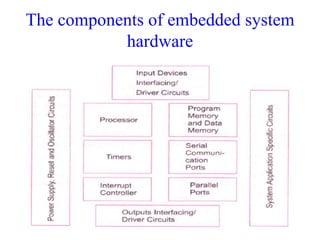
This document provides an introduction to embedded systems. It defines an embedded system as a dedicated computer system with embedded software and hardware to perform specific control functions within a larger system or product. Embedded systems have constraints on available memory, processor speed, and power consumption. They can be classified as small, medium, or sophisticated based on their hardware and software complexities. The document outlines the basic components and characteristics of embedded systems and discusses the different skills required for designers of small, medium, and sophisticated embedded systems.