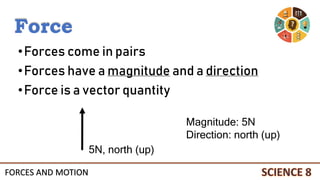
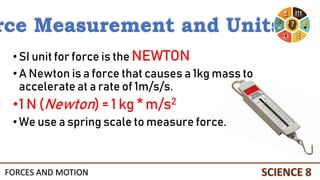
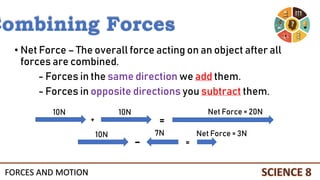
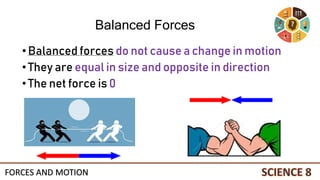
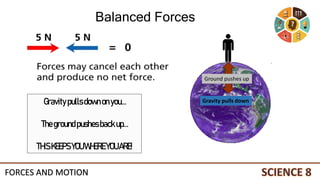
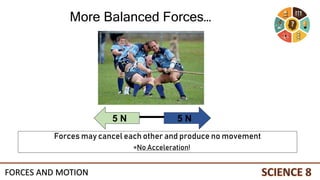
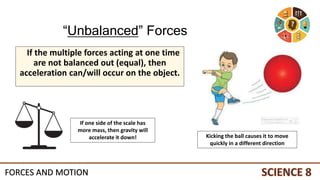
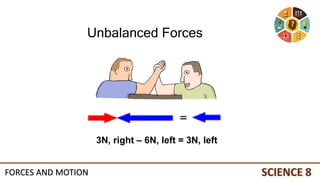
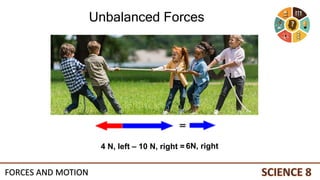
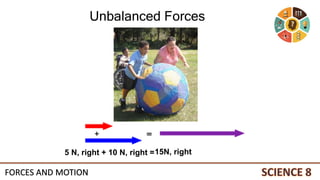
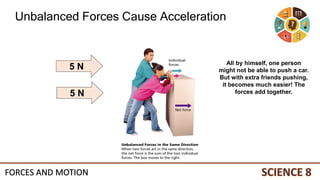
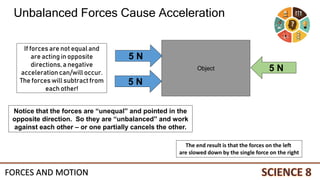
This document discusses forces and motion. It defines a force as a push or pull that can cause an object to move, stop, or change direction. There are two types of forces - contact forces that occur through direct contact between objects, and action-at-a-distance forces that act over a distance without contact, such as gravity and magnetism. Forces can be balanced, resulting in no net force and no change in motion, or unbalanced, resulting in a net force that causes an object to accelerate. The magnitude and direction of forces must be considered to determine the net force and resulting motion of an object.