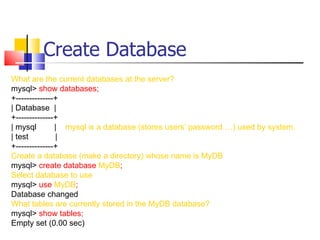
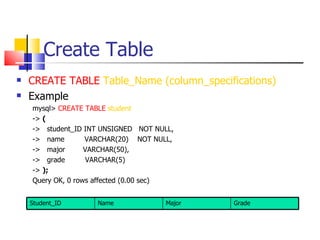
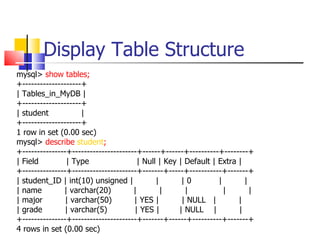
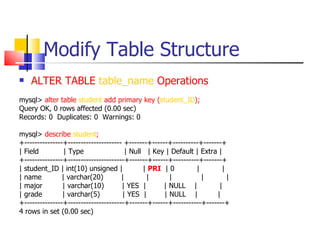
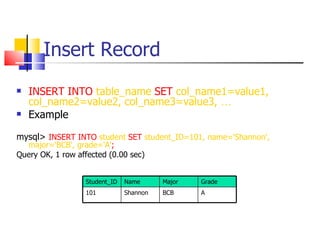
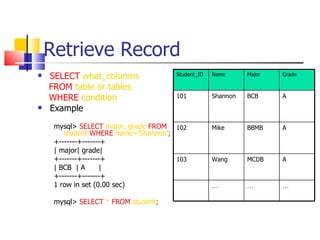
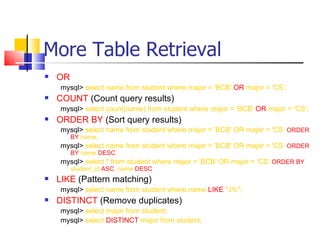
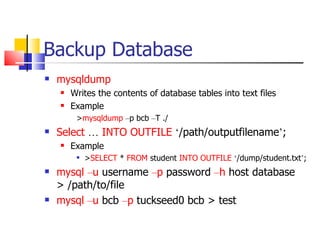
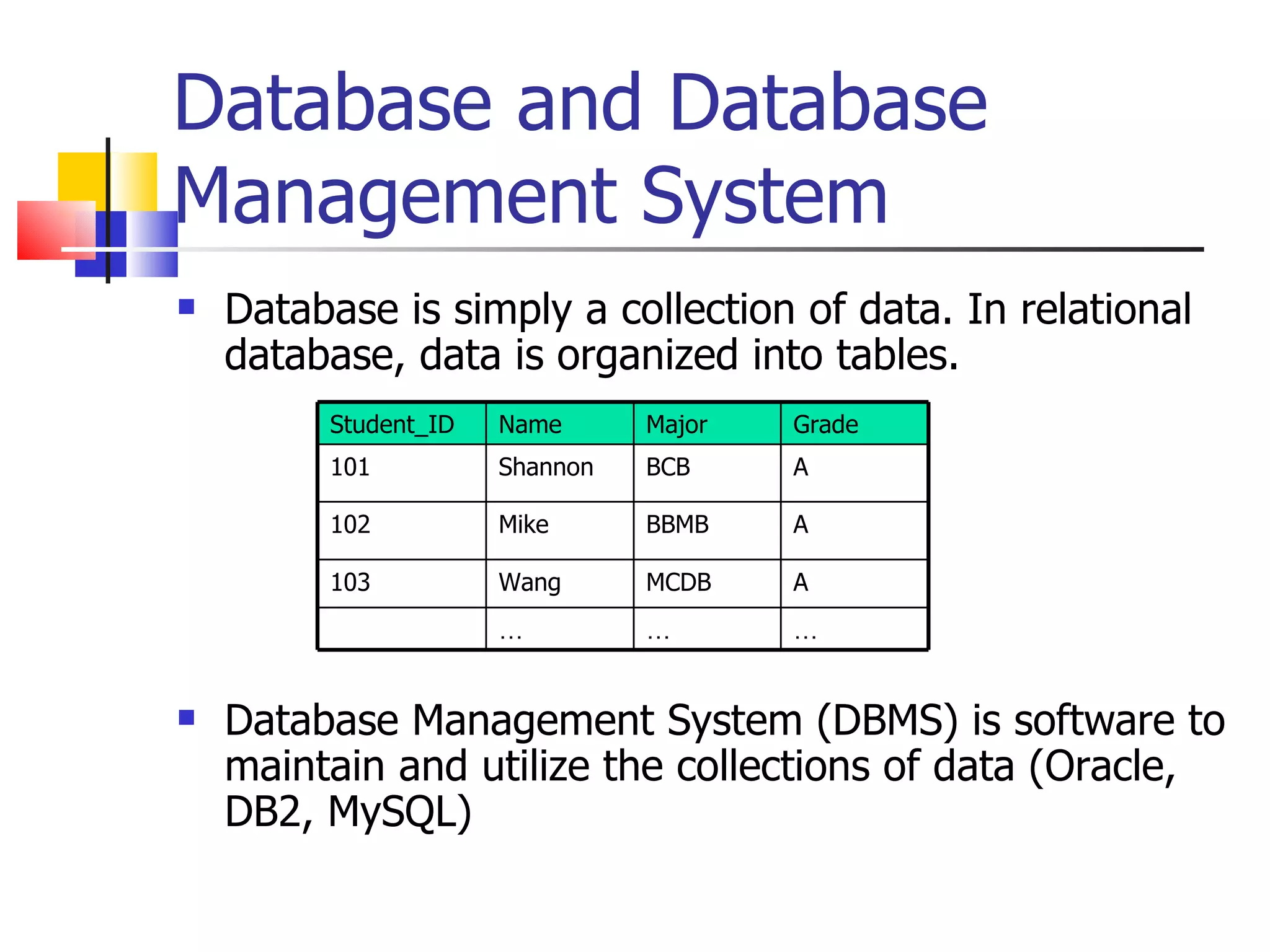
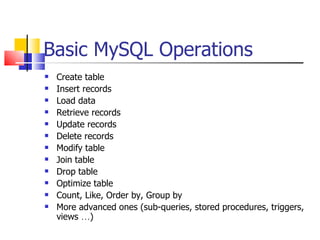
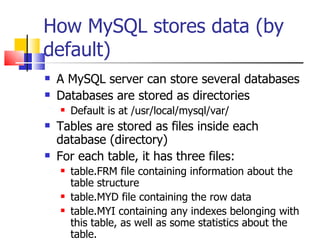
This document provides information about databases, database management systems (DBMS), and basic MySQL operations. It defines a database as a collection of data organized into tables. A DBMS is software that maintains and utilizes these data collections. MySQL is introduced as a free and popular DBMS. The document outlines basic MySQL operations like creating and modifying tables, inserting, retrieving, updating, and deleting records. It also discusses how MySQL stores data and provides examples of SQL queries.
![Login
mysql –h hostname –u username –p
[password]
Example
% mysql -u usrname -p
Enter password: passowrd
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ;
or g. Your MySQL connection id is 23 to server version:
3.23.41.
Type 'help;' or 'h' for help. Type 'c' to clear the buffer.
mysql>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysql2-120426051932-phpapp02/85/My-SQL-5-320.jpg)