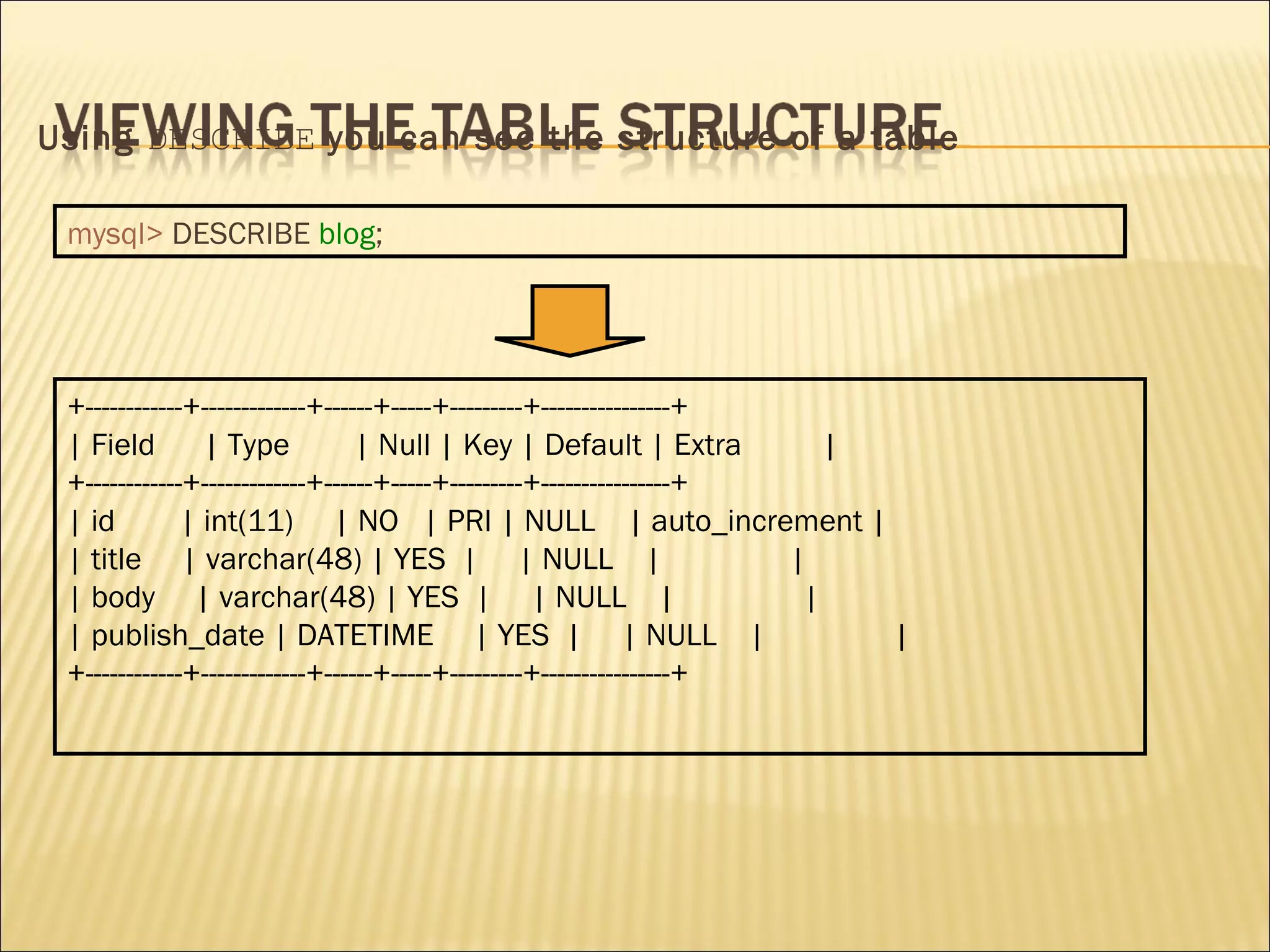
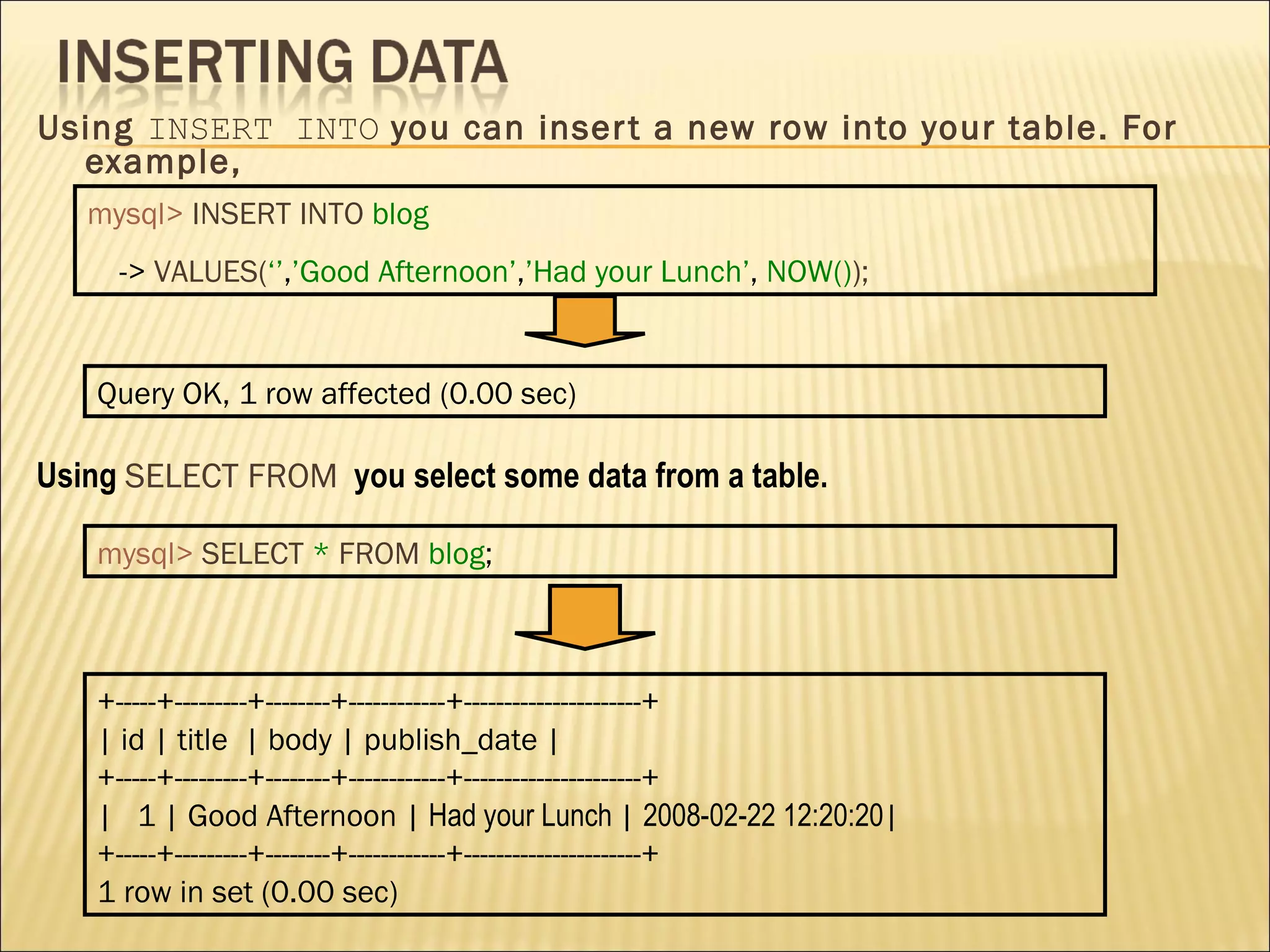
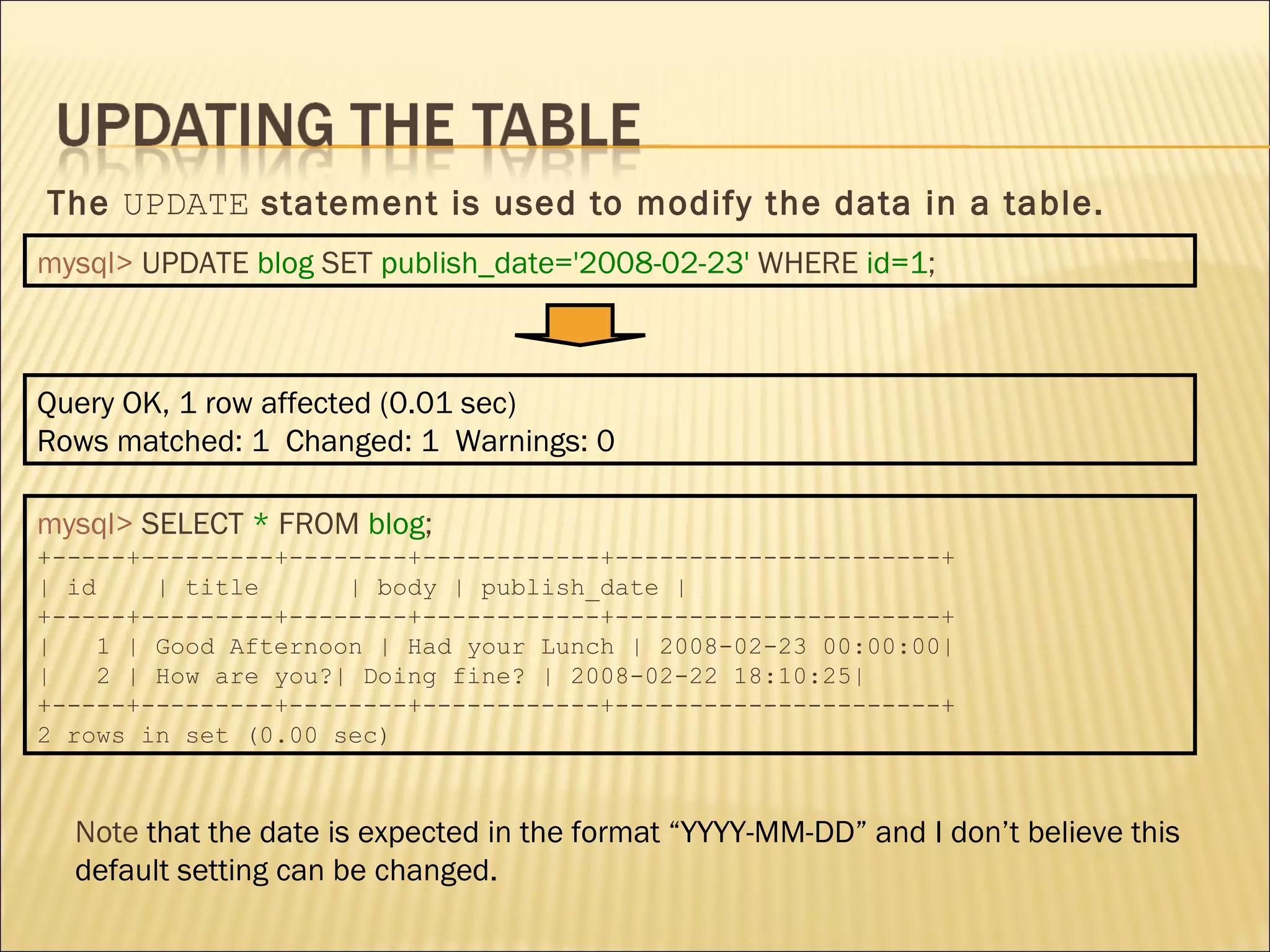
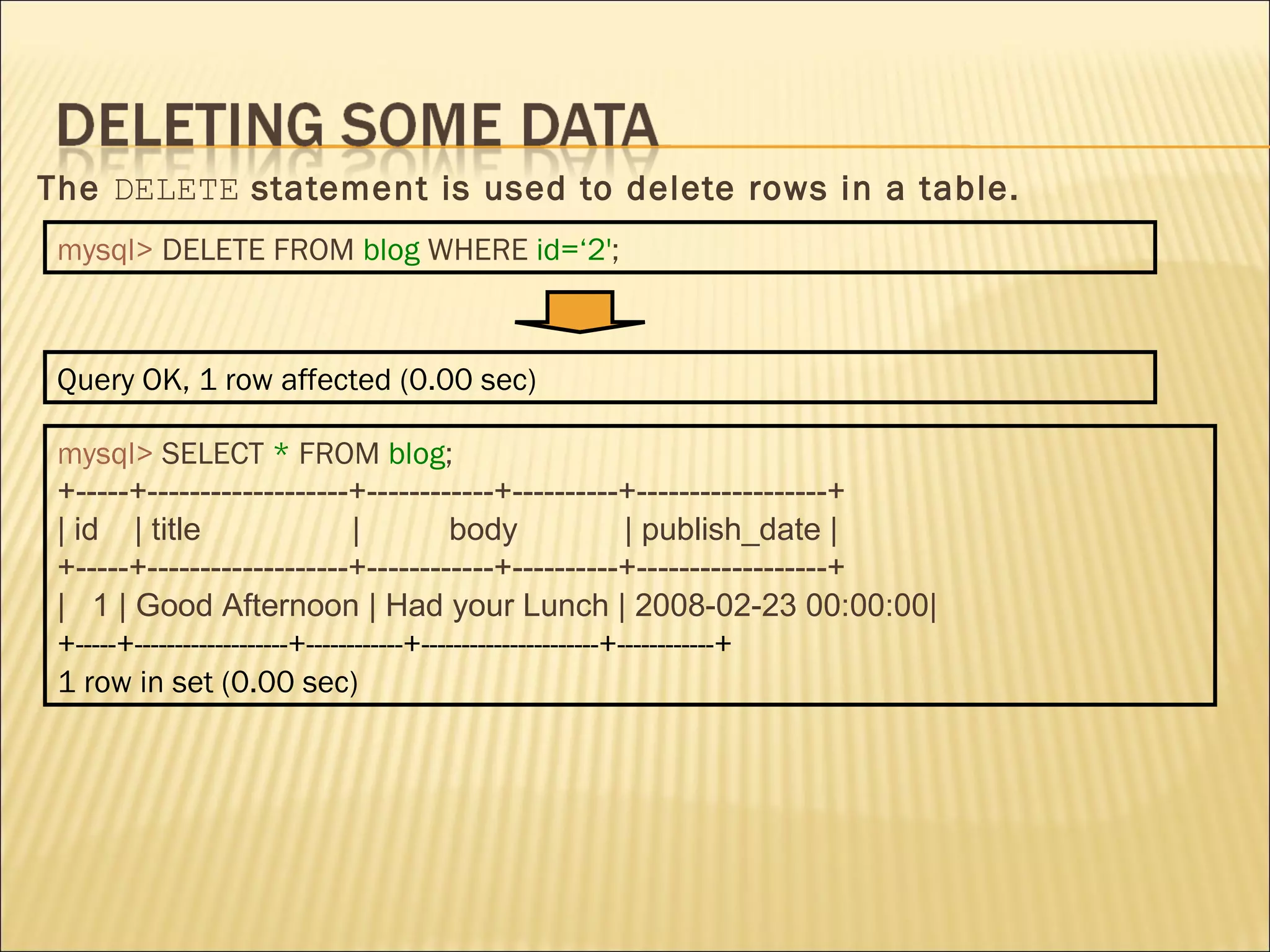
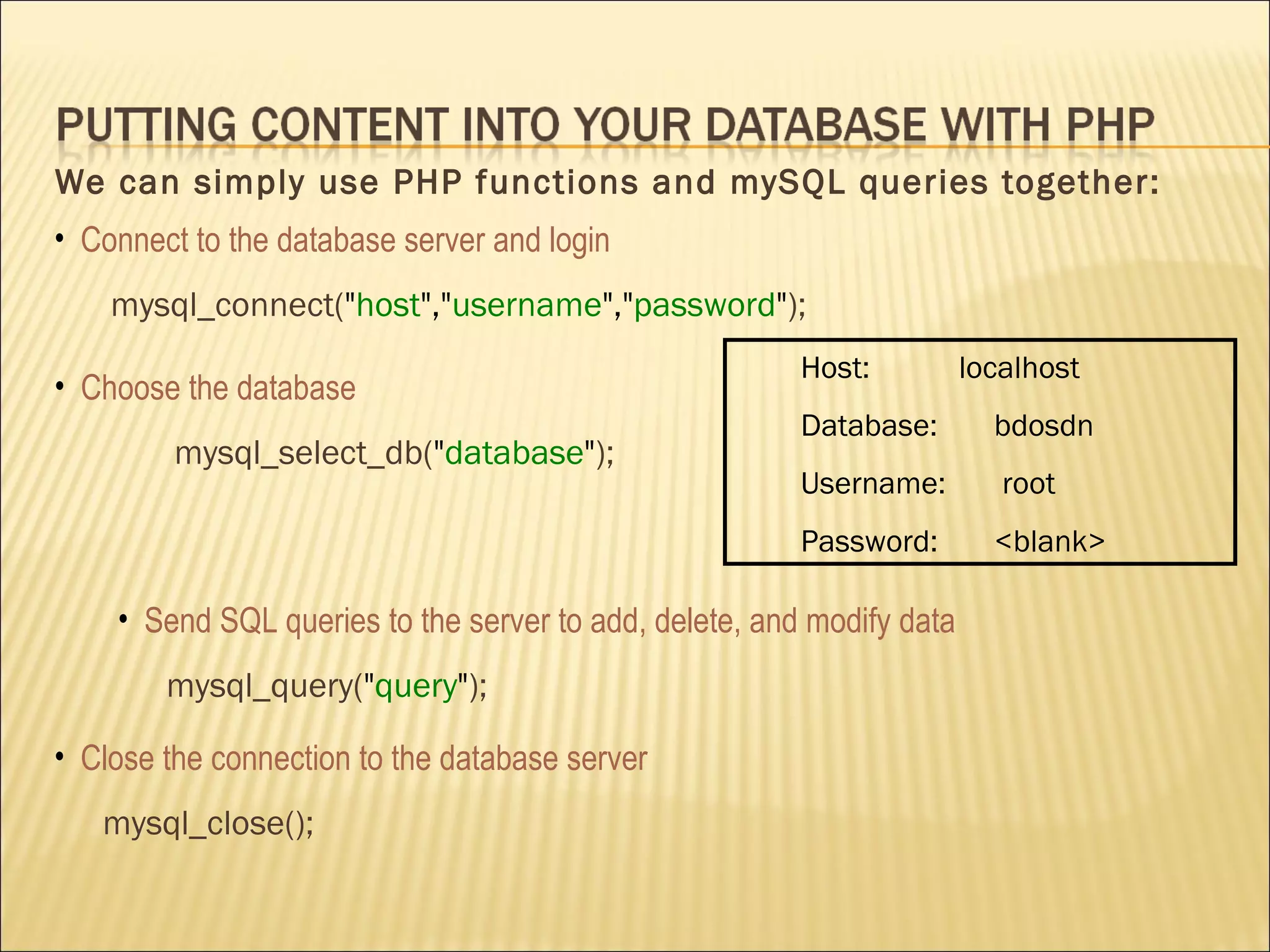
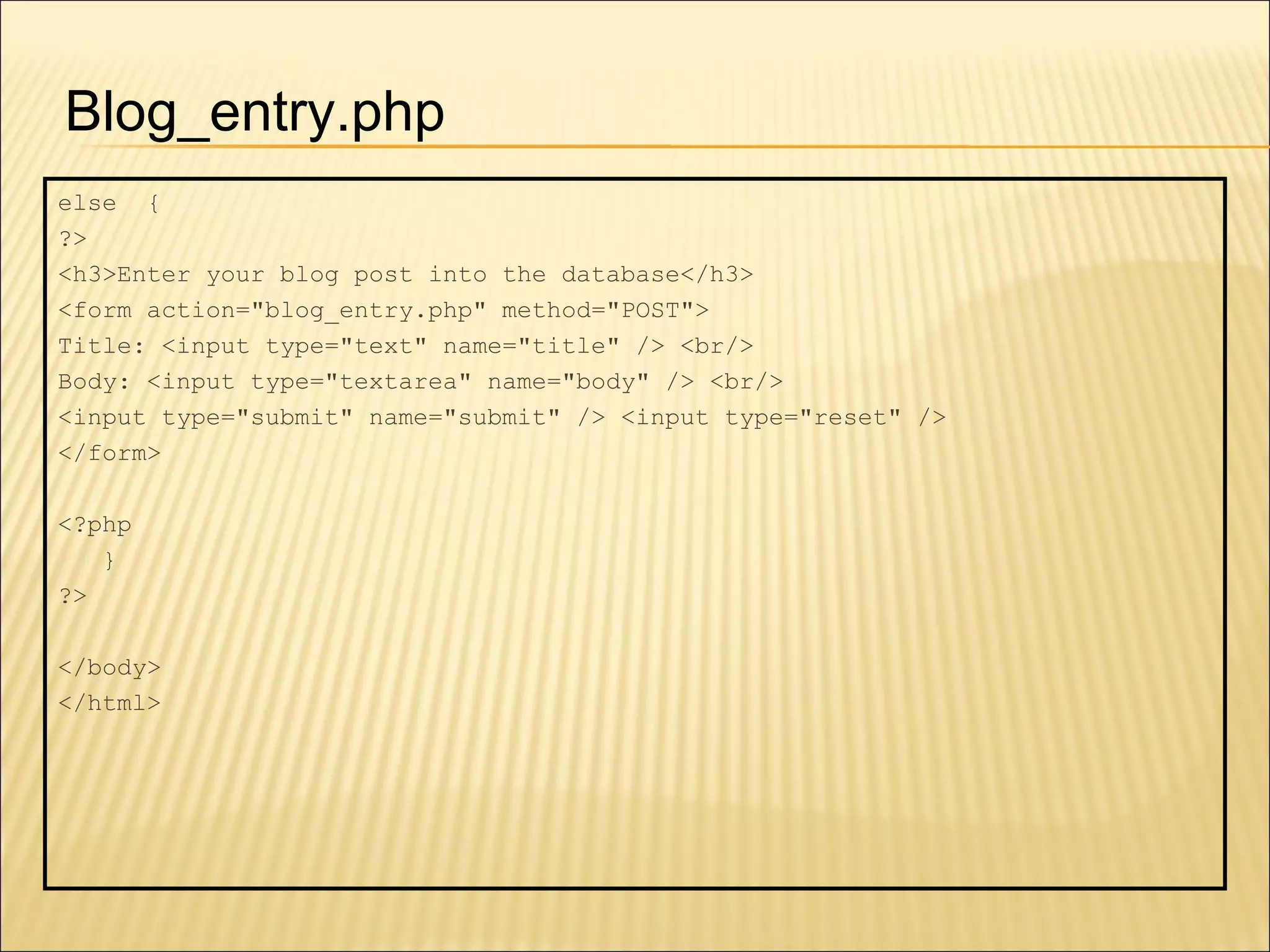
The document discusses SQL and how to interact with databases using SQL. It provides examples of using SQL commands like CREATE TABLE, INSERT, SELECT, UPDATE, and DELETE to structure and manipulate a database. It also shows how to connect to a MySQL database from the command line or using PHP scripts to execute SQL queries and retrieve/modify data in the database.
![Muhammad Abdur Rahman AdnaN jhoroTEK.com [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-lamp-p2-1234254906877169-3/75/Introduction-To-Lamp-P2-1-2048.jpg)







![<html> <head> <title>Putting Data in the DB</title> </head> <body> <?php /*insert blogs into DB*/ if(isset($_POST["submit"])) { $db = mysql_connect("localhost", "root", "root") or die('DB connection error!'); mysql_select_db("bdosdn"); $date=date("Y-m-d"); /* Get the current date in the right SQL format */ $sql="INSERT INTO blog VALUES('','" . $_POST["title"] . "','" . $_POST["body"] . "', NOW())"; /* construct the query */ mysql_query($sql); mysql_close(); echo"<h3>Thank you. The data has been entered.</h3> \n"; echo'<p><a href="blog_entry.php">Back to post</a></p>' . "\n"; echo'<p><a href="blog_view.php ">View the blog lists</a></p>' ."\n"; } Blog_entry.php](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-lamp-p2-1234254906877169-3/75/Introduction-To-Lamp-P2-18-2048.jpg)

![<html> <head> <title>Getting Data out of the DB</title> </head> <body> <h1> Blog Database </h1> <?php /*get blog from the DB */ $db = mysql_connect("localhost", "root", "root") or die('DB connection error!'); mysql_select_db("bdosdn", $db); $sql = "SELECT * FROM blog ORDER BY id desc"; $result=mysql_query($sql); while($row=mysql_fetch_array($result)){ echo "<h4> Title: " . $row["title"] . "</h4> \n"; echo "<h5> Publish Date: " . $row["publish_date"] . "<br/> Body: " . $row["body"] . "</h5> \n"; echo '<hr>'; } mysql_close(); ?> </body> </html> Blog_view.php](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-lamp-p2-1234254906877169-3/75/Introduction-To-Lamp-P2-21-2048.jpg)


