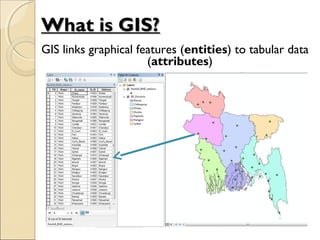
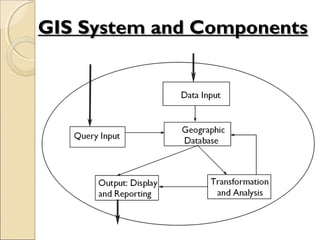
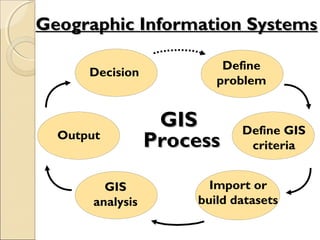
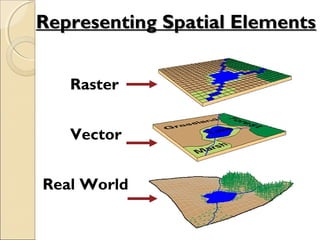
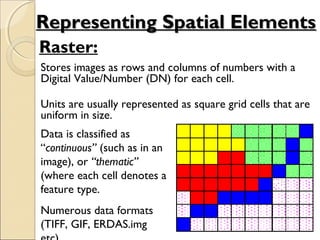
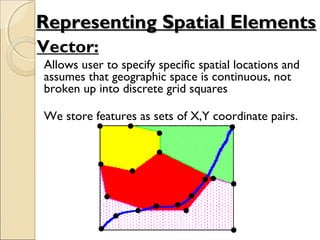
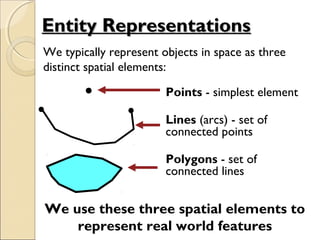
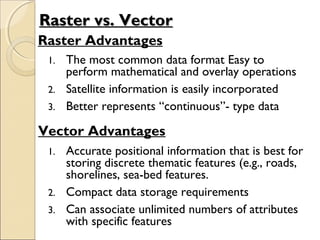
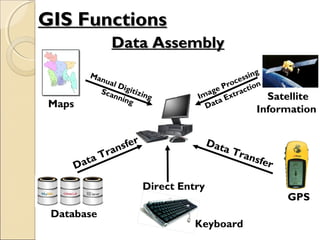
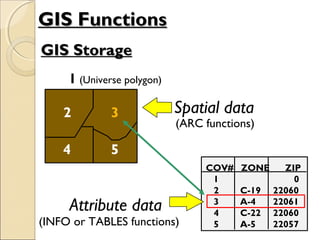
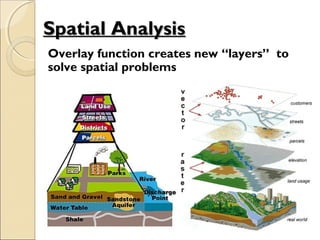
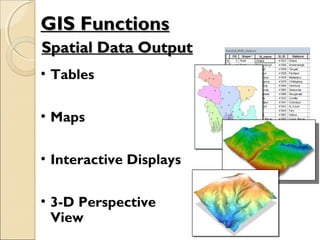
This document provides an overview of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and Remote Sensing. It will cover the theoretical background, tools and techniques used in GIS and remote sensing, and geospatial analysis using ArcGIS. Key topics include what a GIS is, its components and functions like data assembly, storage, analysis, manipulation and output. Representation of spatial elements as raster and vector data, and how attributes are associated with spatial features is also described. The document contrasts raster and vector data, and discusses desktop GIS software like ArcGIS.