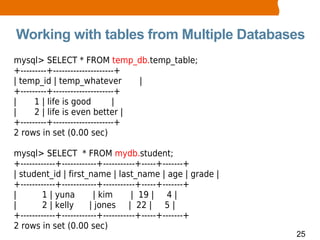
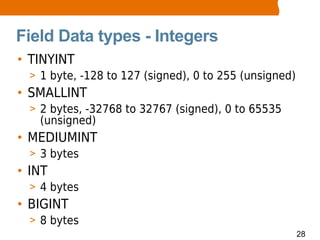
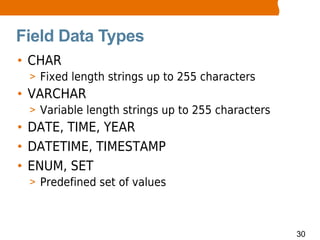
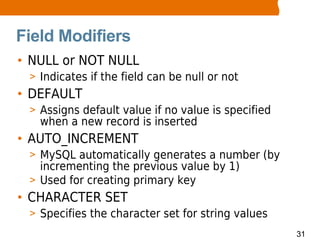
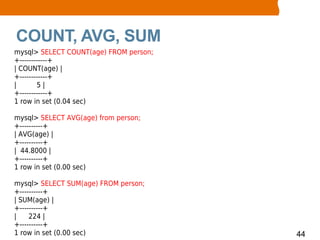
This document provides an overview of MySQL basics including what MySQL is, installing the MySQL server, using the mysql command line client, SQL basics like concepts and terminology for databases, tables and fields, and performing operations like insert, update, delete and select. It also covers retrieving records with select through ordering, limiting and arithmetic functions. The document concludes by explaining how to read and execute SQL statements from a script file.