Structured Query Language (SQL) is a language used to manage data in relational database management systems. It allows users to query, manipulate, and define the structure of data. The document then provides instructions on downloading, installing, and testing MySQL, an open-source relational database management system, along with examples of basic and advanced SQL commands.




![CREATE TABLE SYNTAX: CREATE TABLE [table_name] ( [column_name1] INT AUTO_INCREMENT, [column_name2] VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL, [column_name3] ENUM('guest', 'customer', 'admin')NULL, [column_name4] DATE NULL, [column_name5] VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL, [column_name6] DATETIME NOT NULL, [column_name7] CHAR(1) NULL, [column_name8] BLOB NULL, [column_name9] TEXT NOT NULL, UNIQUE(username), PRIMARY KEY (column_name1) ); Example: CREATE TABLE user ( userid INT AUTO_INCREMENT, username VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL, group_type ENUM('guest', 'customer', 'admin') NULL, date_of_birth DATE NULL, password VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL, registration_date DATETIME NOT NULL, account_disable CHAR(1) NULL, image BLOB NULL, comment TEXT NOT NULL, UNIQUE(username), PRIMARY KEY (userid) );](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-7-320.jpg)


![Add a new column "male" in table user. Syntax: ALTER TABLE [table_name] ADD COLUMN [column_name] CHAR(1) NOT NULL; Example: ALTER TABLE user ADD COLUMN male CHAR(1) NOT NULL;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-11-320.jpg)
![Change column name "male" into "gender" in table user and change the type to VARCHAR(3) and allow NULL values. Syntax: ALTER TABLE [table_name] CHANGE [old_column] [new_column] VARCHAR(3) NULL; Example: ALTER TABLE user CHANGE male gender VARCHAR (3) NULL;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-12-320.jpg)
![Change the size of column "gender" from 3 to 6 in table user. Syntax: ALTER TABLE [table_name] MODIFY [column_name] VARCHAR(6); Example: ALTER TABLE user MODIFY gender VARCHAR(6);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-13-320.jpg)


![Show field formats of the selected table. Syntax: DESCRIBE [table_name]; Example: DESCRIBE mos_menu;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-16-320.jpg)
![To see database's field formats. mysql> describe [table name];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-17-320.jpg)
![To delete a db. mysql> drop database [database name]; Example: DROP DATABASE demodb;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-18-320.jpg)
![To delete a table. mysql> drop table [table name]; Example: DROP TABLE user;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-19-320.jpg)
![Show all data in a table. mysql> SELECT * FROM [table name]; Example: SELECT * FROM mos_menu;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-20-320.jpg)
![Show all records from mos_menu table containing name "Home". SELECT * FROM [table_name] WHERE [field_name]=[value]; Example: SELECT * FROM mos_menu WHERE name = "Home";](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-21-320.jpg)
![Returns the columns and column information pertaining to the designated table. mysql> show columns from [table name];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-22-320.jpg)
![Show certain selected rows with the value "whatever". mysql> SELECT * FROM [table name] WHERE [field name] = "whatever";](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-23-320.jpg)
![Show all records containing the name "Bob" AND the phone number '12345678'. mysql> SELECT * FROM [table name] WHERE name = "Bob" AND phone_number = '12345678';](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-24-320.jpg)
![Show all records not containing the name "Bob" and the phone number '12345678' order by the phone_number field. mysql> SELECT * FROM [table name] WHERE name != "Bob" AND phone_number = '12345678' order by phone_number;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-25-320.jpg)
![Show all records starting with the letters 'bob' AND the phone number '12345678'. mysql> SELECT * FROM [table name] WHERE name like "Bob%" AND phone_number = '12345678';](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-26-320.jpg)
![Show all records starting with the letters 'bob' AND the phone number '12345678' limit to records 1 through 5. mysql> SELECT * FROM [table name] WHERE name like "Bob%" AND phone_number = '12345678' limit 1,5;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-27-320.jpg)
![Use a regular expression to find records. Use "REGEXP BINARY" to force case-sensitivity. This finds any record beginning with a. mysql> SELECT * FROM [table name] WHERE rec RLIKE "^a";](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-28-320.jpg)
![Show unique records. mysql> SELECT DISTINCT [column name] FROM [table name];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-29-320.jpg)
![Show selected records sorted in an ascending (asc) or descending (desc). mysql> SELECT [col1],[col2] FROM [table name] ORDER BY [col2] DESC;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-30-320.jpg)
![Return number of rows. mysql> SELECT COUNT(*) FROM [table name];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-31-320.jpg)
![Sum column. mysql> SELECT SUM(*) FROM [table name];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-32-320.jpg)

![Change a users password from unix shell. # [mysql dir]/bin/mysqladmin -u username -h hostname.blah.org -p password 'new-password'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-35-320.jpg)
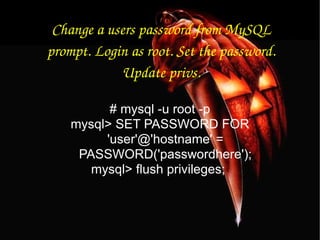
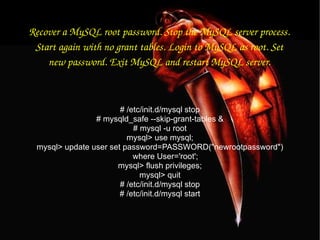
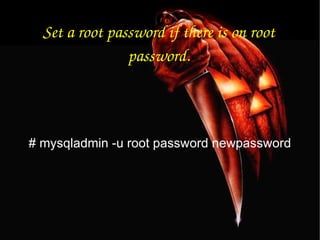
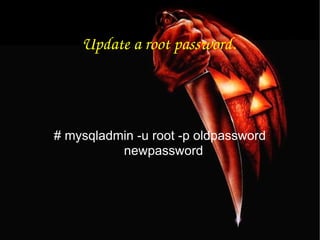
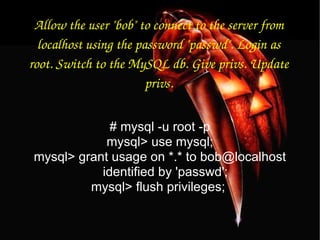

![To update info already in a table. mysql> UPDATE [table name] SET Select_priv = 'Y',Insert_priv = 'Y',Update_priv = 'Y' where [field name] = 'user';](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-42-320.jpg)
![Delete a row(s) from a table. mysql> DELETE from [table name] where [field name] = 'whatever';](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-43-320.jpg)

![Delete a column. mysql> alter table [table name] drop column [column name];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-45-320.jpg)
![Add a new column to db. mysql> alter table [table name] add column [new column name] varchar (20);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-46-320.jpg)
![Change column name. mysql> alter table [table name] change [old column name] [new column name] varchar (50);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-47-320.jpg)
![Make a unique column so you get no dupes. mysql> alter table [table name] add unique ([column name]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-48-320.jpg)
![Make a column bigger. mysql> alter table [table name] modify [column name] VARCHAR(3);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-49-320.jpg)
![Delete unique from table. mysql> alter table [table name] drop index [colmn name];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-50-320.jpg)
![Load a CSV file into a table. mysql> LOAD DATA INFILE '/tmp/filename.csv' replace INTO TABLE [table name] FIELDS TERMINATED BY ',' LINES TERMINATED BY '\n' (field1,field2,field3);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-51-320.jpg)
![Dump all databases for backup. Backup file is sql commands to recreate all db's. # [mysql dir]/bin/mysqldump -u root -ppassword --opt >/tmp/alldatabases.sql](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-52-320.jpg)
![Dump one database for backup. # [mysql dir]/bin/mysqldump -u username -ppassword --databases databasename >/tmp/databasename.sql](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-53-320.jpg)
![Dump a table from a database. # [mysql dir]/bin/mysqldump -c -u username -ppassword databasename tablename > /tmp/databasename.tablename.sql](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-54-320.jpg)
![Restore database (or database table) from backup. # [mysql dir]/bin/mysql -u username -ppassword databasename < /tmp/databasename.sql](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlpresentation-100601002057-phpapp02/85/My-sql-presentation-55-320.jpg)
