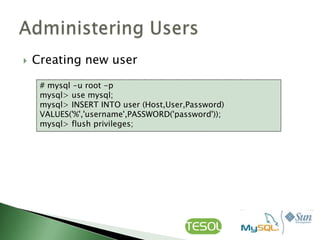
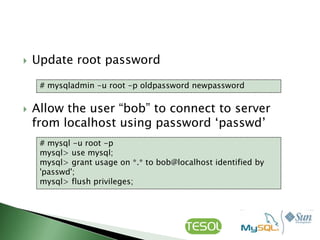
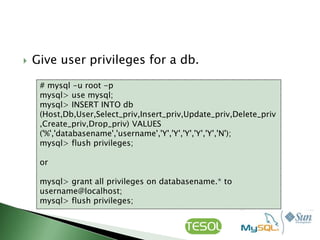
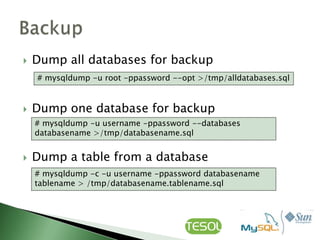
This document discusses various topics related to installing, configuring, and managing MySQL databases including:
- Using command line tools like mysqladmin and mysql to configure and manage MySQL.
- Installing MySQL via packages or source code and configuring startup settings.
- Creating, deleting, and managing databases, tables, and user privileges.
- Performing backups with mysqldump and restoring from backups.
- Monitoring the status of the MySQL server process.








![ Login to MySQL server
#mysql –h hostname –u root -p
Create a database
msql> create database [databasename];
List all databases on the MySQL server
msql> show databases;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqladministration-111228215104-phpapp01/85/My-sql-administration-11-320.jpg)
![ Swicth to a database
msql> use [db_name];
To see all the tables in the db
msql> show tables;
To delete a db
msql> drop database [databasename];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqladministration-111228215104-phpapp01/85/My-sql-administration-12-320.jpg)
![ To see database‟s field formats
msql> describe [table name];
To delete a table
msql> drop table [table name];
Show all data in a table
msql> SELECT * FROM [table name];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqladministration-111228215104-phpapp01/85/My-sql-administration-13-320.jpg)




![ To update info already in table
mysql> UPDATE [table name] SET Select_priv = 'Y',Insert_priv
= 'Y',Update_priv = 'Y' where [field name] = 'user';
Delete a rows from table
mysql> DELETE from [table name] where [field name] =
'whatever';
Update database permissions/privileges
mysql> flush privileges;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqladministration-111228215104-phpapp01/85/My-sql-administration-23-320.jpg)

![ Example
mysql> create table [table name] (personid int(50) not null
auto_increment primary key,firstname varchar(35),middlename
varchar(50),lastnamevarchar(50) default „yasin');
mysql> CREATE TABLE [table name] (firstname
VARCHAR(20), middleinitial VARCHAR(3), lastname
VARCHAR(35),suffix VARCHAR(3),officeid VARCHAR(10),userid
VARCHAR(15),username VARCHAR(8),email VARCHAR(35),phone
VARCHAR(25), groups VARCHAR(15),datestamp DATE,timestamp
time,pgpemail VARCHAR(255));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqladministration-111228215104-phpapp01/85/My-sql-administration-26-320.jpg)
