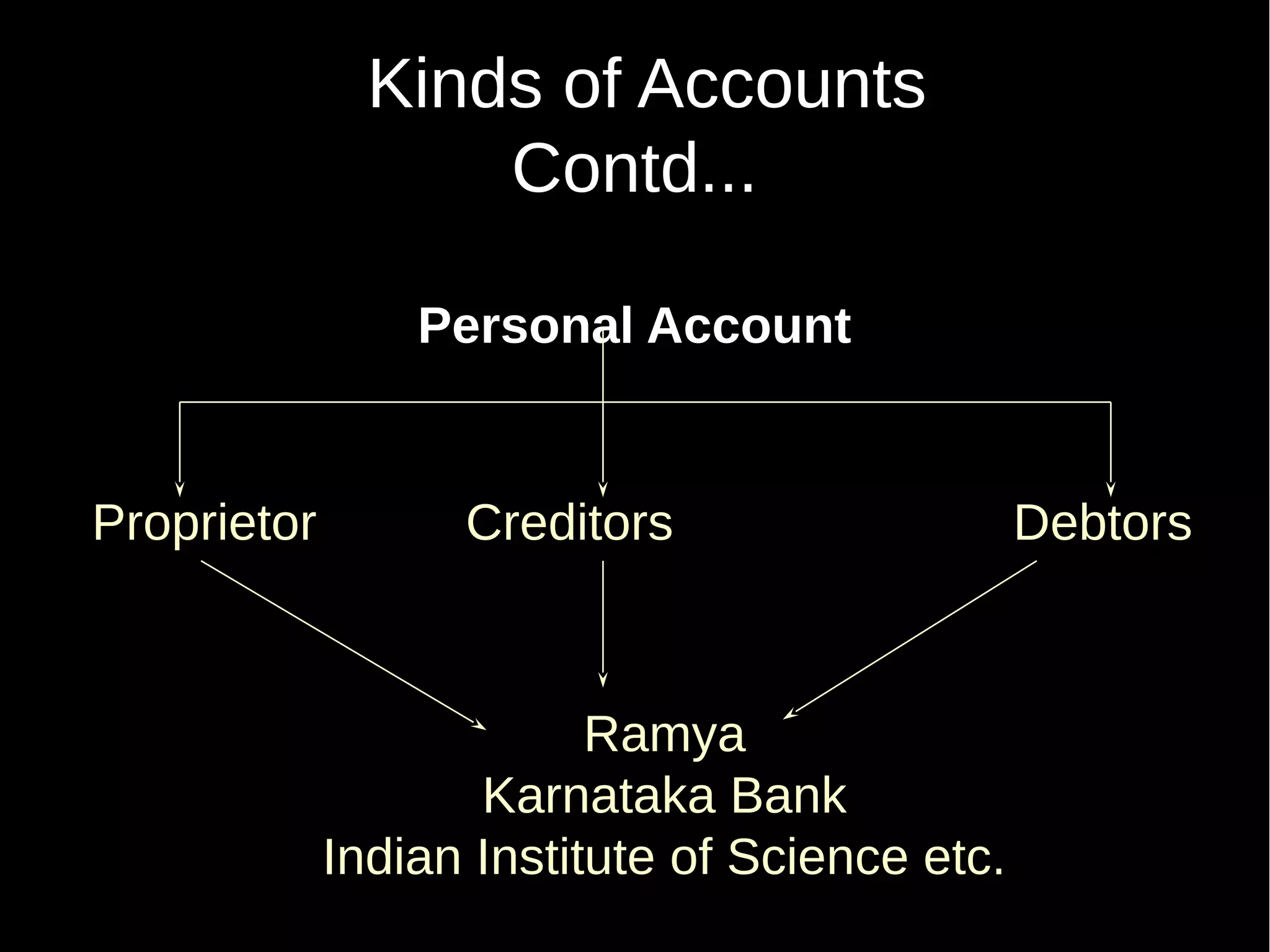
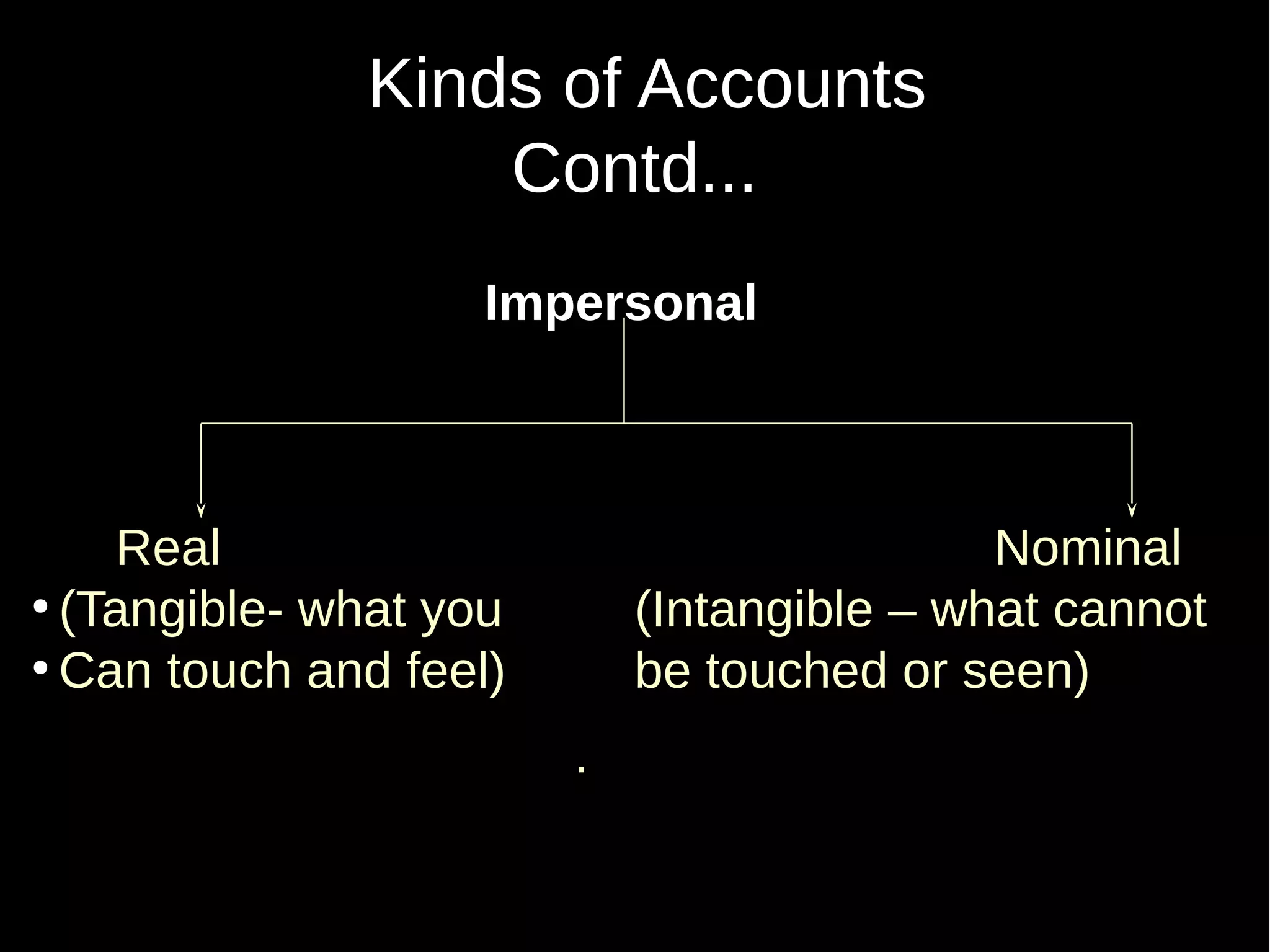
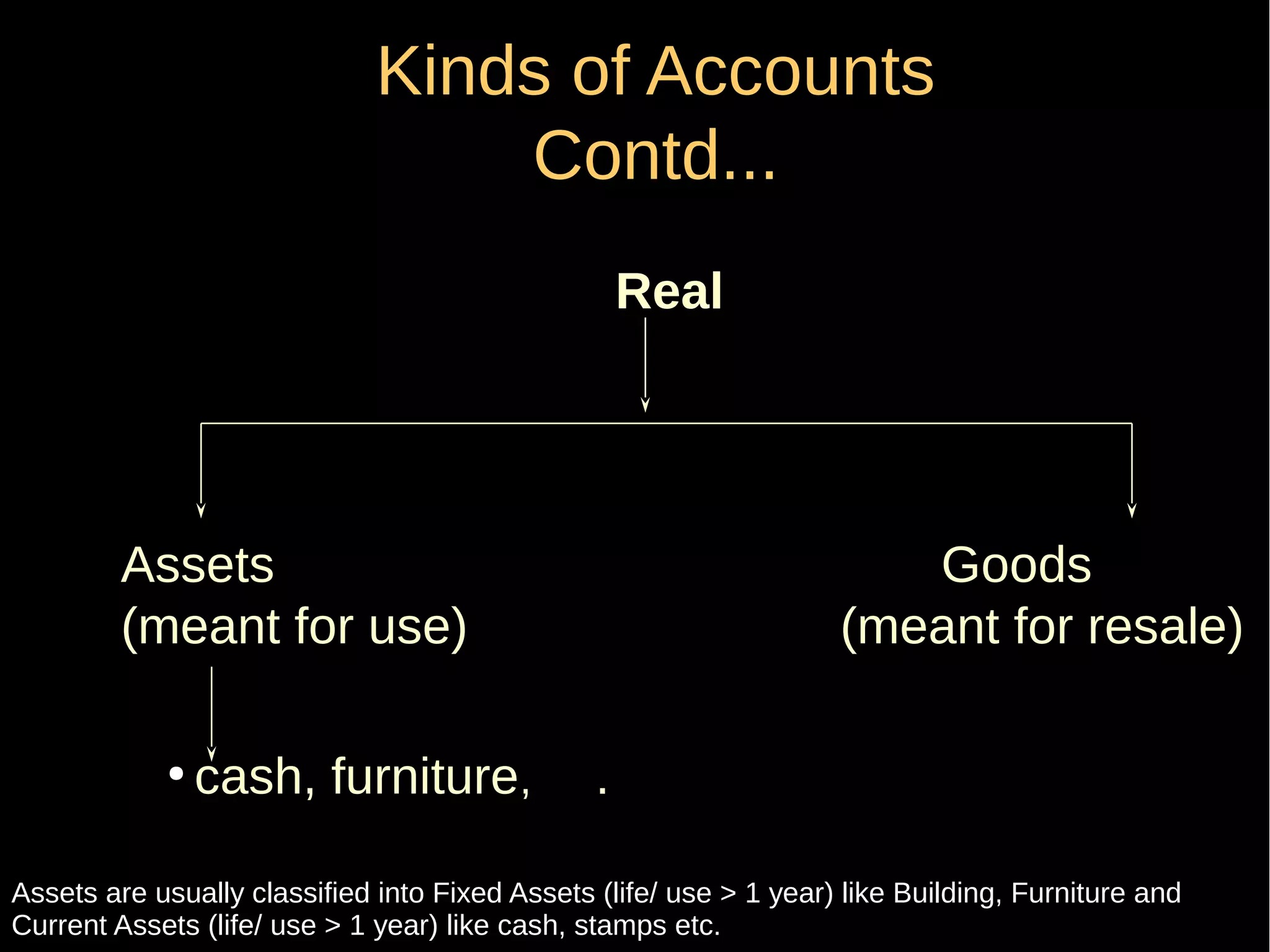
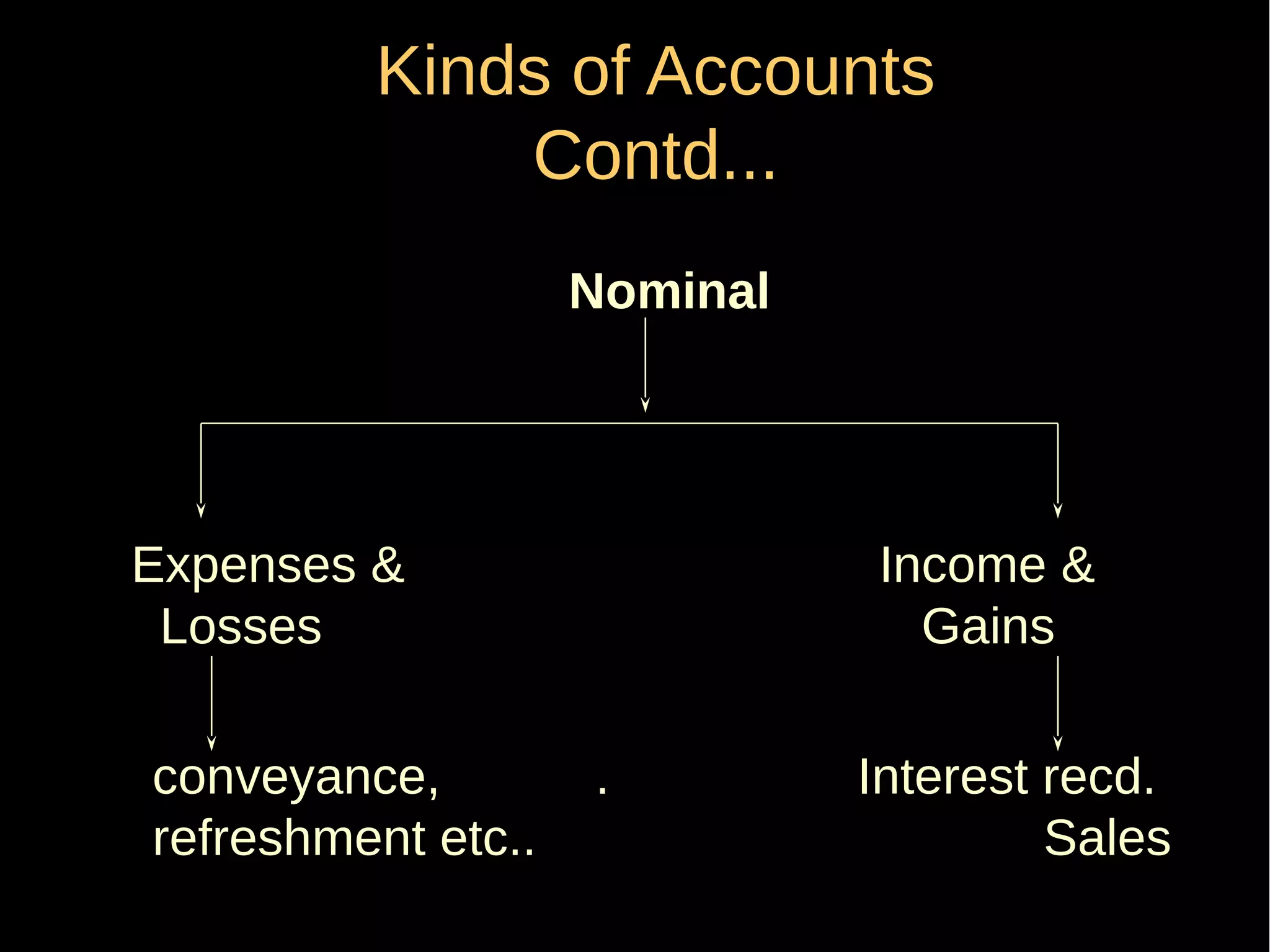
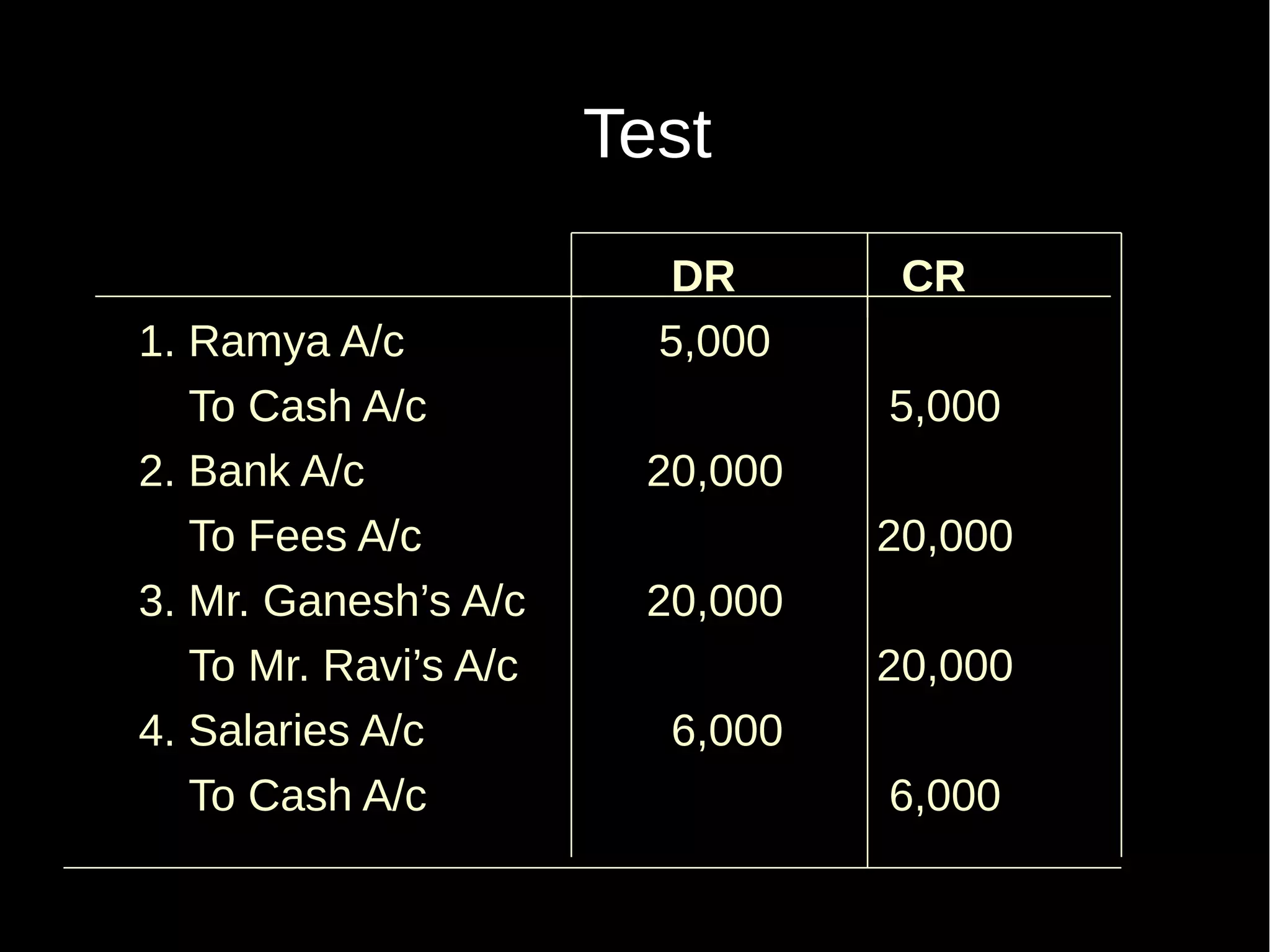
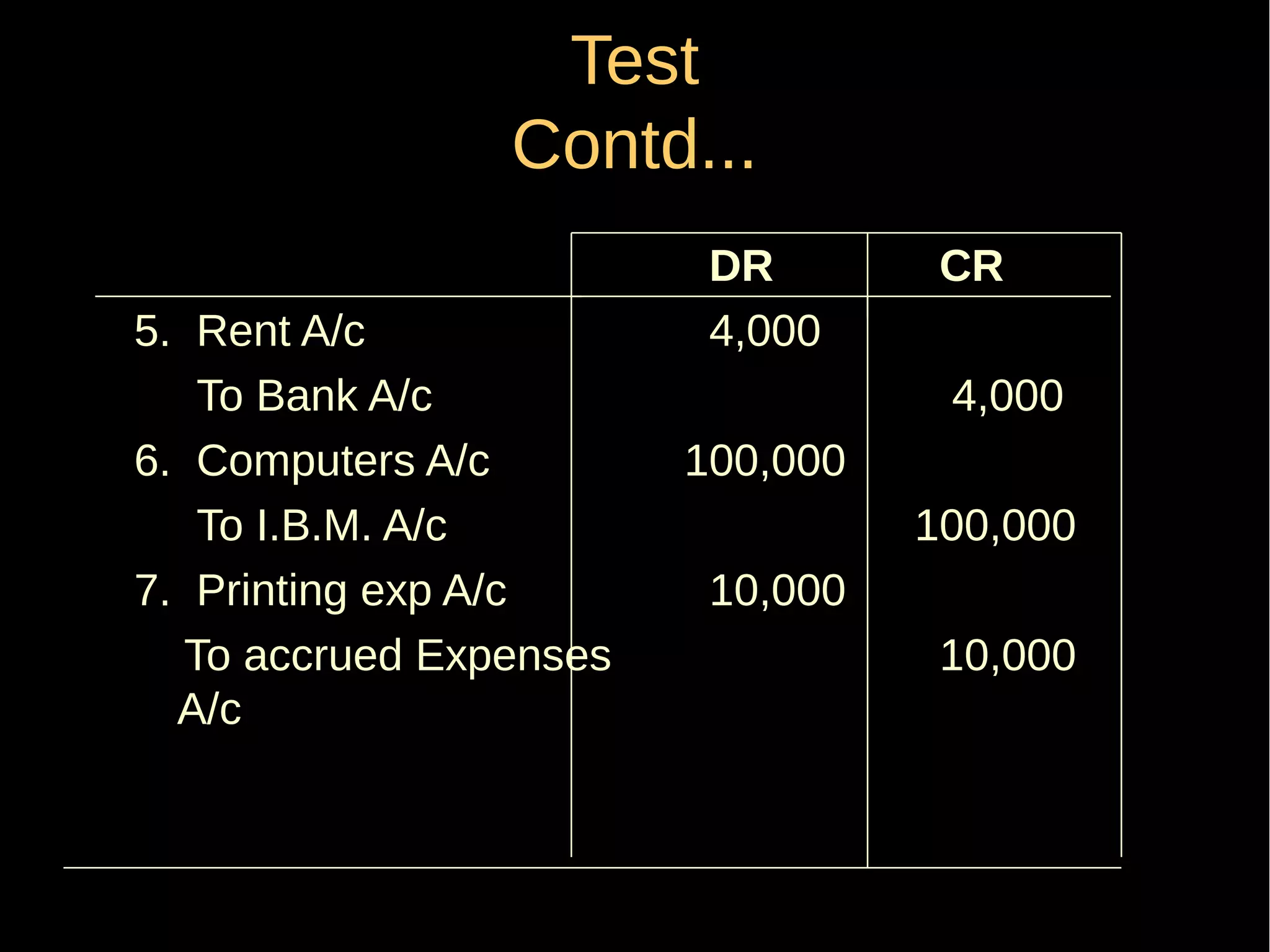
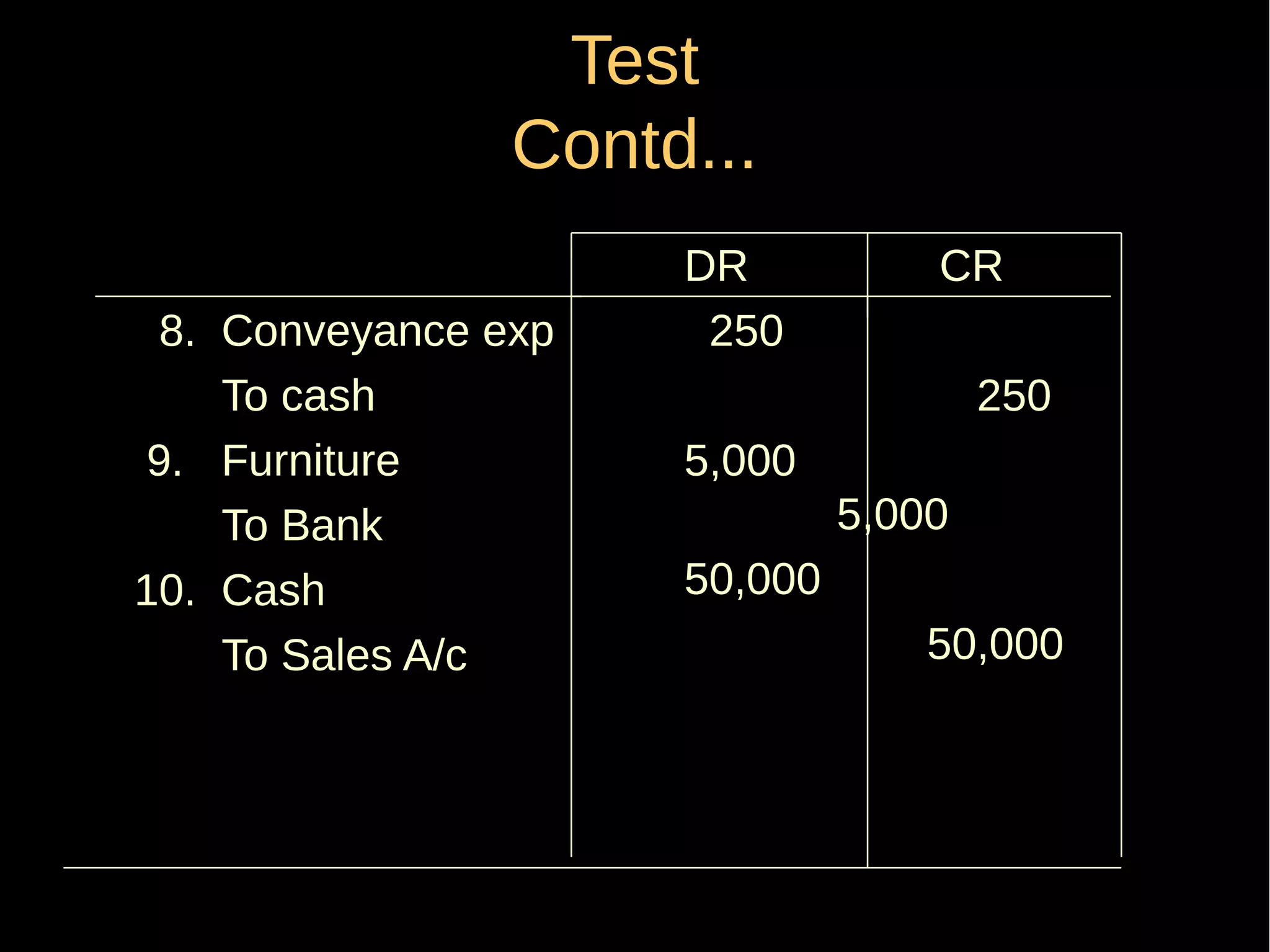
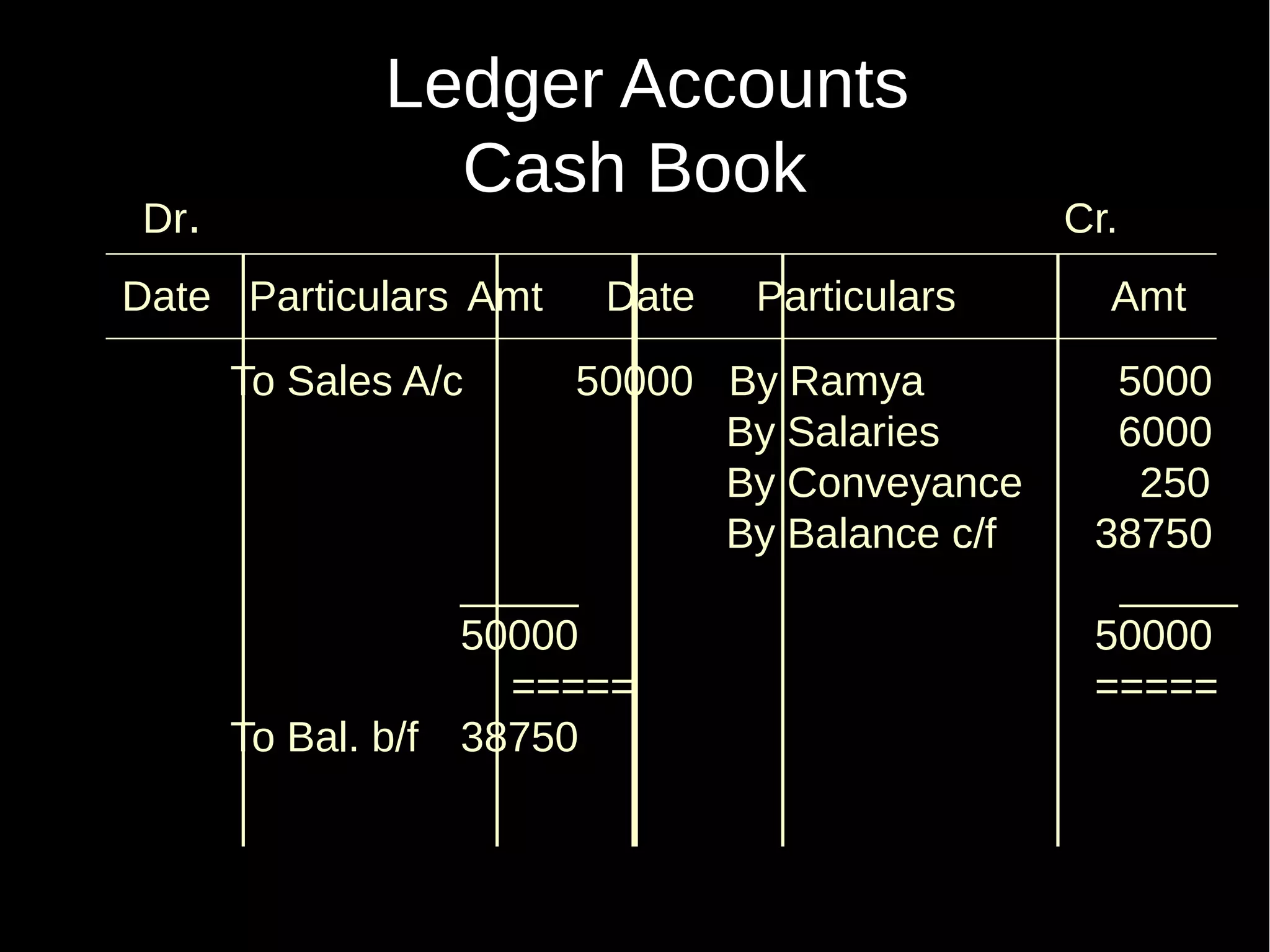
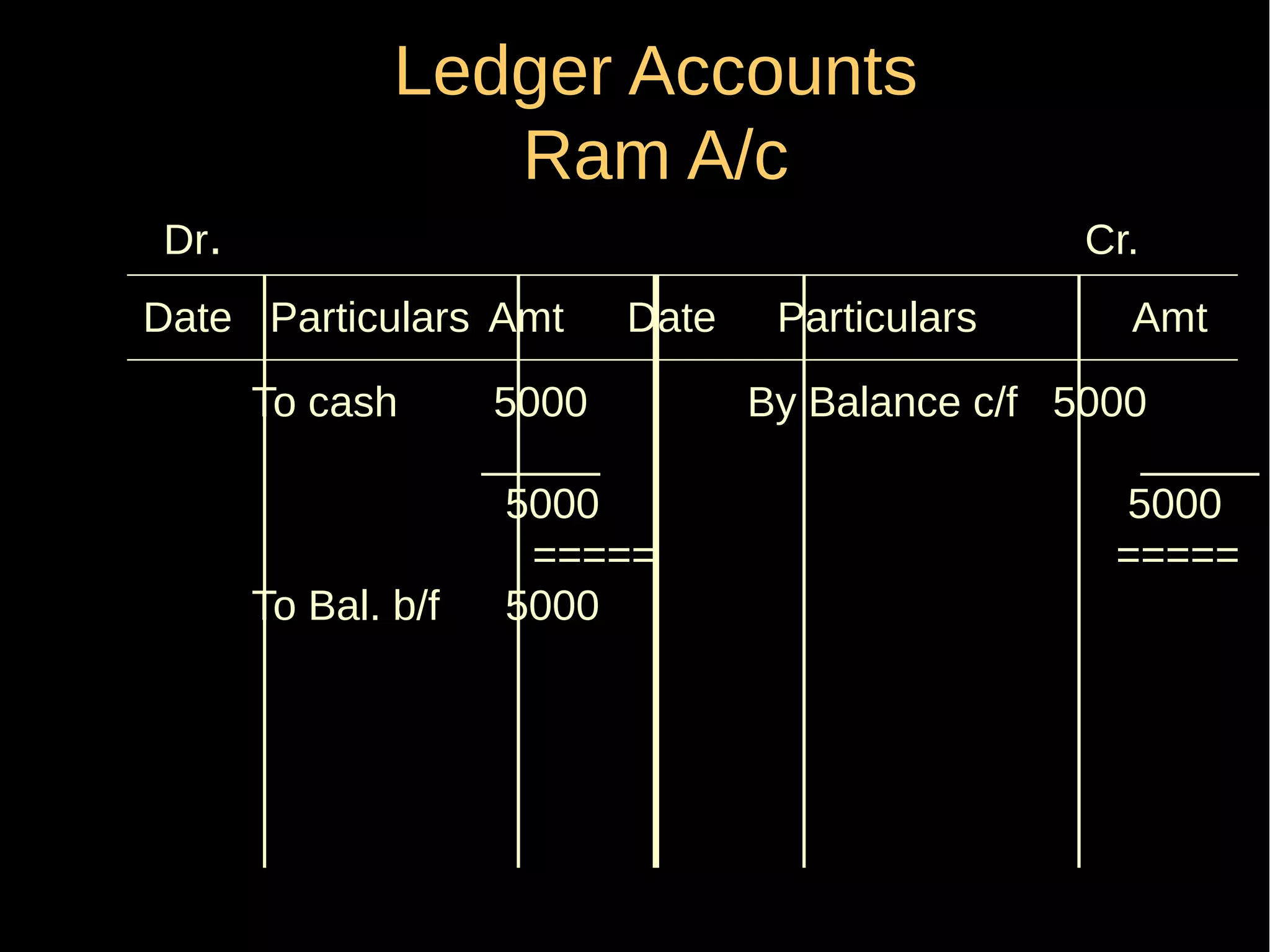
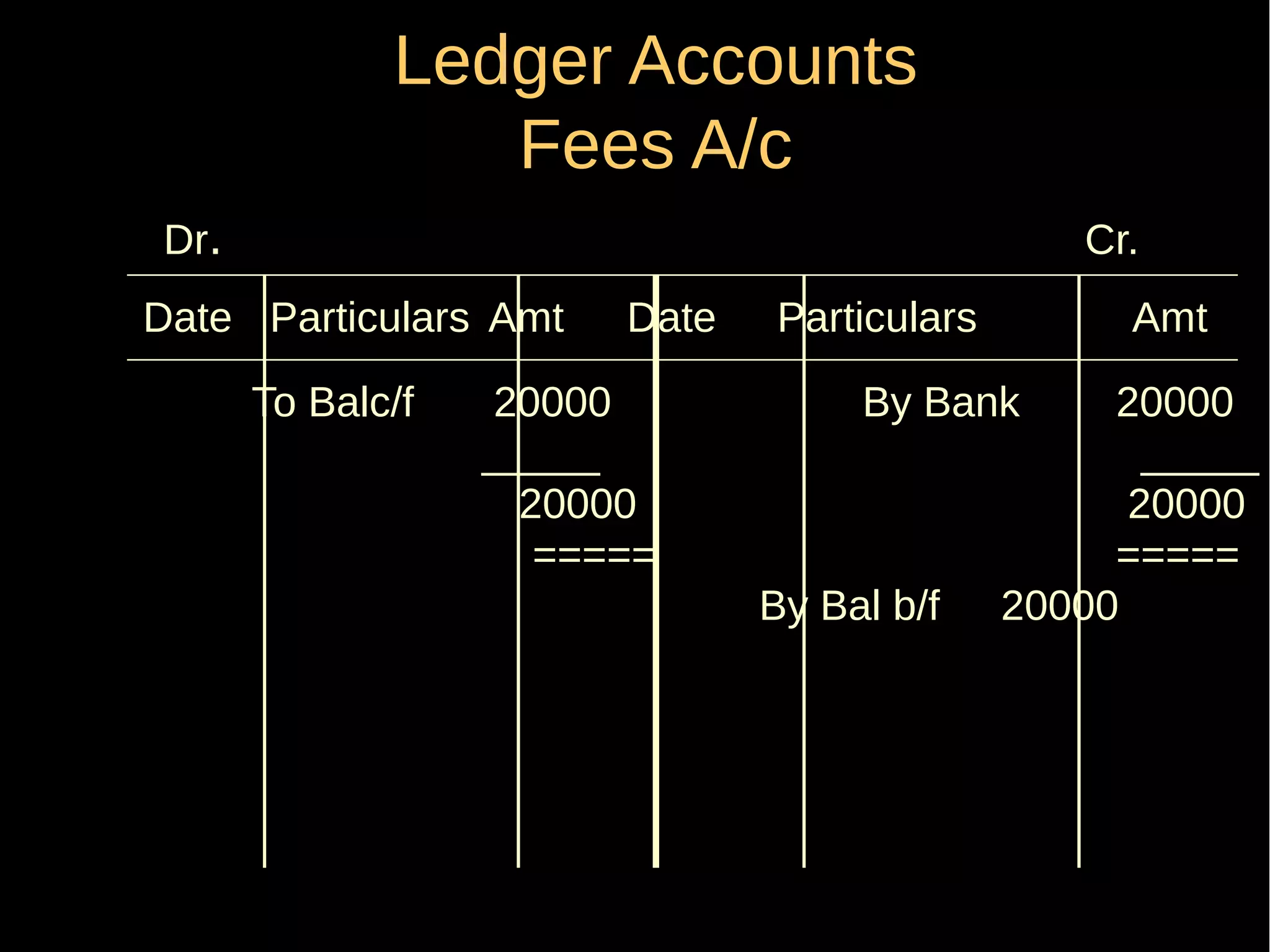
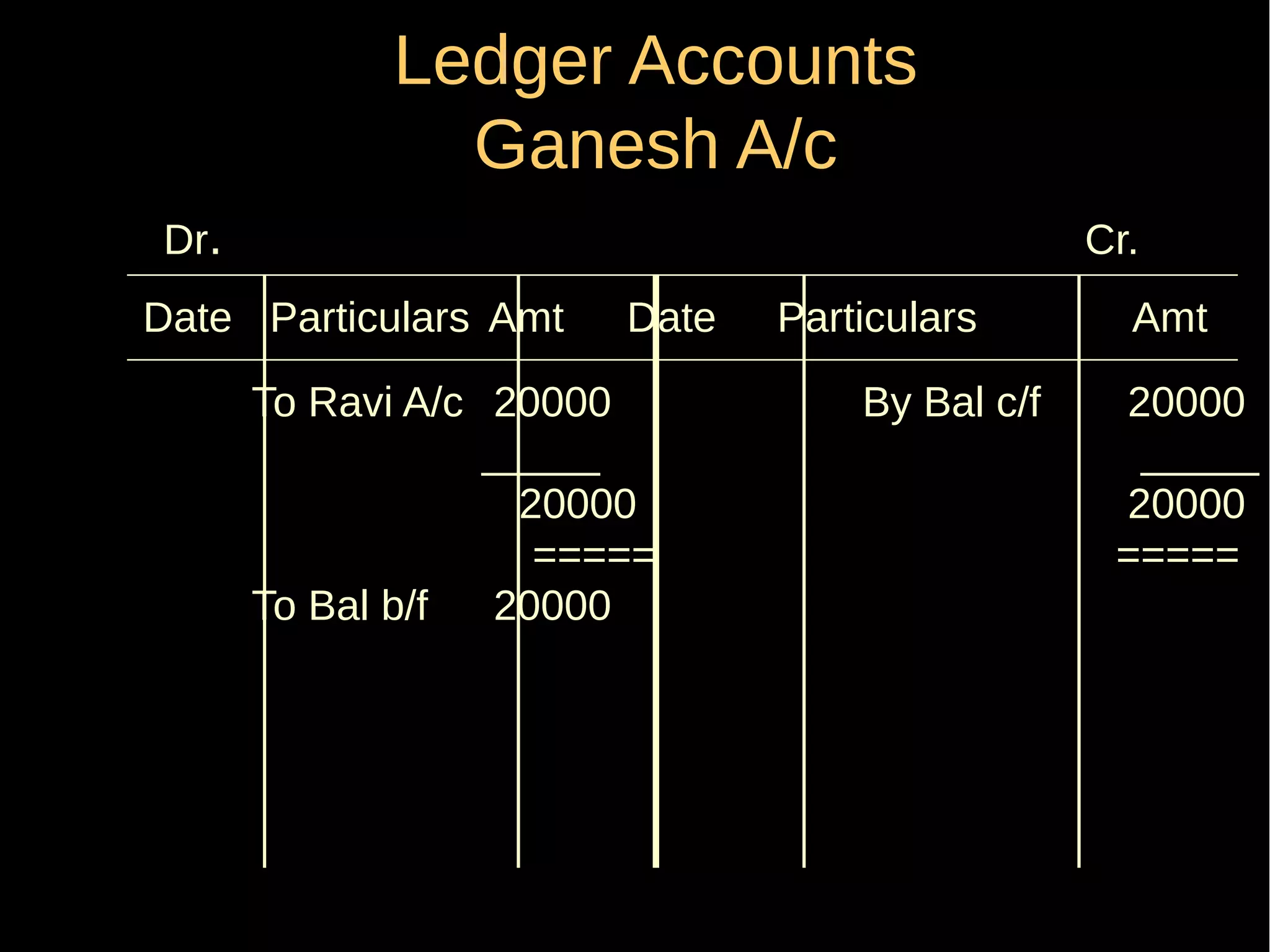
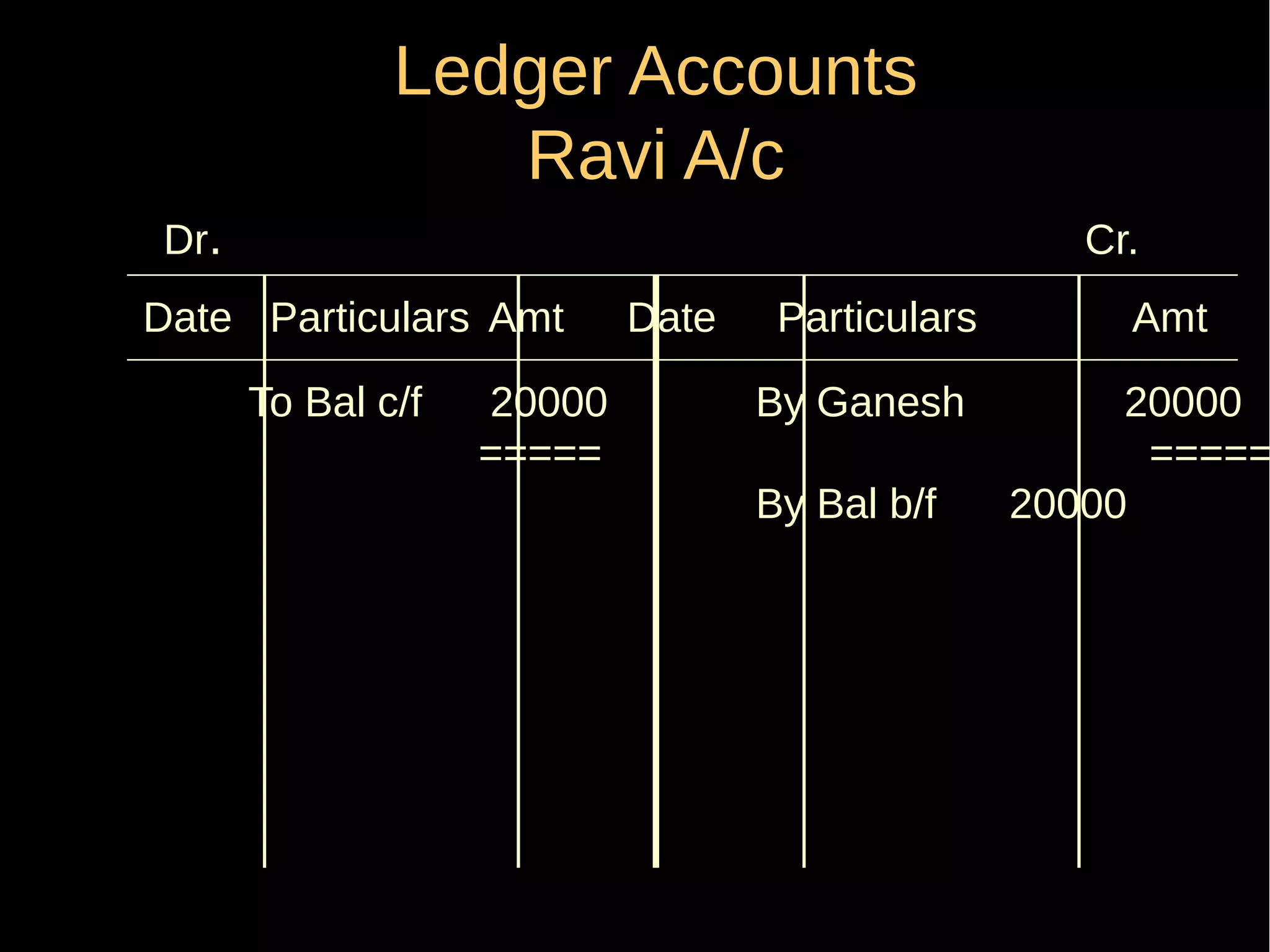
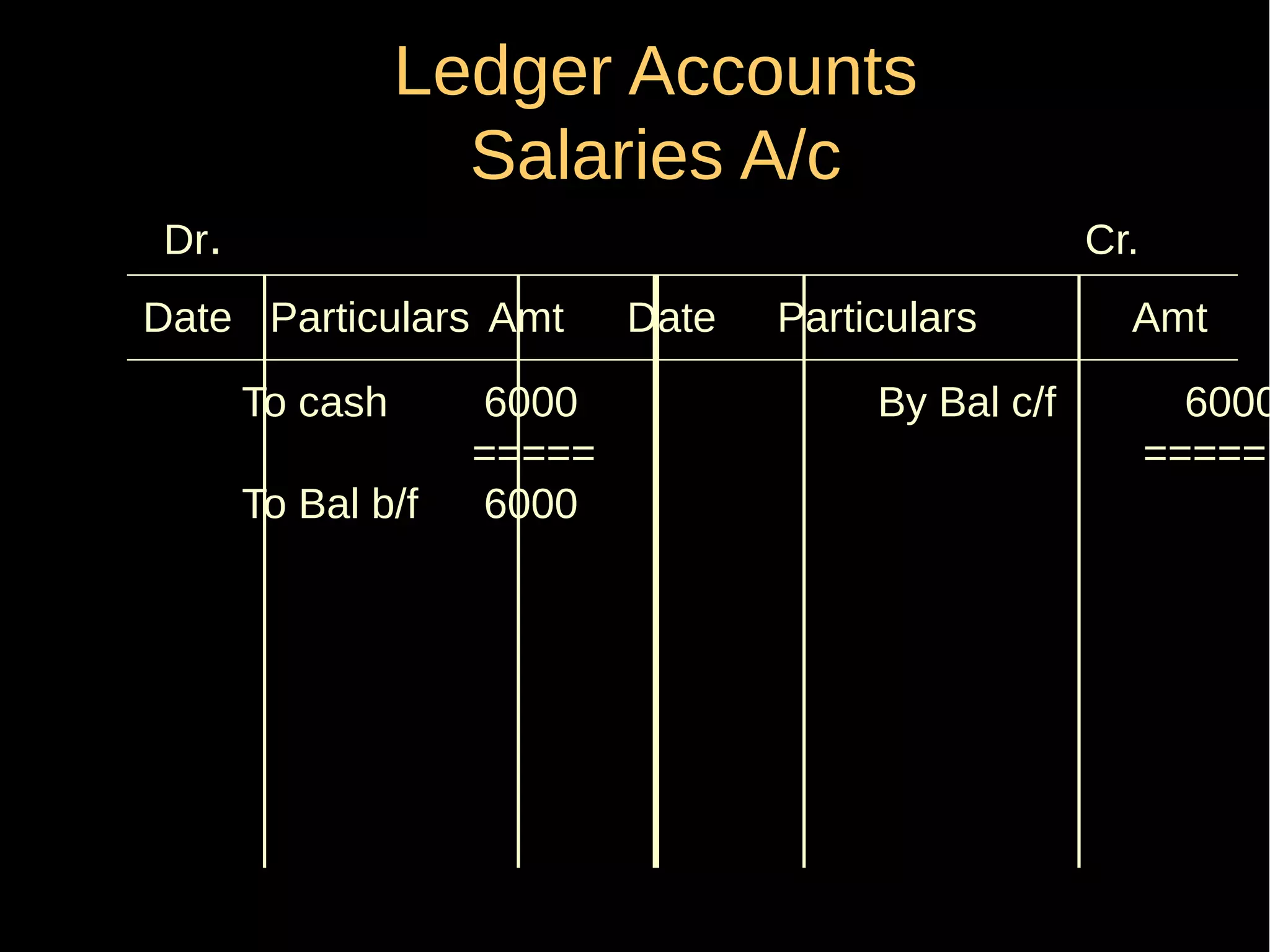
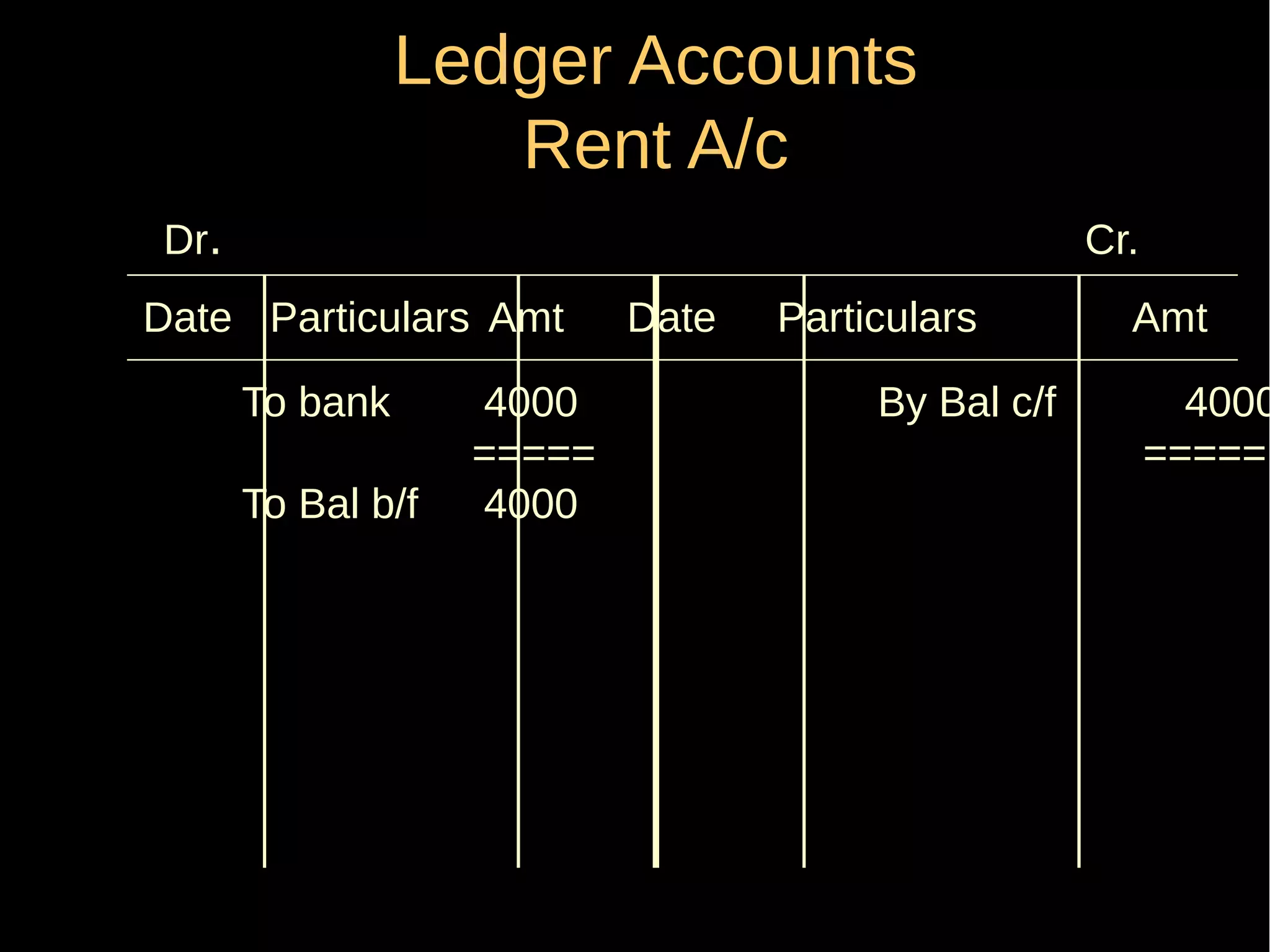
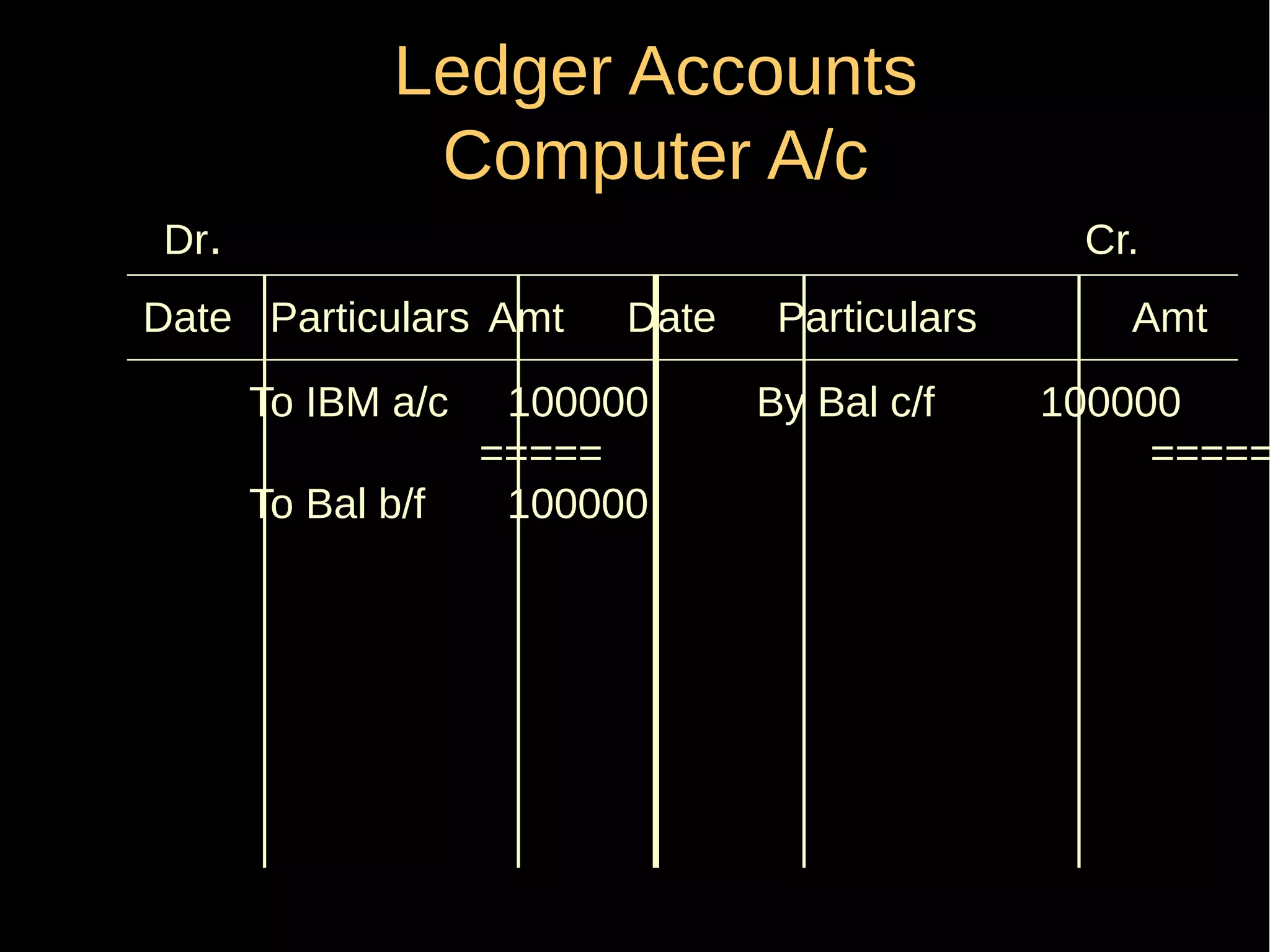
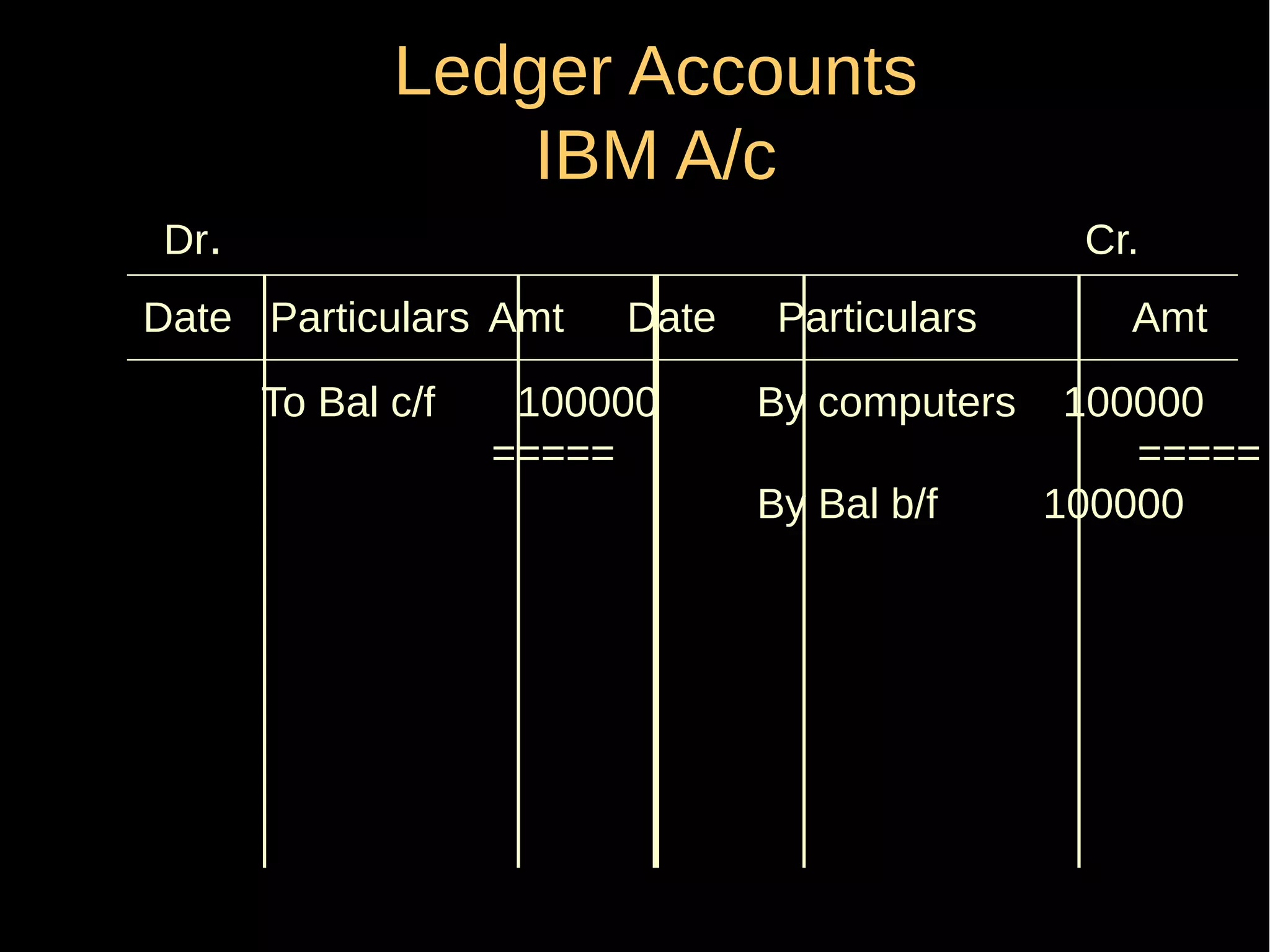
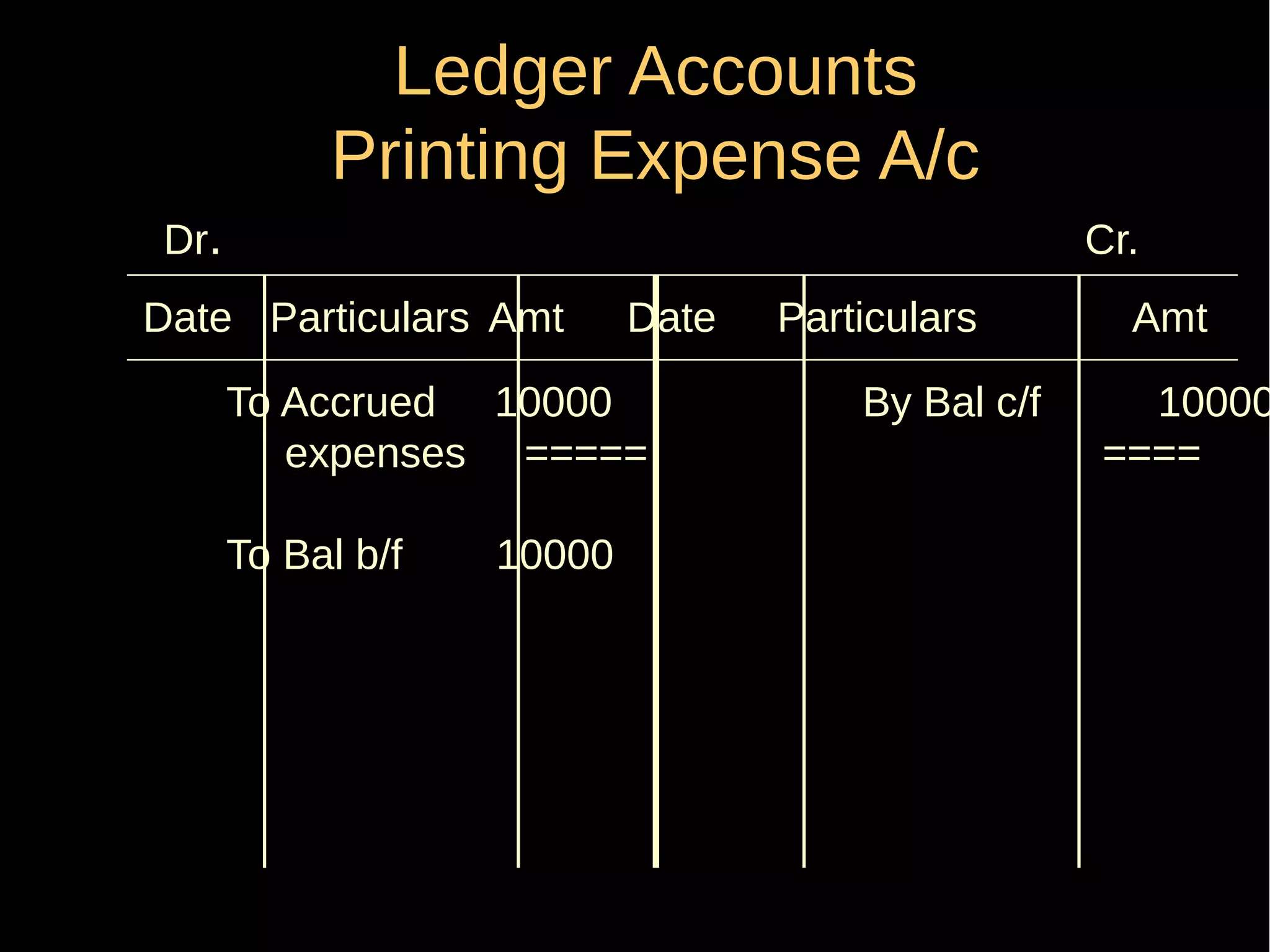
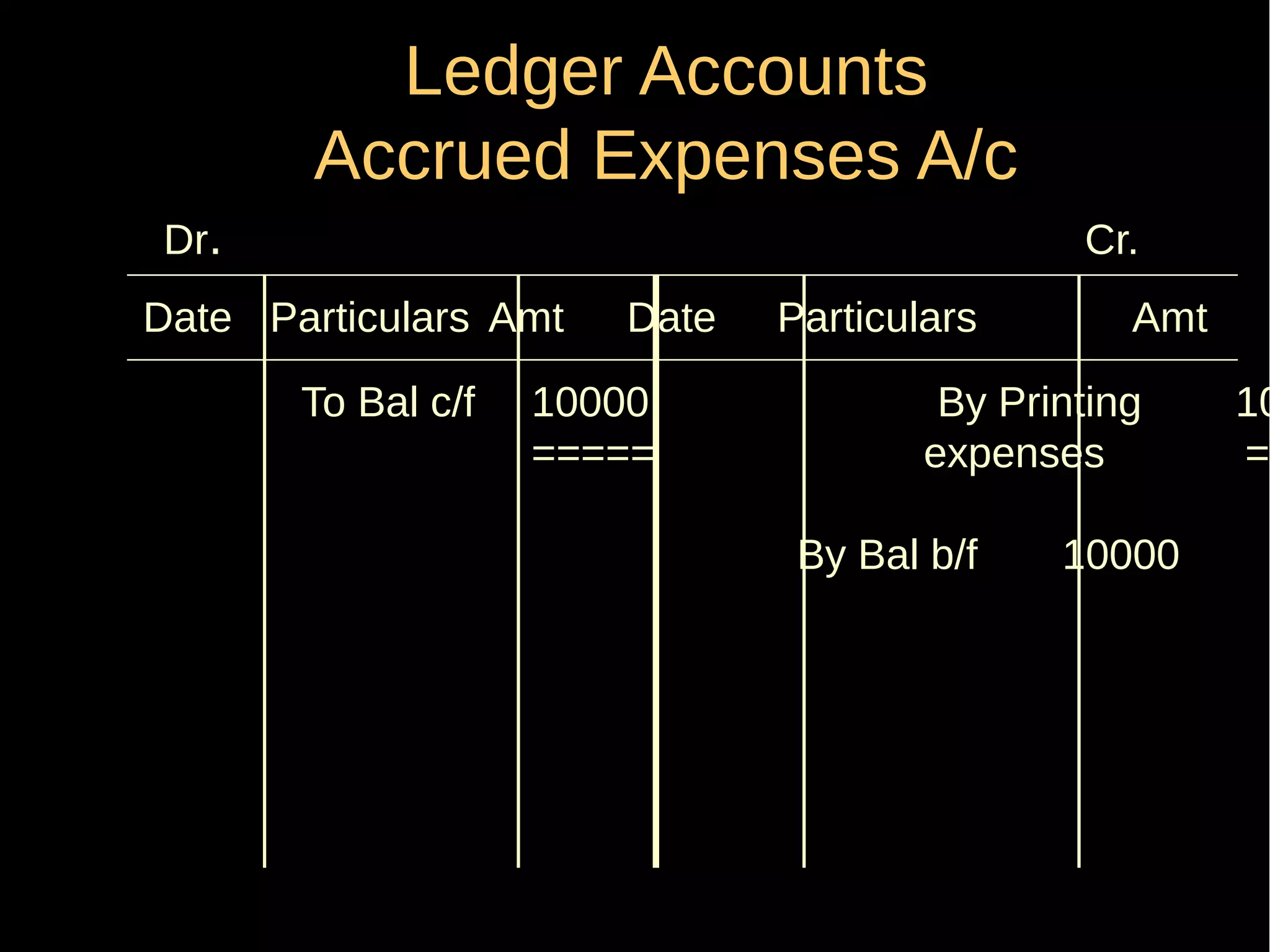
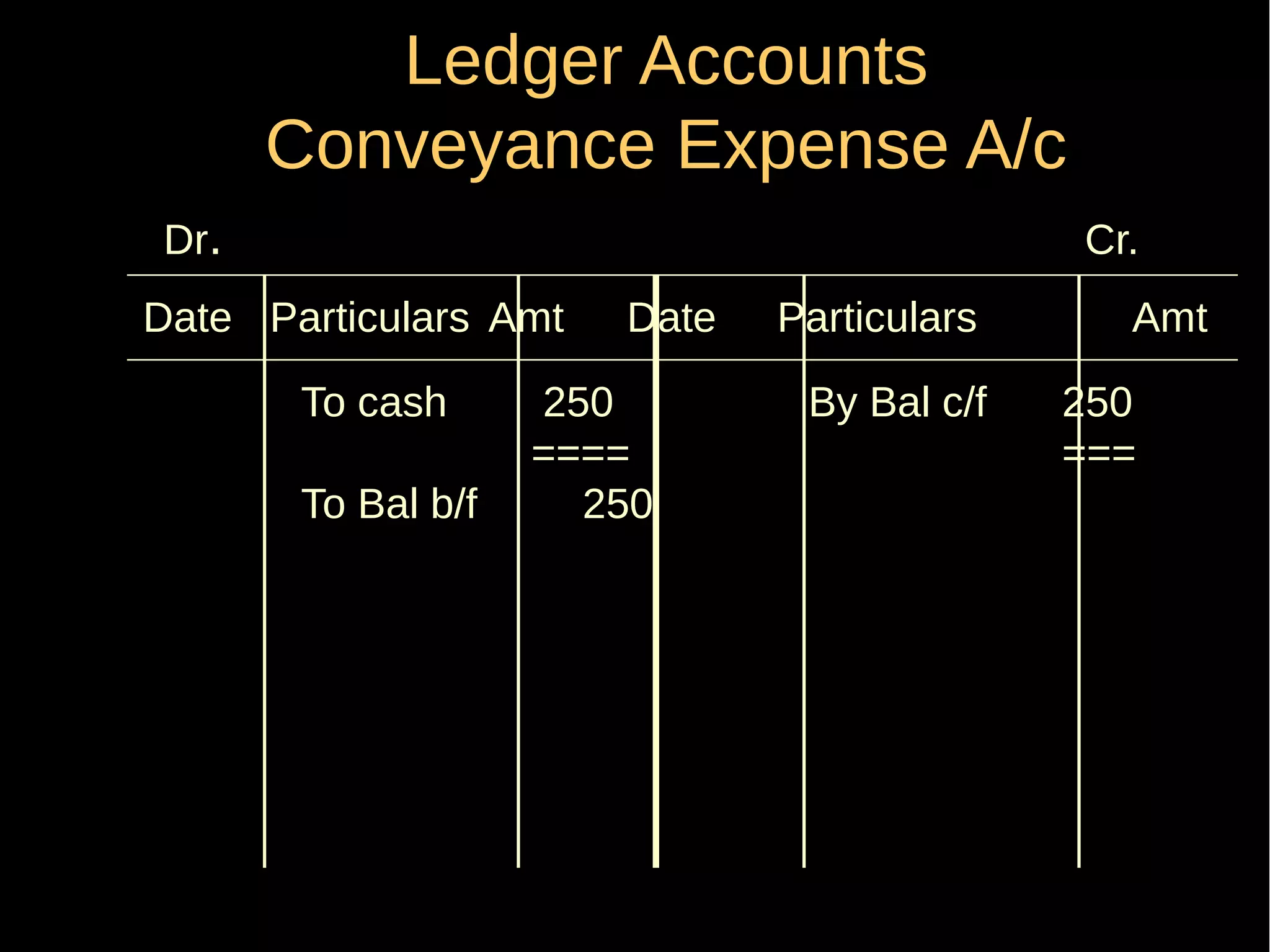
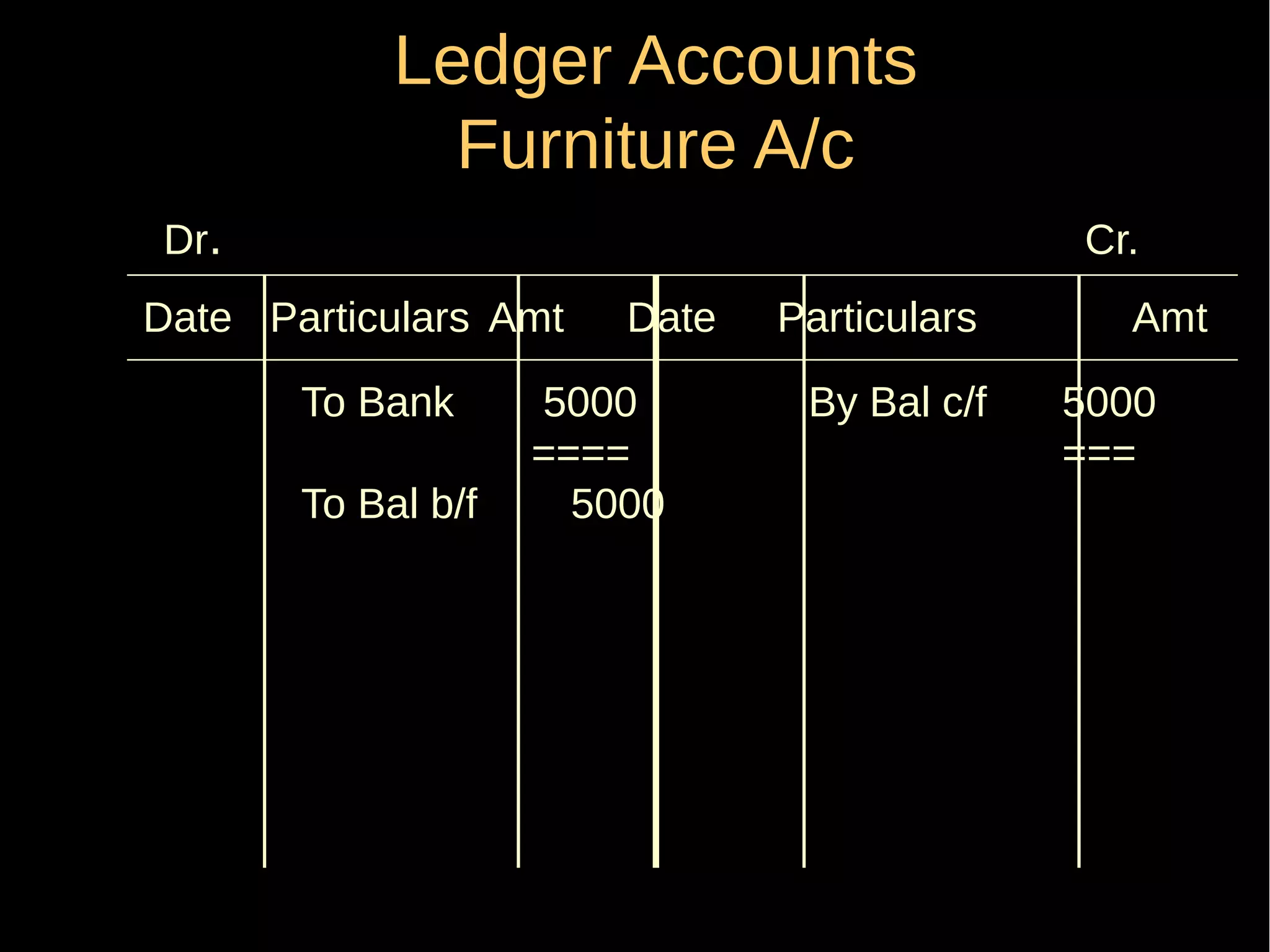
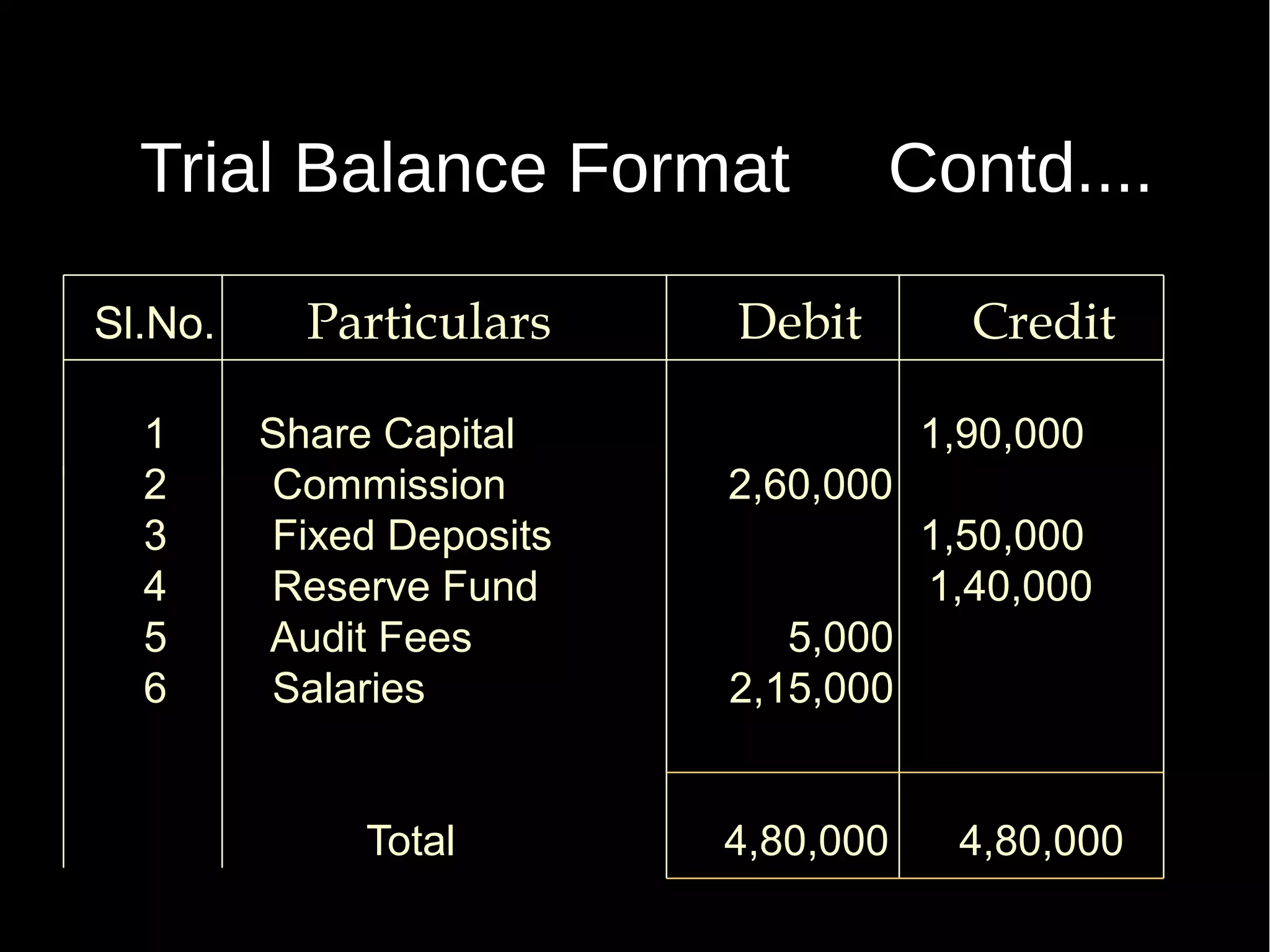
This document provides an introduction to financial accounting. It defines accounting as recording, classifying, and summarizing financial transactions and interpreting results. Key groups interested in accounting information are identified. Accounting is required to determine profit/loss, financial position, amounts owed and due, and information for decision making. The document outlines the basic types of accounts, rules for debit and credit entries, books of accounts, accounting concepts and conventions, and the preparation of trial balance, balance sheet and income statement.